6.3 KiB
Tables
Usage
Requires Python 3.5 or greater and the wcwidth library, which users can install with: pip3 install wcwidth.
Complete versions of all of the examples below and more can be found in the test.py file.
Run with: python3 test.py.
Output char array as table
import tables
# Set array
tables.array(array, None, None, headerrow=True, headercolumn=True)
Table cells can contain Unicode characters, but not newlines and tabs.
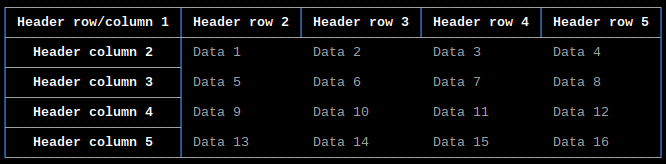
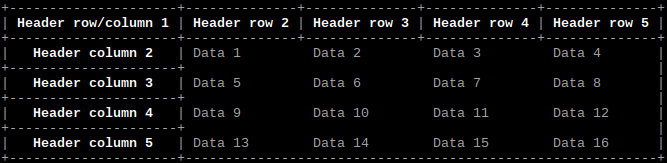
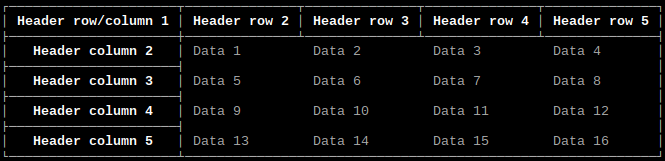
Output array as table with separate header row and column
import tables
headerrow = ["Header row/column 1", "Header row 2", "Header row 3", "Header row 4", "Header row 5"]
headercolumn = ["Header column 2", "Header column 3", "Header column 4", "Header column 5"]
# Set array
tables.array(array, headerrow, headercolumn, headerrow=True, headercolumn=True)
Output same as example above.
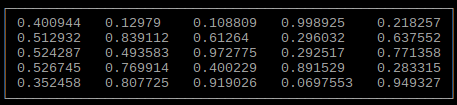
Output array as table
import tables
# Set array
tables.array(array, None, None)
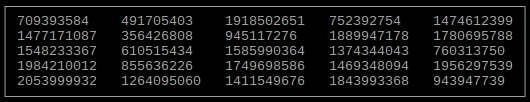
Output sorted array as table
import tables
# Set array
sortdimension = 0 # Column to sort by
array = sorted(array, key=lambda x: x[sortdimension])
tables.array(array, None, None)
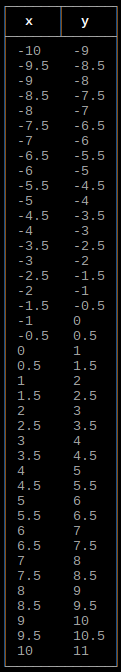
Output single function as table
import tables
def afunction(x):
return x + 1
xmin = -10
xmax = 10
xscl = 2
tables.function(xmin, xmax, xscl, afunction, headerrow=True)
Output multiple functions as table
import tables
def function1(x):
return 2 * x
def function2(x):
return x ** 2
xmin = -10
xmax = 10
xscl = 2
# Function parameter and return value can be any data type, as long as they are the same
functions = [function1, function2]
tables.functions(xmin, xmax, xscl, functions, headerrow=True)
Options
Header row
Option: headerrow
Default value: False
Header rows are bolded, centered and have a border.
Header column
Option: headercolumn
Default value: False
Header columns are bolded, centered and have a border.
Table border
Option: tableborder
Default value: False
Cell border
Option: cellborder
Default value: False
Cell padding
Option: padding
Default value: 1
Alignment
Option: alignment
Values:
False(left, default)True(right)
Title
Option: title
Default value: None
The title is word wrapped based on the current width of the terminal. Handles newlines, tabs and Unicode characters.
