add docker support
4
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,7 +1,5 @@
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
build/
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
tmp/
|
||||
doc/html
|
||||
doc/man
|
||||
data/
|
||||
installer
|
||||
@ -7,10 +7,13 @@ include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
|
||||
|
||||
# ExprTK库在macOS 15.4中编译会有错误 添加以下命令对应检查项
|
||||
add_compile_options(-Wno-missing-template-arg-list-after-template-kw)
|
||||
if(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME STREQUAL "Darwin")
|
||||
# ExprTK库在macOS 15.4中编译会有错误 添加以下命令对应检查项
|
||||
add_compile_options(-Wno-missing-template-arg-list-after-template-kw)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加编译选项
|
||||
option(GCTL_DOCKER "Compile the docker image" OFF)
|
||||
option(GCTL_OPENMP "Use the OpenMP library" ON)
|
||||
option(GCTL_NETCDF "Use the NetCDF library" ON)
|
||||
option(GCTL_FFTW3 "Use the FFTW3 library" ON)
|
||||
@ -27,6 +30,7 @@ set(DIR_VAR ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Platform: " ${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Install prefix: " ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Processor: " ${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR})
|
||||
message(STATUS "[GCTL] Compile the docker image: " ${GCTL_DOCKER})
|
||||
message(STATUS "[GCTL] Use the OpenMP library: " ${GCTL_OPENMP})
|
||||
message(STATUS "[GCTL] Use the NetCDF library: " ${GCTL_NETCDF})
|
||||
message(STATUS "[GCTL] Use the FFTW3 library: " ${GCTL_FFTW3})
|
||||
@ -102,5 +106,7 @@ configure_file(
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加库源文件地址
|
||||
add_subdirectory(lib)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(example)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(tool)
|
||||
if(NOT GCTL_DOCKER)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(example)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(tool)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
41
Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
# 编译平台
|
||||
FROM ubuntu:20.04 AS builder
|
||||
# 安装编译工具
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y g++ make cmake
|
||||
# 安装依赖库
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y libfftw3-dev libnetcdf-dev gmt libgmt-dev libgsl-dev libncurses-dev
|
||||
# 创建工作目录
|
||||
WORKDIR /gctl
|
||||
|
||||
# 1. 编译安装EEMD
|
||||
# 拷贝libeemd相关内容
|
||||
COPY dep/libeemd /gctl/dep/libeemd
|
||||
# 编译安装libeemd
|
||||
RUN mkdir /gctl/dep/libeemd/build && cd /gctl/dep/libeemd/build && cmake .. && make && make install
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. 编译安装netcdfcxx_legacy
|
||||
# 拷贝netcdfcxx_legacy相关内容
|
||||
COPY dep/netcdfcxx_legacy /gctl/dep/netcdfcxx_legacy
|
||||
# 编译安装netcdfcxx_legacy
|
||||
RUN mkdir /gctl/dep/netcdfcxx_legacy/build && cd /gctl/dep/netcdfcxx_legacy/build && cmake .. && make && make install
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. 拷贝partow模版文件
|
||||
COPY dep/partow/include /usr/local/include
|
||||
|
||||
# 将gctl源代码
|
||||
COPY lib /gctl/lib
|
||||
COPY CMakeLists.txt .
|
||||
COPY config.h.in .
|
||||
COPY GCTLConfig.cmake.in .
|
||||
# 将CMake配置文件拷贝到系统路径
|
||||
COPY dep/cmake /usr/local/lib/cmake
|
||||
# 编译gctl动态库
|
||||
RUN mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DGCTL_DOCKER=ON && make && make install
|
||||
|
||||
# 运行平台
|
||||
FROM ubuntu:20.04
|
||||
# 安装运行时必要依赖
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libstdc++6
|
||||
# 从构建阶段复制编译后的库和头文件
|
||||
COPY --from=builder /usr/local/lib /usr/local/lib
|
||||
COPY --from=builder /usr/local/include /usr/local/include
|
||||
@ -6,18 +6,16 @@ macro(set_and_check _var _file)
|
||||
endmacro()
|
||||
|
||||
# change the following options as needed
|
||||
set(FFTW3_VERSION "3.5.8")
|
||||
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Darwin")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_INC_DIR "/opt/homebrew/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_LIB_DIR "/opt/homebrew/lib")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_INCLUDE_DIRS "/opt/homebrew/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_LIBRARY_DIRS "/opt/homebrew/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
elseif(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_INC_DIR "/usr/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_LIB_DIR "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_INCLUDE_DIRS "/usr/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(FFTW3_LIBRARY_DIRS "/usr/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
else()
|
||||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Unset operation system for FFTW3. Please edit the FFTW3Config.cmake file.")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
set(FFTW3_LIB fftw3)
|
||||
set(FFTW3_LIBRARIES fftw3)
|
||||
21
dep/cmake/GMT/GMTConfig.cmake
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
macro(set_and_check _var _file)
|
||||
set(${_var} "${_file}")
|
||||
if(NOT EXISTS "${_file}")
|
||||
message(FATAL_ERROR "File or directory ${_file} referenced by variable ${_var} does not exist !")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endmacro()
|
||||
|
||||
# change the following options as needed
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Darwin")
|
||||
set_and_check(GMT_INC_DIR "/opt/homebrew/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(GMT_LIB_DIR "/opt/homebrew/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
elseif(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
set_and_check(GMT_INC_DIR "/usr/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(GMT_LIB_DIR "/usr/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
else()
|
||||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Unset operation system for GMT. Please edit the GMTConfig.cmake file.")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
set(GMT_LIB gmt)
|
||||
1
dep/libeemd
Submodule
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Subproject commit bd7aceff23f8722c6c102b5dd72d94b22a0be1d6
|
||||
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15.2)
|
||||
# 设置项目名称与语言
|
||||
project(LibMagTess VERSION 1.0)
|
||||
# 添加配置配件编写的函数
|
||||
include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
|
||||
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Windows")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX D:/Library)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX /opt/stow/magtess)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
message(STATUS "Platform: " ${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Install prefix: " ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Build type: " ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE})
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加库源文件地址
|
||||
add_subdirectory(lib)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(toolkits)
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
BSD 2-Clause License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2012-2015, Leonardo Uieda
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2017-2020, Eldar Baykiev
|
||||
All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
|
||||
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
|
||||
list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
|
||||
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Neither the name of Leonardo Uieda nor the names of any contributors*
|
||||
may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
|
||||
without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
|
||||
AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
|
||||
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
|
||||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
|
||||
FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
|
||||
DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
|
||||
SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
|
||||
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
|
||||
OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
|
||||
OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
|
||||
* Contributors to the original tesseroids source and binary forms, which are
|
||||
under BSD 3-Clause License
|
||||
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
@PACKAGE_INIT@
|
||||
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_Version "@PROJECT_VERSION@")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INSTALL_PREFIX "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INC_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INCULDE_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIB_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/lib")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIBRARY_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIB magtess)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIBRARY magtess)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_FOUND 1)
|
||||
|
||||
# include target information
|
||||
include("${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@PROJECT_NAME@Targets.cmake")
|
||||
@ -1,122 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Forward modeling of magnetic field in spherical coordinates
|
||||
|
||||
Magnetic tesseroids is a collection of command-line tools for modelling of the magnetic field with spherical prisms (tesseroids) used as magnetic sources.
|
||||
|
||||
To cite _magnetic tesseroids_ in publications, please use our paper published in Computers & Geosciences:
|
||||
|
||||
>**Eldar Baykiev**, **Jörg Ebbing**, **Marco Brönner**, **Karl Fabian**, Forward modeling magnetic fields of induced and remanent magnetization in the lithosphere using tesseroids, _Computers & Geosciences_, Volume 96, November 2016, Pages 124-135, ISSN 0098-3004, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2016.08.004.
|
||||
|
||||
Article can also be found here http://goo.gl/x9g7gi (researchgate).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage of _magnetic tesseroids_
|
||||
_Magnetic tesseroids_ are based on the existing program of Leonardo Uieda called tesseroids (Uieda, 2013) of version 1.1 (https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/releases/tag/v1.1). It inherits the interface of tesseroids-1.1 but with several changes. Present appendix describes constants and units used be the program, as well as input and output format.
|
||||
### Constants
|
||||
1. Geocentric mean Earth's radius _R_E_ = 6378.137 km.
|
||||
1. Magnetic permeability of a free space _µ_0_ = 4π × 10^-7 H·m^-1
|
||||
|
||||
### List of programs
|
||||
The tessbx, tessby, tessbz are programs that calculate the corresponding components (x - north, y - east, **z - up**) of the magnetic field of the tesseroid model on the computational grid.
|
||||
|
||||
### Input: tesseroid model
|
||||
The input model file should be a text file where each line describe one tesseroid in such space separated format:
|
||||
> `W E S N HEIGHT_OF_TOP HEIGHT_OF_BOTTOM DENSITY SUSCEPTIBILITY BX BY BZ`
|
||||
|
||||
`W`, `E`, `S`, `N` correspond to the western, eastern, southern and northern edges of a tesseroid (_λ_1_, _λ_2_, _ϕ_1_, _ϕ_2_ respectively) expressed in decimal degrees [°].
|
||||
`HEIGHT_OF_TOP` and `HEIGHT_OF_BOTTOM` define the top and the bottom of tesseroid (_r_2_ and _r_1_ respectively). Both are counted from geocentric mean Earth's radius in meters [m]. If a tesseroid should be placed beneath the mean surface, than the values of these parameters should be negative. Note that `HEIGHT_OF_TOP` > `HEIGHT_OF_BOTTOM`.
|
||||
`DENSITY` is the density _ρ_ of tesseroid in kilogram per cubic meter [kg/m^3]
|
||||
`SUSCEPTIBILITY` is the susceptibility _χ_ of tesseroid in SI units.
|
||||
`BX`, `BY` and `BZ` are the components of the magnetizing field in the local North-East-Up Cartesian coordinate system of a tesseroids' geometric center. They can be taken from any core field's model. Values are given in nanotesla [nT].
|
||||
In case of remanent magnetic field modeling, susceptibility must be set 1 SI and `BX`, `BY` and `BZ` values than would define the direction of remanent magnetization vector.
|
||||
This example shows a model made of 3 neighboring tesseroids near the North Pole:
|
||||
> `-74 -73 89 90 -1000.000000 -11650.000000 1.000000 1.000000 334.9504973176 -1969.9308033594 -56572.6324041700`
|
||||
|
||||
> `-73 -72 89 90 -1000.000000 -11650.000000 1.000000 1.000000 370.1879538142 -1968.1093976826 -56571.2826313492`
|
||||
|
||||
> `-72 -71 89 90 -1000.000000 -11650.000000 1.000000 1.000000 405.4388222633 -1965.6409379187 -56569.9502088641`
|
||||
|
||||
### Input: computation grid
|
||||
Computation grid can be regular or irregular and should be also a text file where each line describe the position of one computation point in such space separated format:
|
||||
>`LON LAT ALT`
|
||||
|
||||
`LON` and `LAT` correspond to the longitude and latitude of the point in decimal degrees [°].
|
||||
`ALT` corresponds to the altitude of the point above the mean surface in meters [m].
|
||||
Note that the program tessgrd from original tesseroids-1.1 can be used to create a regular computation grid (see Uieda, 2013).
|
||||
This example shows a grid made of 6 points with the same latitude and the altitude of 400 km:
|
||||
> `-6 51 400000 `
|
||||
|
||||
> `-5.8 51 400000 `
|
||||
|
||||
> `-5.6 51 400000 `
|
||||
|
||||
> `-5.4 51 400000 `
|
||||
|
||||
> `-5.2 51 400000 `
|
||||
|
||||
> `-5 51 400000`
|
||||
|
||||
### Performing calculations
|
||||
Example: to calculate the vertical component of the magnetic field of a model in file modelfile.txt on a grid from file gridpoints.txt one can simply use a console command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
tessbz modelfile.txt < gridpoints.txt > gz_output.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The result would be written in the file gz_output.txt.
|
||||
### Output format
|
||||
The programs' output is a modified grid file where in the end of each line the calculated value of a corresponding magnetic field component would be written. Values are given in nanotesla [nT] in the local North-East-Up coordinate system of a computational point.
|
||||
### Additional features
|
||||
Magnetic tesseroids support features like piping and integration accuracy adjustment from tesseroids-1.1. Please, check sections in the tesseroids-1.1 manual (Uieda, 2013) relative to the gravity calculation programs to get more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
### tessutil_magnetize_model
|
||||
This program is made to 'magnetize' any existing tesseroid model by any given main field spherical harmonic model.
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
```
|
||||
tessutil_magnetize_model [SH coeff file] [input tesseroid model file] [day] [month] [year] [output tesseroid model file]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### tessutil_gradient_calculator
|
||||
Gradient calculator (Baykiev et al., in press).
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
```
|
||||
tessutil_gradient_calculator -bx[Bx grid file] -by[By grid file] -bz[Bx grid file] -o[output component] -c2 >> output_file.dat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
All grid files should be in tessgrd format. With option `-c1` program reads input grid bz as its direction is upward, with option `-c2` - downward, just as in magnetic tesseroids output. Output of gradient calculator is always in North-East-Down coordinate system.
|
||||
|
||||
Known issue: rounding error when processing grids with spacing equal or less than 0.2 degrees.
|
||||
|
||||
### tessutil_combine_grids
|
||||
Sums calculated grids.