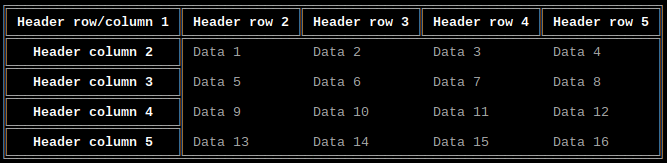
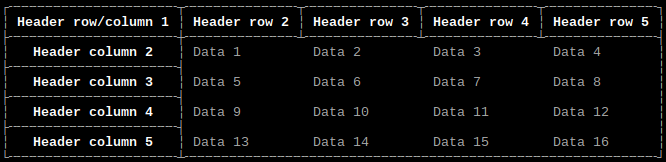
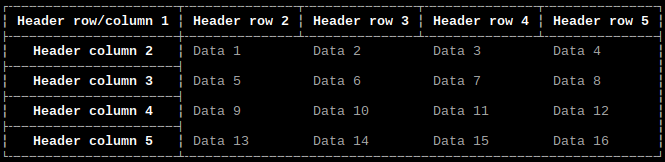
Border style
Option: style
Values:
Graphs/Plots
Usage
Requires Python 3.5 or greater and the wcwidth library, which users can install with: pip3 install wcwidth.
Complete versions of all of the examples below and more can be found in the test.py file.
Run with: python3 test.py.
If height is 0, it will be set to the current height of the terminal (number of rows times four). If width is 0, it will be set to the current width of the terminal (number of columns times two).
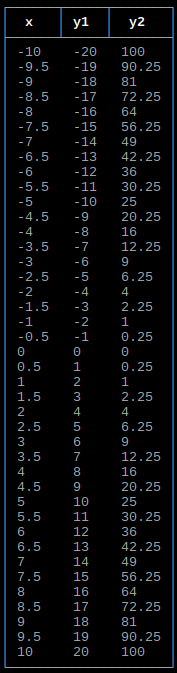
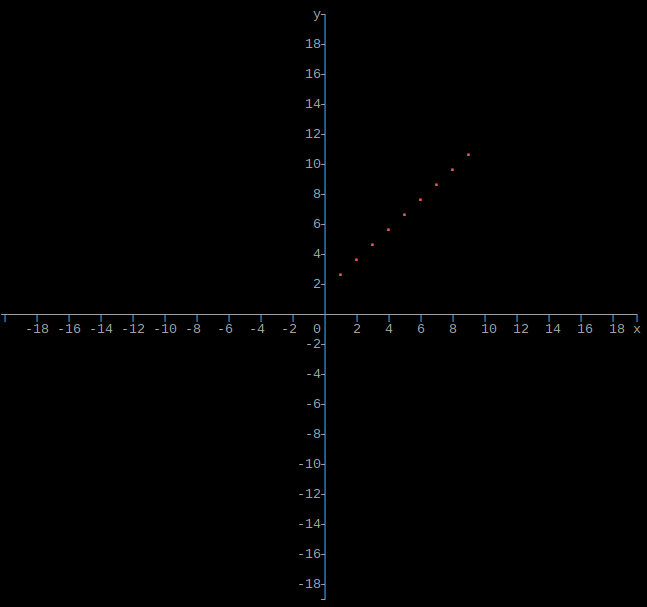
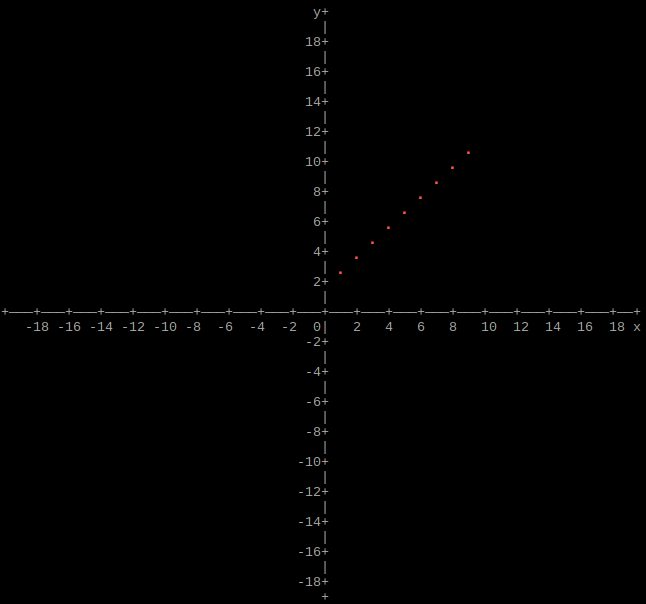
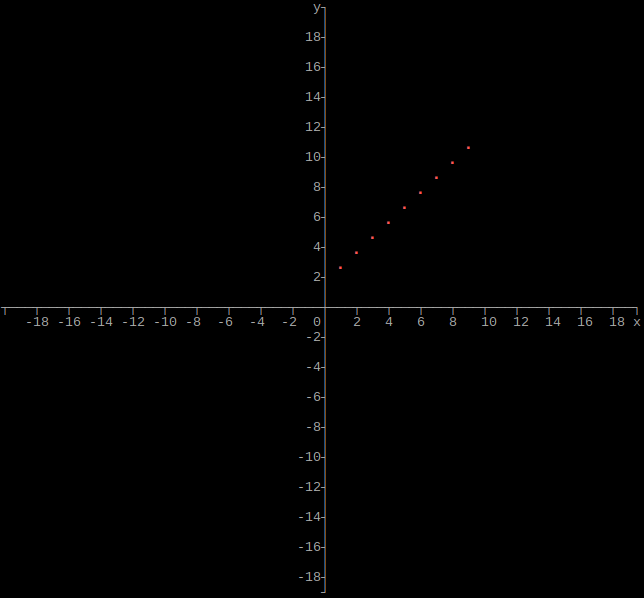