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
```
|
||||
tessutil_combine_grids [grid file1] [factor1] ... [grid fileN] [factorN] >> output_file.dat
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each grid is multiplied by factor (susceptibility) and then the sum of all grids is calculated.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation (version 1.1)
|
||||
1. Download source code from [GitHub](https://github.com/eldarbaykiev/magnetic-tesseroids):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/eldarbaykiev/magnetic-tesseroids.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. On **Linux**, install [OpenBLAS](https://www.openblas.net/) library:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libopenblas-base libopenblas-dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On **macOS**, make sure that [Xcode](https://developer.apple.com/xcode/) is installed and [Accelerate framework](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/accelerate) is available.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run **make**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
make
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To compile all utilities, run
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
make tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -O3")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -O3")
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Windows")
|
||||
# set OpenBLAS directory manually
|
||||
set(OpenBLAS_DIR D:/Library/lib/cmake/openblas)
|
||||
find_library(OpenBLAS REQUIRED)
|
||||
include_directories(${OpenBLAS_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
||||
elseif(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Darwin")
|
||||
# set OpenBLAS directory manually
|
||||
set(OpenBLAS_DIR /opt/homebrew/Cellar/openblas/0.3.24/lib/cmake/openblas)
|
||||
find_package(OpenBLAS REQUIRED)
|
||||
include_directories(${OpenBLAS_INCLUDE_DIRS})
|
||||
elseif(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -lm")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -lm")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置库文件的输出地址
|
||||
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
# 设定库源文件
|
||||
aux_source_directory(. LIBMAGTESS_SRC)
|
||||
|
||||
# 以下部分为库的编译
|
||||
# 注意目标名必须唯一 所以不能直接生成相同名称的动态库与静态库
|
||||
# 注意此处不必为目标名称添加lib前缀和相应后缀,cmake会自行添加
|
||||
add_library(magtess SHARED ${LIBMAGTESS_SRC})
|
||||
# 首先添加静态库的生成命令
|
||||
add_library(magtess_static STATIC ${LIBMAGTESS_SRC})
|
||||
# 设置静态库的输出名称从而获得与动态库名称相同的静态库
|
||||
set_target_properties(magtess_static PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME "magtess")
|
||||
# 设置输出目标属性以同时输出动态库与静态库
|
||||
set_target_properties(magtess PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
set_target_properties(magtess_static PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
# 设置动态库的版本号
|
||||
set_target_properties(magtess PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}.${PROJECT_VERSION_MINOR})
|
||||
|
||||
target_link_libraries(magtess PUBLIC ${OpenBLAS_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(magtess_static ${OpenBLAS_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
target_link_libraries(magtess PUBLIC m)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(magtess PUBLIC openblas)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
set(CONFIG_FILE_PATH lib/cmake/${PROJECT_NAME})
|
||||
|
||||
configure_package_config_file(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake.in
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake
|
||||
INSTALL_DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH}
|
||||
NO_CHECK_REQUIRED_COMPONENTS_MACRO)
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_package_version_file(${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}ConfigVersion.cmake
|
||||
VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION}
|
||||
COMPATIBILITY SameMajorVersion)
|
||||
|
||||
# 库的安装命令
|
||||
if(WIN32)
|
||||
install(TARGETS magtess DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
install(TARGETS magtess_static DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
install(TARGETS magtess magtess_static
|
||||
EXPORT ${PROJECT_NAME}Targets
|
||||
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
|
||||
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
install(EXPORT ${PROJECT_NAME}Targets
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH})
|
||||
install(FILES
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}ConfigVersion.cmake
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH})
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
file(GLOB LIBMEGTESS_HEAD *.h)
|
||||
install(FILES ${LIBMEGTESS_HEAD} DESTINATION include/magtess)
|
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Define constants used, like the gravitational constant and unit conversions.
|
||||
|
||||
Values are assigned in file constants.c
|
||||
|
||||
All values are in SI units!
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_CONSTANTS_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_CONSTANTS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/* Mean Earth radius [\f$ m \f$] */
|
||||
const double MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS = 6378137.0;
|
||||
const double EARTH_RADIUS_IGRF_KM = 6371.2;
|
||||
|
||||
/* The gravitational constant [\f$ m^3*kg^{-1}*s^{-1} \f$] */
|
||||
const double G = 0.00000000006673;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to Eotvos
|
||||
[\f$ \frac{1}{s^2} = 10^9\ Eotvos \f$] */
|
||||
const double SI2EOTVOS = 1000000000.0;
|
||||
const double EOTVOS2SI = 0.000000001;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to mGal
|
||||
[\f$ 1 \frac{m}{s^2} = 10^5\ mGal \f$] */
|
||||
const double SI2MGAL = 100000.0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Pi */
|
||||
#ifdef __cplusplus
|
||||
const double PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832795
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* minimum distance-to-size ratio for potential computations to be accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_POT_SIZE_RATIO = 1.5;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity computations to be accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GX_SIZE_RATIO = 3;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GY_SIZE_RATIO = 3;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GZ_SIZE_RATIO = 2;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity gradient computations to be
|
||||
accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO = 3;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO = 4.5;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO = 4;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GYY_SIZE_RATIO = 3;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GYZ_SIZE_RATIO = 4;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GZZ_SIZE_RATIO = 3;
|
||||
|
||||
const double M_0 = 4 * (PI) * 0.0000001;
|
||||
|
||||
const double DEG2RAD = (PI)/180.0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#define FALSE 0
|
||||
#define TRUE 1
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Data structures for geometric elements and functions that operate on them.
|
||||
Defines the TESSEROID, SPHERE, and PRISM structures.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Split a tesseroid into 8. */
|
||||
void split_tess(MAG_TESSEROID tess, MAG_TESSEROID *split)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double dlon = 0.5*(tess.e - tess.w),
|
||||
dlat = 0.5*(tess.n - tess.s),
|
||||
dr = 0.5*(tess.r2 - tess.r1),
|
||||
ws[2], ss[2], r1s[2];
|
||||
int i, j, k, t = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
ws[0] = tess.w;
|
||||
ws[1] = tess.w + dlon;
|
||||
ss[0] = tess.s;
|
||||
ss[1] = tess.s + dlat;
|
||||
r1s[0] = tess.r1;
|
||||
r1s[1] = tess.r1 + dr;
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < 2; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < 2; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < 2; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
split[t].w = ws[i];
|
||||
split[t].e = ws[i] + dlon;
|
||||
split[t].s = ss[j];
|
||||
split[t].n = ss[j] + dlat;
|
||||
split[t].r1 = r1s[k];
|
||||
split[t].r2 = r1s[k] + dr;
|
||||
split[t].density = tess.density;
|
||||
t++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Data structures for geometric elements and functions that operate on them.
|
||||
Defines the TESSEROID, SPHERE, and PRISM structures.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _MAG_TESSEROIDS_GEOMETRY_H_
|
||||
#define _MAG_TESSEROIDS_GEOMETRY_H_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Store information on a tesseroid */
|
||||
typedef struct magtess_struct {
|
||||
/* s, n, w, e in degrees. r1 and r2 are the smaller and larger radius */
|
||||
double density; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double w; /* western longitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double e; /* eastern longitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double s; /* southern latitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double n; /* northern latitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double r1; /* smallest radius border in SI units */
|
||||
double r2; /* largest radius border in SI units */
|
||||
double suscept; /* magnetic susceptibility */
|
||||
double Bx; /* x-component of ambient magnetic field */
|
||||
double By; /* y-component of ambient magnetic field */
|
||||
double Bz; /* z-component of ambient magnetic field */
|
||||
|
||||
double cos_a1;
|
||||
double sin_a1;
|
||||
double cos_b1;
|
||||
double sin_b1;
|
||||
//double Rx;
|
||||
//double Ry;
|
||||
//double Rz;
|
||||
} MAG_TESSEROID;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void split_tess(MAG_TESSEROID tess, MAG_TESSEROID *split);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,265 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions for implementing a Gauss-Legendre Quadrature numerical integration.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "glq.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make a new GLQ structure and set all the parameters needed */
|
||||
GLQ * glq_new(int order, double lower, double upper)
|
||||
{
|
||||
GLQ *glq;
|
||||
int rc;
|
||||
|
||||
glq = (GLQ *)malloc(sizeof(GLQ));
|
||||
if(glq == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq->order = order;
|
||||
glq->nodes = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*order);
|
||||
if(glq->nodes == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
free(glq);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq->nodes_unscaled = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*order);
|
||||
if(glq->nodes_unscaled == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
free(glq);
|
||||
free(glq->nodes);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq->weights = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*order);
|
||||
if(glq->weights == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
free(glq);
|
||||
free(glq->nodes);
|
||||
free(glq->nodes_unscaled);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
rc = glq_nodes(order, glq->nodes_unscaled);
|
||||
if(rc != 0 && rc != 3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(rc)
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
log_error("glq_nodes invalid GLQ order %d. Should be >= 2.",
|
||||
order);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
log_error("glq_nodes NULL pointer for nodes");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
log_error("glq_nodes unknown error code %g", rc);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq_free(glq);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if(rc == 3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("glq_nodes max iterations reached in root finder");
|
||||
log_warning("nodes might not have desired accuracy %g", GLQ_MAXERROR);
|
||||
}
|
||||
rc = glq_weights(order, glq->nodes_unscaled, glq->weights);
|
||||
if(rc != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(rc)
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
log_error("glq_weights invalid GLQ order %d. Should be >= 2.",
|
||||
order);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
log_error("glq_weights NULL pointer for nodes");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
log_error("glq_weights NULL pointer for weights");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
log_error("glq_weights unknown error code %d\n", rc);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq_free(glq);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(glq_set_limits(lower, upper, glq) != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
glq_free(glq);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return glq;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Free the memory allocated to make a GLQ structure */
|
||||
void glq_free(GLQ *glq)
|
||||
{
|
||||
free(glq->nodes);
|
||||
|
||||
free(glq->nodes_unscaled);
|
||||
free(glq->weights);
|
||||
free(glq);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates the GLQ nodes using glq_next_root. */
|
||||
int glq_nodes(int order, double *nodes)
|
||||
{
|
||||
register int i;
|
||||
int rc = 0;
|
||||
double initial;
|
||||
|
||||
if(order < 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(nodes == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
initial = cos(PI*(order - i - 0.25)/(order + 0.5));
|
||||
if(glq_next_root(initial, i, order, nodes) == 3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return rc;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Put the GLQ nodes to the integration limits IN PLACE. */
|
||||
int glq_set_limits(double lower, double upper, GLQ *glq)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Only calculate once to optimize the code */
|
||||
double tmpplus = 0.5*(upper + lower), tmpminus = 0.5*(upper - lower);
|
||||
register int i;
|
||||
|
||||
if(glq->order < 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(glq->nodes == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(glq->nodes_unscaled == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq->order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
glq->nodes[i] = tmpminus*glq->nodes_unscaled[i] + tmpplus;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the next Legendre polynomial root given the previous root found. */
|
||||
int glq_next_root(double initial, int root_index, int order, double *roots)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double x1, x0, pn, pn_2, pn_1, pn_line, sum;
|
||||
int it = 0;
|
||||
register int n;
|
||||
|
||||
if(order < 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(root_index < 0 || root_index >= order)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
x1 = initial;
|
||||
do
|
||||
{
|
||||
x0 = x1;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate Pn(x0) */
|
||||
/* Starting from P0(x) and P1(x), */
|
||||
/* find the others using the recursive relation: */
|
||||
/* Pn(x)=(2n-1)xPn_1(x)/n - (n-1)Pn_2(x)/n */
|
||||
pn_1 = 1.; /* This is Po(x) */
|
||||
pn = x0; /* and this P1(x) */
|
||||
for(n = 2; n <= order; n++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
pn_2 = pn_1;
|
||||
pn_1 = pn;
|
||||
pn = ( ((2*n - 1)*x0*pn_1) - ((n - 1)*pn_2) )/n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Now calculate Pn'(x0) using another recursive relation: */
|
||||
/* Pn'(x)=n(xPn(x)-Pn_1(x))/(x*x-1) */
|
||||
pn_line = order*(x0*pn - pn_1)/(x0*x0 - 1);
|
||||
/* Sum the roots found so far */
|
||||
for(n = 0, sum = 0; n < root_index; n++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
sum += 1./(x0 - roots[n]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Update the estimate for the root */
|
||||
x1 = x0 - (double)pn/(pn_line - pn*sum);
|
||||
|
||||
/** Compute the absolute value of x */
|
||||
#define GLQ_ABS(x) ((x) < 0 ? -1*(x) : (x))
|
||||
} while(GLQ_ABS(x1 - x0) > GLQ_MAXERROR && ++it <= GLQ_MAXIT);
|
||||
#undef GLQ_ABS
|
||||
|
||||
roots[root_index] = x1;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Tell the user if stagnation occurred */
|
||||
if(it > GLQ_MAXIT)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates the weighting coefficients for the GLQ integration. */
|
||||
int glq_weights(int order, double *nodes, double *weights)
|
||||
{
|
||||
register int i, n;
|
||||
double xi, pn, pn_2, pn_1, pn_line;
|
||||
|
||||
if(order < 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(nodes == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(weights == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < order; i++){
|
||||
|
||||
xi = nodes[i];
|
||||
|
||||
/* Find Pn'(xi) with the recursive relation to find Pn and Pn-1: */
|
||||
/* Pn(x)=(2n-1)xPn_1(x)/n - (n-1)Pn_2(x)/n */
|
||||
/* Then use: Pn'(x)=n(xPn(x)-Pn_1(x))/(x*x-1) */
|
||||
|
||||
/* Find Pn and Pn-1 stating from P0 and P1 */
|
||||
pn_1 = 1; /* This is Po(x) */
|
||||
pn = xi; /* and this P1(x) */
|
||||
for(n = 2; n <= order; n++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
pn_2 = pn_1;
|
||||
pn_1 = pn;
|
||||
pn = ((2*n - 1)*xi*pn_1 - (n - 1)*pn_2)/n;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pn_line = order*(xi*pn - pn_1)/(xi*xi - 1.);
|
||||
/* ith weight is: wi = 2/(1 - xi^2)(Pn'(xi)^2) */
|
||||
weights[i] = 2./((1 - xi*xi)*pn_line*pn_line);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,182 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions for implementing a Gauss-Legendre Quadrature numerical integration
|
||||
(Hildebrand, 1987).
|
||||
|
||||
Usage example
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
||||
To integrate the cossine function from 0 to 90 degrees:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include "src/c/glq.h"
|
||||
|
||||
int main(){
|
||||
// Create a new glq structure
|
||||
GLQ *glq;
|
||||
double result = 0, a = 0, b = 0.5*3.14;
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
glq = glq_new(5, a, b);
|
||||
|
||||
if(glq == NULL){
|
||||
printf("malloc error");
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate the integral
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq->order; i++)
|
||||
result += glq->weights[i]*cos(glq->nodes[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
// Need to multiply by a scale factor of the integration limits
|
||||
result *= 0.5*(b - a);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Integral of cossine from 0 to 90 degrees = %lf\n", result);
|
||||
|
||||
// Free allocated memory
|
||||
glq_free(glq);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
References
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
* Hildebrand, F.B (1987): Introduction to numerical analysis.
|
||||
Courier Dover Publications, 2. ed.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_GLQ_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_GLQ_H_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** \var GLQ_MAXIT
|
||||
Max iterations of the root-finder algorithm */
|
||||
const int GLQ_MAXIT = 1000;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** \var GLQ_MAXERROR
|
||||
Max error allowed for the root-finder algorithm */
|
||||
const double GLQ_MAXERROR = 0.000000000000001;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Store the nodes and weights needed for a GLQ integration */
|
||||
typedef struct glq_struct
|
||||
{
|
||||
int order; /**< order of the quadrature, ie number of nodes */
|
||||
double *nodes; /**< abscissas or discretization points of the quadrature */
|
||||
double *weights; /**< weighting coefficients of the quadrature */
|
||||
double *nodes_unscaled; /**< nodes in [-1,1] interval */
|
||||
} GLQ;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Make a new GLQ structure and set all the parameters needed
|
||||
|
||||
<b>WARNING</b>: Don't forget to free the memory malloced by this function using
|
||||
glq_free()!