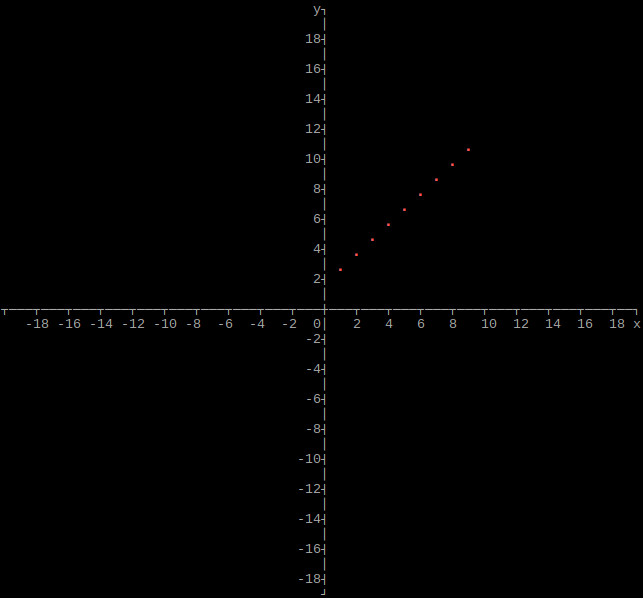
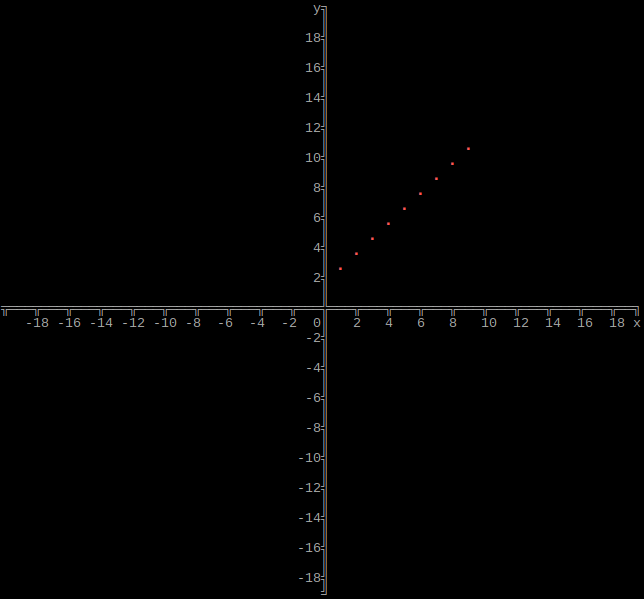
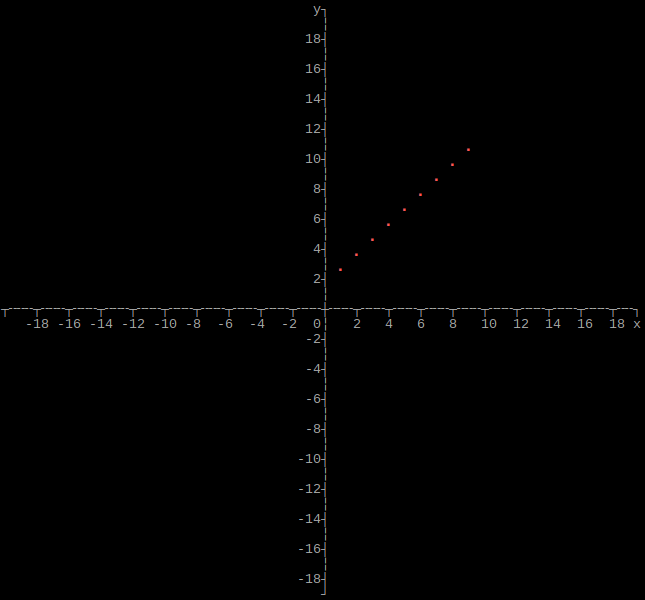
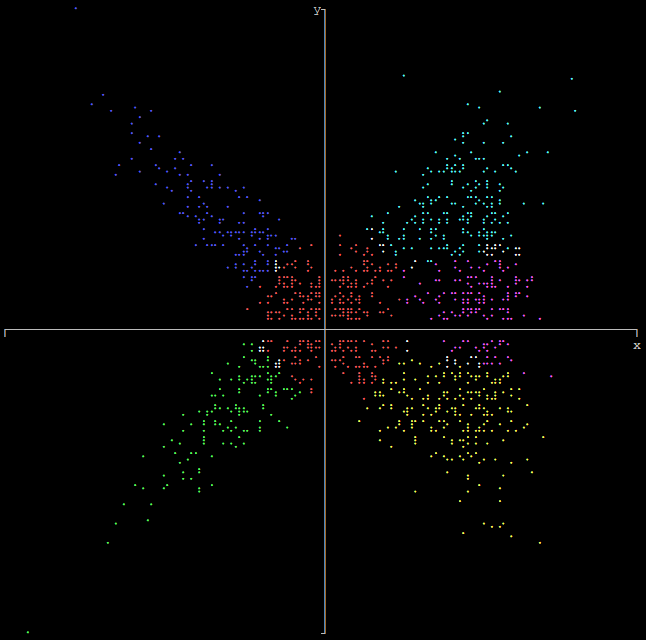
Output array as plot
import graphs
height = 160
width = 160
xmin = -20
xmax = 20
ymin = -20
ymax = 20
# Set array
graphs.array(height, width, xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, array)
If xmin and xmax are both 0, they will be set to the respective minimum and maximum values of x in the array. If ymin and ymax are both 0, they will be set to the respective minimum and maximum values of y in the array.
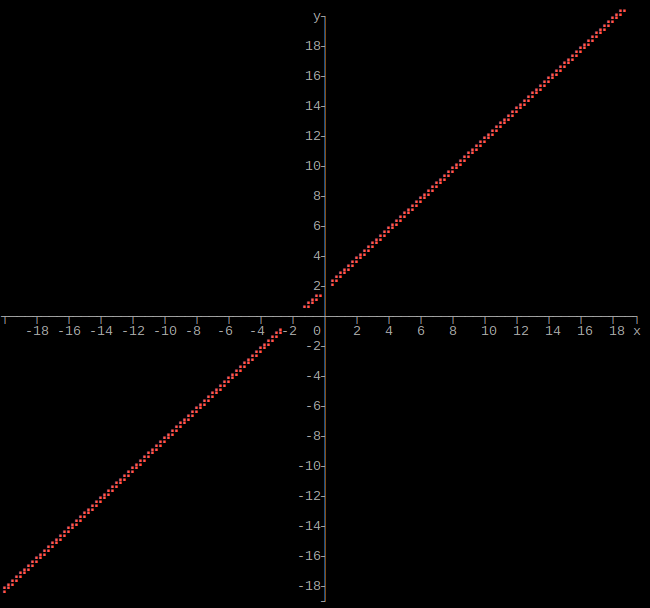
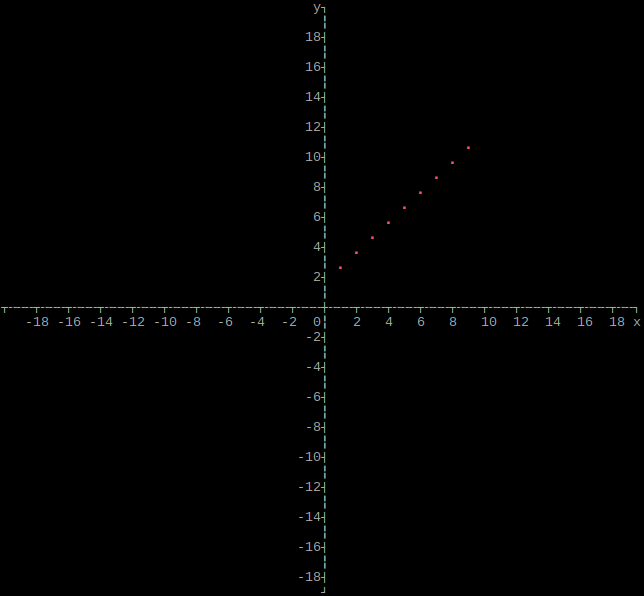
Output single function as graph
import graphs
def afunction(x):
return x + 1