|
||||
|
||||
Prints error and warning messages using the logging.h module.
|
||||
|
||||
@param order order of the quadrature, ie number of nodes
|
||||
@param lower lower integration limit
|
||||
@param upper upper integration limit
|
||||
|
||||
@return GLQ data structure with the nodes and weights calculated. NULL if there
|
||||
was an error with allocation.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
GLQ * glq_new(int order, double lower, double upper);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Free the memory allocated to make a GLQ structure
|
||||
|
||||
@param glq pointer to the allocated memory
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void glq_free(GLQ *glq);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Put the GLQ nodes to the integration limits <b>IN PLACE</b>.
|
||||
|
||||
Will replace the values of glq.nodes with ones in the specified integration
|
||||
limits.
|
||||
|
||||
In case the GLQ structure was created with glq_new(), the integration limits can
|
||||
be reset using this function.
|
||||
|
||||
@param lower lower integration limit
|
||||
@param upper upper integration limit
|
||||
@param glq pointer to a GLQ structure created with glq_new() and with all
|
||||
necessary memory allocated
|
||||
|
||||
@return Return code:
|
||||
- 0: if everything went OK
|
||||
- 1: if invalid order
|
||||
- 2: if NULL pointer for nodes or nodes_unscaled
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int glq_set_limits(double lower, double upper, GLQ *glq);
|
||||
/** Calculates the GLQ nodes using glq_next_root.
|
||||
|
||||
Nodes will be in the [-1,1] interval. To convert them to the integration limits
|
||||
use glq_scale_nodes
|
||||
|
||||
@param order order of the quadrature, ie how many nodes. Must be >= 2.
|
||||
@param nodes pre-allocated array to return the nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
@return Return code:
|
||||
- 0: if everything went OK
|
||||
- 1: if invalid order
|
||||
- 2: if NULL pointer for nodes
|
||||
- 3: if number of maximum iterations was reached when calculating the root.
|
||||
This usually means that the desired accuracy was not achieved. Default
|
||||
desired accuracy is GLQ_MAXERROR. Default maximum iterations is
|
||||
GLQ_MAXIT.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int glq_nodes(int order, double *nodes);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Calculate the next Legendre polynomial root given the previous root found.
|
||||
|
||||
Uses the root-finder algorithm of:
|
||||
|
||||
Barrera-Figueroa, V., Sosa-Pedroza, J. and López-Bonilla, J., 2006,
|
||||
"Multiple root finder algorithm for Legendre and Chebyshev polynomials via
|
||||
Newton's method", 2006, Annales mathematicae et Informaticae, 33, pp 3-13
|
||||
|
||||
@param initial initial estimate of the next root. I recommend the use of
|
||||
\f$ \cos\left(\pi\frac{(N - i - 0.25)}{N + 0.5}\right) \f$,
|
||||
where \f$ i \f$ is the index of the desired root
|
||||
@param root_index index of the desired root, starting from 0
|
||||
@param order order of the Legendre polynomial, ie number of roots.
|
||||
@param roots array with the roots found so far. Will return the next root in
|
||||
roots[root_index], so make sure to malloc enough space.
|
||||
|
||||
@return Return code:
|
||||
- 0: if everything went OK
|
||||
- 1: if order is not valid
|
||||
- 2: if root_index is not valid (negative)
|
||||
- 3: if number of maximum iterations was reached when calculating the root.
|
||||
This usually means that the desired accuracy was not achieved. Default
|
||||
desired accuracy is GLQ_MAXERROR. Default maximum iterations is
|
||||
GLQ_MAXIT.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int glq_next_root(double initial, int root_index, int order,
|
||||
double *roots);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Calculates the weighting coefficients for the GLQ integration.
|
||||
|
||||
@param order order of the quadrature, ie number of nodes and weights.
|
||||
@param nodes array containing the GLQ nodes calculated by glq_nodes.
|
||||
<b>IMPORTANT</b>: needs the nodes in [-1,1] interval! Scaled nodes
|
||||
will result in wrong weights!
|
||||
@param weights pre-allocated array to return the weights
|
||||
|
||||
@return Return code:
|
||||
- 0: if everything went OK
|
||||
- 1: if order is not valid
|
||||
- 2: if nodes is a NULL pointer
|
||||
- 3: if weights is a NULL pointer
|
||||
*/
|
||||
int glq_weights(int order, double *nodes, double *weights);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,628 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions that calculate the gravitational potential and its first and second
|
||||
derivatives for the tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
References
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
* Grombein, T.; Seitz, K.; Heck, B. (2010): Untersuchungen zur effizienten
|
||||
Berechnung topographischer Effekte auf den Gradiententensor am Fallbeispiel der
|
||||
Satellitengradiometriemission GOCE.
|
||||
KIT Scientific Reports 7547, ISBN 978-3-86644-510-9, KIT Scientific Publishing,
|
||||
Karlsruhe, Germany.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
#include "glq.h"
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "grav_tess.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates the field of a tesseroid model at a given point. */
|
||||
double calc_tess_model(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r, double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ))
|
||||
{
|
||||
double res;
|
||||
int tess;
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
for(tess = 0; tess < size; tess++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(lonp >= model[tess].w && lonp <= model[tess].e &&
|
||||
latp >= model[tess].s && latp <= model[tess].n &&
|
||||
rp >= model[tess].r1 && rp <= model[tess].r2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Point (%g %g %g) is on tesseroid %d: %g %g %g %g %g %g %g. Can't guarantee accuracy.",
|
||||
lonp, latp, rp - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, tess,
|
||||
model[tess].w, model[tess].e, model[tess].s,
|
||||
model[tess].n, model[tess].r2 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].r1 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].density);
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].w, model[tess].e, glq_lon);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].s, model[tess].n, glq_lat);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].r1, model[tess].r2, glq_r);
|
||||
res += field(model[tess], lonp, latp, rp, *glq_lon, *glq_lat, *glq_r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void calc_tess_model_triple(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r, void (*field_triple)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ, double*), double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double r1, r2, r3, ri[3];
|
||||
int tess;
|
||||
|
||||
res[0] = 0;
|
||||
res[1] = 0;
|
||||
res[2] = 0;
|
||||
for(tess = 0; tess < size; tess++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ri[0] = 0;
|
||||
ri[1] = 0;
|
||||
ri[2] = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if(lonp >= model[tess].w && lonp <= model[tess].e &&
|
||||
latp >= model[tess].s && latp <= model[tess].n &&
|
||||
rp >= model[tess].r1 && rp <= model[tess].r2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Point (%g %g %g) is on tesseroid %d: %g %g %g %g %g %g %g. Can't guarantee accuracy.",
|
||||
lonp, latp, rp - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, tess,
|
||||
model[tess].w, model[tess].e, model[tess].s,
|
||||
model[tess].n, model[tess].r2 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].r1 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].density);
|
||||
}
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].w, model[tess].e, glq_lon);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].s, model[tess].n, glq_lat);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].r1, model[tess].r2, glq_r);
|
||||
field_triple(model[tess], lonp, latp, rp, *glq_lon, *glq_lat, *glq_r, ri);
|
||||
|
||||
res[0] += ri[0];
|
||||
res[1] += ri[1];
|
||||
res[2] += ri[2];
|
||||
}
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Adaptatively calculate the field of a tesseroid model at a given point */
|
||||
double calc_tess_model_adapt(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r, double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ), double ratio)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double res, dist, lont, latt, rt, d2r = PI/180.;
|
||||
int tess;
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID split[8];
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
for(tess = 0; tess < size; tess++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rt = model[tess].r2;
|
||||
lont = 0.5*(model[tess].w + model[tess].e);
|
||||
latt = 0.5*(model[tess].s + model[tess].n);
|
||||
dist = sqrt(rp*rp + rt*rt - 2*rp*rt*(sin(d2r*latp)*sin(d2r*latt) +
|
||||
cos(d2r*latp)*cos(d2r*latt)*cos(d2r*(lonp - lont))));
|
||||
|
||||
/* Would get stuck in infinite loop if dist = 0 and get wrong results if
|
||||
inside de tesseroid. Still do the calculation but warn user that it's
|
||||
probably wrong. */
|
||||
if(lonp >= model[tess].w && lonp <= model[tess].e &&
|
||||
latp >= model[tess].s && latp <= model[tess].n &&
|
||||
rp >= model[tess].r1 && rp <= model[tess].r2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Point (%g %g %g) is on top of tesseroid %d: %g %g %g %g %g %g %g. Can't guarantee accuracy.",
|
||||
lonp, latp, rp - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, tess,
|
||||
model[tess].w, model[tess].e, model[tess].s,
|
||||
model[tess].n, model[tess].r2 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].r1 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].density);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].w, model[tess].e, glq_lon);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].s, model[tess].n, glq_lat);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].r1, model[tess].r2, glq_r);
|
||||
res += field(model[tess], lonp, latp, rp, *glq_lon, *glq_lat,
|
||||
*glq_r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Check if the computation point is at an acceptable distance. If not
|
||||
split the tesseroid using the given ratio */
|
||||
else if(
|
||||
dist < ratio*MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS*d2r*(model[tess].e - model[tess].w) ||
|
||||
dist < ratio*MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS*d2r*(model[tess].n - model[tess].s) ||
|
||||
dist < ratio*(model[tess].r2 - model[tess].r1))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_debug("Splitting tesseroid %d (%g %g %g %g %g %g %g) at point (%g %g %g) using ratio %g",
|
||||
tess, model[tess].w, model[tess].e, model[tess].s,
|
||||
model[tess].n, model[tess].r2 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS,
|
||||
model[tess].r1 - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, model[tess].density,
|
||||
lonp, latp, rp - MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, ratio);
|
||||
/* Do it recursively until ratio*size is smaller than distance */
|
||||
split_tess(model[tess], split);
|
||||
res += calc_tess_model_adapt(split, 8, lonp, latp, rp, glq_lon,
|
||||
glq_lat, glq_r, field, ratio);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].w, model[tess].e, glq_lon);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].s, model[tess].n, glq_lat);
|
||||
glq_set_limits(model[tess].r1, model[tess].r2, glq_r);
|
||||
res += field(model[tess], lonp, latp, rp, *glq_lon, *glq_lat,
|
||||
*glq_r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gxx caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gxx(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, kphi, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, rc, kappa, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*(sinlatp*sinlatc +
|
||||
coslatp*coslatc*coslon);
|
||||
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*rc*kphi*rc*kphi - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gxy caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gxy(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, kphi, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, sinlon, rc, kappa, deltax, deltay, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*(sinlatp*sinlatc +
|
||||
coslatp*coslatc*coslon);
|
||||
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltax = rc*kphi;
|
||||
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltay)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gxz caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gxz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, kphi, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltax, deltaz, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltax = rc*kphi;
|
||||
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gyy caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gyy(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, sinlon, rc, kappa, deltay, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*(sinlatp*sinlatc +
|
||||
coslatp*coslatc*coslon);
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltay*deltay - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gyz caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gyz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, sinlon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltay, deltaz, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltay*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculates gzz caused by a tesseroid. */
|
||||
double tess_gzz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc,
|
||||
coslon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltaz, res;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltaz*deltaz - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*Calculate three gravity gradient components simultaneously*/
|
||||
void tess_gxz_gyz_gzz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc, sinlon,
|
||||
coslon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltaz, deltax, deltay, kphi,
|
||||
res_gxz, res_gyz, res_gzz;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxz = 0;
|
||||
res_gyz = 0;
|
||||
res_gzz = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltax = rc*kphi;
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxz += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyz += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltay*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gzz += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltaz*deltaz - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxz *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyz *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gzz *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res[0] = res_gxz;
|
||||
res[1] = res_gyz;
|
||||
res[2] = res_gzz;
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void tess_gxx_gxy_gxz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc, sinlon,
|
||||
coslon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltaz, deltax, deltay, kphi,
|
||||
res_gxx, res_gxy, res_gxz;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxx = 0;
|
||||
res_gxy = 0;
|
||||
res_gxz = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltax = rc*kphi;
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxx += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*rc*kphi*rc*kphi - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxy += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltay)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxz += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxx *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxy *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxz *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res[0] = res_gxx;
|
||||
res[1] = res_gxy;
|
||||
res[2] = res_gxz;
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void tess_gxy_gyy_gyz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon,
|
||||
GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., l_sqr, coslatp, coslatc, sinlatp, sinlatc, sinlon,
|
||||
coslon, cospsi, rc, kappa, deltaz, deltax, deltay, kphi,
|
||||
res_gxy, res_gyy, res_gyz;
|
||||
register int i, j, k;
|
||||
|
||||
coslatp = cos(d2r*latp);
|
||||
sinlatp = sin(d2r*latp);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxy = 0;
|
||||
res_gyy = 0;
|
||||
res_gyz = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(k = 0; k < glq_lon.order; k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j = 0; j < glq_lat.order; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(i = 0; i < glq_r.order; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
rc = glq_r.nodes[i];
|
||||
sinlatc = sin(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslatc = cos(d2r*glq_lat.nodes[j]);
|
||||
coslon = cos(d2r*(lonp - glq_lon.nodes[k]));
|
||||
sinlon = sin(d2r*(glq_lon.nodes[k] - lonp));
|
||||
cospsi = sinlatp*sinlatc + coslatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
|
||||
l_sqr = rp*rp + rc*rc - 2*rp*rc*cospsi;
|
||||
kphi = coslatp*sinlatc - sinlatp*coslatc*coslon;
|
||||
kappa = rc*rc*coslatc;
|
||||
|
||||
deltax = rc*kphi;
|
||||
deltay = rc*coslatc*sinlon;
|
||||
deltaz = rc*cospsi - rp;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxy += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltax*deltay)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyy += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltay*deltay - l_sqr)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyz += glq_lon.weights[k]*glq_lat.weights[j]*glq_r.weights[i]*
|
||||
kappa*(3*deltay*deltaz)/pow(l_sqr, 2.5);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res_gxy *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyy *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res_gyz *= SI2EOTVOS*G*tess.density*d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*d2r*(tess.n - tess.s)*
|
||||
(tess.r2 - tess.r1)*0.125;
|
||||
|
||||
res[0] = res_gxy;
|
||||
res[1] = res_gyy;
|
||||
res[2] = res_gyz;
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions that calculate the gravitational potential and its first and second
|
||||
derivatives for the MAG_tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
The gravity gradients can be calculated using the general formula of
|
||||
Grombein et al. (2010).
|
||||
The integrals are solved using the Gauss-Legendre Quadrature rule
|
||||
(Asgharzadeh et al., 2007).
|
||||
|
||||
The derivatives of the potential are made with respect to the local coordinate
|
||||
system x->North, y->East, z->Up (away from center of the Earth).
|
||||
|
||||
To maintain the standard convention, only for component gz the z axis is
|
||||
inverted, so a positive density results in positive gz.