height = 160
width = 160
xmin = -20
xmax = 20
ymin = -20
ymax = 20
graphs.function(height, width, xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, afunction)
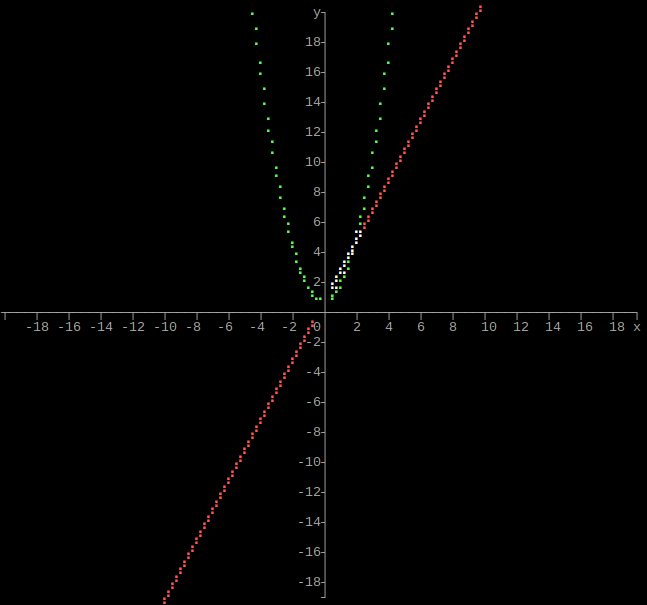
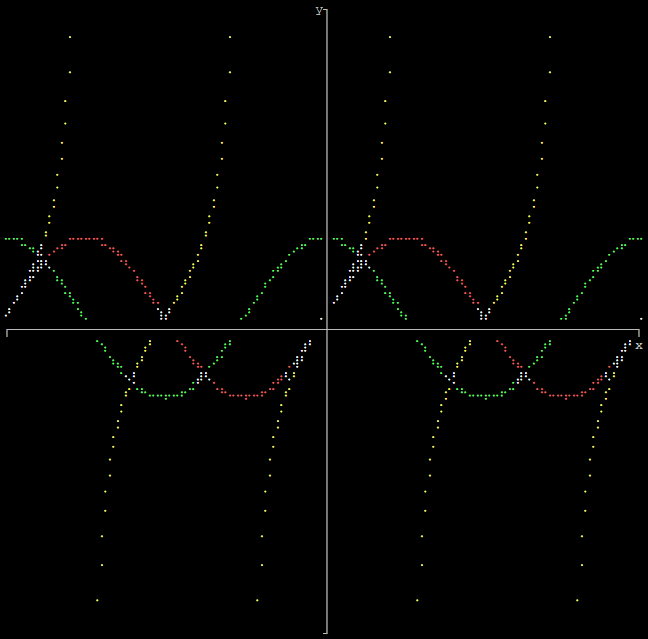
Output multiple functions as graph
import graphs
def function1(x):
return 2 * x
def function2(x):
return x ** 2
height = 160
width = 160
xmin = -20
xmax = 20
ymin = -20
ymax = 20
# Function parameter and return value can be any data type, as long as they are the same
functions = [function1, function2]
graphs.functions(height, width, xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax, functions)
Options
Border/Axis
Option: border
Default value: False
Axis labels
Option: axislabel
Default value: False
Requires border to be False.
Axis units labels
Option: axisunitslabel
Default value: False
Requires border and axislabel to be False.
Title
Option: title
Default value: None
The title is word wrapped based on the current width of the terminal. Handles newlines, tabs and Unicode characters.
Axis/Border style
Option: style
Values:
Graph/Plot Color
Option: color
Values:
- System default
- Black
- Red (default)
- Green
- Yellow
- Blue
- Cyan
- Light gray
- Dark gray
- Light red
- Light green
- Light yellow
- Light blue
- Light cyan
- White
See here for examples of the colors.
Only used for plots and when graphing a single function.
When graphing multiple functions, colors 2 - 14 are used inorder. Color 0 is used where the functions cross.