|
||||
|
||||
Example
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
To calculate the gzz component due to a MAG_tesseroid on a regular grid:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include "glq.h"r
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "grav_tess.h"
|
||||
|
||||
int main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID tess = {1000, 44, 46, -1, 1, MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS - 100000,
|
||||
MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS};
|
||||
GLQ *glqlon, *glqlat, *glqr;
|
||||
double lon, lat, r = MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS + 1500000, res;
|
||||
int order = 8;
|
||||
|
||||
glqlon = glq_new(order, tess.w, tess.e);
|
||||
glqlat = glq_new(order, tess.s, tess.n);
|
||||
glqr = glq_new(order, tess.r1, tess.r2);
|
||||
|
||||
for(lat = 20; lat <= 70; lat += 0.5)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(lon = -25; lon <= 25; lon += 0.5)
|
||||
{
|
||||
res = tess_gzz(tess, lon, lat, r, *glqlon, *glqlat, *glqr);
|
||||
printf("%g %g %g\n", lon, lat, res);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
glq_free(glqlon);
|
||||
glq_free(glqlat);
|
||||
glq_free(glqr);
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
References
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Asgharzadeh, M.F., von Frese, R.R.B., Kim, H.R., Leftwich, T.E. & Kim, J.W.
|
||||
(2007): Spherical prism gravity effects by Gauss-Legendre quadrature integration.
|
||||
Geophysical Journal International, 169, 1-11.
|
||||
|
||||
Grombein, T.; Seitz, K.; Heck, B. (2010): Untersuchungen zur effizienten
|
||||
Berechnung topographischer Effekte auf den Gradiententensor am Fallbeispiel der
|
||||
Satellitengradiometriemission GOCE.
|
||||
KIT Scientific Reports 7547, ISBN 978-3-86644-510-9, KIT Scientific Publishing,
|
||||
Karlsruhe, Germany.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _MAG_TESSEROIDS_GRAV_TESS_H_
|
||||
#define _MAG_TESSEROIDS_GRAV_TESS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Needed for definition of MAG_TESSEROID */
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
/* Needed for definition of GLQ */
|
||||
#include "glq.h"
|
||||
|
||||
double calc_tess_model(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r, double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ));
|
||||
void calc_tess_model_triple(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r,
|
||||
void (*field_triple)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ, double*), double *res);
|
||||
double calc_tess_model_adapt(MAG_TESSEROID *model, int size, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ *glq_lon, GLQ *glq_lat, GLQ *glq_r, double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ), double ratio);
|
||||
|
||||
double tess_gxx(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
double tess_gxy(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
double tess_gxz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
double tess_gyy(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
double tess_gyz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
double tess_gzz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r);
|
||||
|
||||
void tess_gxz_gyz_gzz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res);
|
||||
void tess_gxx_gxy_gxz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res);
|
||||
void tess_gxy_gyy_gyz(MAG_TESSEROID tess, double lonp, double latp, double rp, GLQ glq_lon, GLQ glq_lat, GLQ glq_r, double *res);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,144 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions matrix and vector multiplications.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "linalg.h"
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
//macOS only!
|
||||
//#include <Accelerate/Accelerate.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef __linux__ // Debian, Ubuntu, Gentoo, Fedora, openSUSE, RedHat, Centos and other
|
||||
#include <cblas.h>
|
||||
#elif _WINDOWS || __WIN32__ // Added for windows by Yi Zhang on 2021-08-26
|
||||
#include <cblas.h>
|
||||
#elif defined(__APPLE__) && defined(__MACH__)
|
||||
#include <Accelerate/Accelerate.h>
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate magnetization vector in a coordinate system of a given point */
|
||||
void conv_vect_cblas(double *vect, double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2, double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double a1 = DEG2RAD*lat1;
|
||||
double b1 = DEG2RAD*lon1;
|
||||
double a2 = DEG2RAD*lat2;
|
||||
double b2 = DEG2RAD*lon2;
|
||||
|
||||
double cos_a1 = cos(PI/2.0-a1);
|
||||
double sin_a1 = sin(PI/2.0-a1);
|
||||
double cos_a2 = cos(PI/2.0-a2);
|
||||
double sin_a2 = sin(PI/2.0-a2);
|
||||
|
||||
double cos_b1 = cos(b1);
|
||||
double sin_b1 = sin(b1);
|
||||
double cos_b2 = cos(b2);
|
||||
double sin_b2 = sin(b2);
|
||||
|
||||
double Z1Y1[9] = {cos_a1*cos_b1, -sin_b1, cos_b1*sin_a1, cos_a1*sin_b1, cos_b1, sin_a1*sin_b1, -sin_a1, 0, cos_a1};
|
||||
double Z2Y2t[9] = {-cos_a2*cos_b2, -cos_a2*sin_b2, sin_a2, -sin_b2, cos_b2, 0, cos_b2*sin_a2, sin_a2*sin_b2, cos_a2};
|
||||
double R[9];
|
||||
|
||||
cblas_dgemm(CblasColMajor, CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 3, 3, 3, 1.0, Z1Y1, 3, Z2Y2t, 3, 0.0, R, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
R[0] = -R[0];
|
||||
R[3] = -R[3];
|
||||
R[6] = -R[6];
|
||||
|
||||
cblas_dgemv(CblasRowMajor, CblasNoTrans, 3, 3, 1.0, R, 3, vect, 1, 0.0, res, 1);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void conv_vect_cblas_precalc(double *vect, double cos_a1, double sin_a1, double cos_b1, double sin_b1, double cos_a2, double sin_a2, double cos_b2, double sin_b2, double *res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// double a1 = DEG2RAD*lat1;
|
||||
// double b1 = DEG2RAD*lon1;
|
||||
// double a2 = DEG2RAD*lat2;
|
||||
// double b2 = DEG2RAD*lon2;
|
||||
|
||||
// double cos_a1 = cos(PI/2.0-a1);
|
||||
// double sin_a1 = sin(PI/2.0-a1);
|
||||
// double cos_a2 = cos(PI/2.0-a2);
|
||||
// double sin_a2 = sin(PI/2.0-a2);
|
||||
|
||||
// double cos_b1 = cos(b1);
|
||||
// double sin_b1 = sin(b1);
|
||||
// double cos_b2 = cos(b2);
|
||||
// double sin_b2 = sin(b2);
|
||||
|
||||
double Z1Y1[9] = {cos_a1*cos_b1, -sin_b1, cos_b1*sin_a1, cos_a1*sin_b1, cos_b1, sin_a1*sin_b1, -sin_a1, 0, cos_a1};
|
||||
double Z2Y2t[9] = {-cos_a2*cos_b2, -cos_a2*sin_b2, sin_a2, -sin_b2, cos_b2, 0, cos_b2*sin_a2, sin_a2*sin_b2, cos_a2};
|
||||
double R[9];
|
||||
|
||||
cblas_dgemm(CblasColMajor, CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, 3, 3, 3, 1.0, Z1Y1, 3, Z2Y2t, 3, 0.0, R, 3);
|
||||
|
||||
R[0] = -R[0];
|
||||
R[3] = -R[3];
|
||||
R[6] = -R[6];
|
||||
|
||||
cblas_dgemv(CblasRowMajor, CblasNoTrans, 3, 3, 1.0, R, 3, vect, 1, 0.0, res, 1);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void from_loc_sphr_to_cart(double* columnvect_xyzloc, double colatitude, double longitude, double* columnvect_res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/*IMPORTANT: this subroutine is in the coordinate system NED*/
|
||||
|
||||
double phi = colatitude*DEG2RAD;
|
||||
double lambda = longitude*DEG2RAD;
|
||||
|
||||
double cos_phi = cos(phi);
|
||||
double sin_phi = sin(phi);
|
||||
double cos_lambda = cos(lambda);
|
||||
double sin_lambda = sin(lambda);
|
||||
|
||||
double columnvect_phi_unit[3] = {-sin_phi*cos_lambda, -sin_phi*sin_lambda, cos_phi};
|
||||
double columnvect_lambda_unit[3] = {-sin_lambda, cos_lambda, 0};
|
||||
double columnvect_r_unit[3] = {cos_phi*cos_lambda, cos_phi*sin_lambda, sin_phi};
|
||||
|
||||
columnvect_res[0] = columnvect_phi_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzloc[0]+columnvect_lambda_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzloc[1]+columnvect_r_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzloc[2];
|
||||
columnvect_res[1] = columnvect_phi_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzloc[0]+columnvect_lambda_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzloc[1]+columnvect_r_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzloc[2];
|
||||
columnvect_res[2] = columnvect_phi_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzloc[0]+columnvect_lambda_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzloc[1]+columnvect_r_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzloc[2];
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void from_cart_to_loc_sphr(double* columnvect_xyzglob, double colatitude, double longitude, double* columnvect_res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/*IMPORTANT: this subroutine is in the coordinate system NED*/
|
||||
|
||||
double phi = colatitude*DEG2RAD;
|
||||
double lambda = longitude*DEG2RAD;
|
||||
|
||||
double cos_phi = cos(phi);
|
||||
double sin_phi = sin(phi);
|
||||
double cos_lambda = cos(lambda);
|
||||
double sin_lambda = sin(lambda);
|
||||
|
||||
double rowvect_phi_unit[3] = {-sin_phi*cos_lambda, -sin_phi*sin_lambda, cos_phi};
|
||||
double rowvect_lambda_unit[3] = {-sin_lambda, cos_lambda, 0};
|
||||
double rowvect_r_unit[3] = {cos_phi*cos_lambda, cos_phi*sin_lambda, sin_phi};
|
||||
|
||||
columnvect_res[0] = rowvect_phi_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzglob[0]+rowvect_phi_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzglob[1]+rowvect_phi_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzglob[2];
|
||||
columnvect_res[1] = rowvect_lambda_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzglob[0]+rowvect_lambda_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzglob[1]+rowvect_lambda_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzglob[2];
|
||||
columnvect_res[2] = rowvect_r_unit[0]*columnvect_xyzglob[0]+rowvect_r_unit[1]*columnvect_xyzglob[1]+rowvect_r_unit[2]*columnvect_xyzglob[2];
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(double* columnvect_xyzloc, double colatitude1, double longitude1, double colatitude2, double longitude2, double* columnvect_res)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double columnvect_xyzglob[3];
|
||||
from_loc_sphr_to_cart(columnvect_xyzloc, colatitude1, longitude1, columnvect_xyzglob);
|
||||
from_cart_to_loc_sphr(columnvect_xyzglob, colatitude2, longitude2, columnvect_res);
|
||||
return;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#ifndef _LINALG_H_
|
||||
#define _LINALG_H_
|
||||
|
||||
void conv_vect_cblas(double *vect, double lon1, double lat1, double lon2, double lat2, double *res);
|
||||
void conv_vect_cblas_precalc(double *vect, double cos_a1, double sin_a1, double cos_b1, double sin_b1, double cos_a2, double sin_a2, double cos_b2, double sin_b2, double *res);
|
||||
|
||||
void from_loc_sphr_to_cart(double* columnvect_xyzloc, double colatitude, double longitude, double* columnvect_res);
|
||||
void from_cart_to_loc_sphr(double* columnvect_xyzglob, double colatitude, double longitude, double* columnvect_res);
|
||||
void from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(double* columnvect_xyzloc, double colatitude1, double longitude1, double colatitude2, double longitude2, double* columnvect_res);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions to set up logging.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdarg.h>
|
||||
#include <time.h>
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Initialize the logger so that it doesn't print by default */
|
||||
LOGGER logger = {100, 0, 100, NULL};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Setup logging to stderr.*/
|
||||
void log_init(int level)
|
||||
{
|
||||
logger.level = level;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set logging to a file. */
|
||||
void log_tofile(FILE *logfile, int level)
|
||||
{
|
||||
logger.filelogging = 1;
|
||||
logger.logfile = logfile;
|
||||
logger.file_level = level;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Log a message at debug level */
|
||||
void log_debug(const char *fmt, ...)
|
||||
{
|
||||
char msg[10000];
|
||||
va_list args;
|
||||
va_start(args, fmt);
|
||||
vsprintf(msg, fmt, args);
|
||||
va_end(args);
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.level <= LOG_DEBUG)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "DEBUG: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.filelogging && (logger.file_level <= LOG_DEBUG))
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(logger.logfile, "DEBUG: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Log a message at info level */
|
||||
void log_info(const char *fmt, ...)
|
||||
{
|
||||
char msg[10000];
|
||||
va_list args;
|
||||
va_start(args, fmt);
|
||||
vsprintf(msg, fmt, args);
|
||||
va_end(args);
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.level <= LOG_INFO)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.filelogging && logger.file_level <= LOG_INFO)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(logger.logfile, "%s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Log a message at warning level */
|
||||
void log_warning(const char *fmt, ...)
|
||||
{
|
||||
char msg[10000];
|
||||
va_list args;
|
||||
va_start(args, fmt);
|
||||
vsprintf(msg, fmt, args);
|
||||
va_end(args);
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.level <= LOG_WARNING)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "WARNING: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.filelogging && logger.file_level <= LOG_WARNING)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(logger.logfile, "WARNING: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Log a message at error level */
|
||||
void log_error(const char *fmt, ...)
|
||||
{
|
||||
char msg[10000];
|
||||
va_list args;
|
||||
va_start(args, fmt);
|
||||
vsprintf(msg, fmt, args);
|
||||
va_end(args);
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.level <= LOG_ERROR)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(logger.filelogging && logger.file_level <= LOG_ERROR)
|
||||
{
|
||||
fprintf(logger.logfile, "ERROR: %s\n", msg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Functions to set up logging.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
Logging to stderr:
|
||||
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void my_func(){
|
||||
log_info("From my_func!\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(){
|
||||
// Enable logging to stderr in debug level
|
||||
// will only print messages of level DEBUG or higher
|
||||
log_init(LOG_DEBUG);
|
||||
log_debug("debug line. The code is %d", LOG_DEBUG);
|
||||
log_info("info line. The code is %d", LOG_INFO);
|
||||
log_warning("warning line. The code is %d", LOG_WARNING);
|
||||
log_error("error line. The code is %d", LOG_ERROR);
|
||||
my_func();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
will print:
|
||||
|
||||
DEBUG: debug line. The code is 0
|
||||
info line. The code is 1
|
||||
WARNING: warning line. The code is 2
|
||||
ERROR: error line. The code is 3
|
||||
From my_func!
|
||||
|
||||
If function log_init() is not called than logging to stderr is disabled and no
|
||||
messages will be printed.
|
||||
|
||||
Logging to a file:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void my_func(){
|
||||
log_info("From my_func!\n");
|
||||
log_debug("Should not appear in log file\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int main(){
|
||||
// Enable logging to file "log.txt" in info level
|
||||
// will not print DEBUG level messages
|
||||
// since log_init was not called, there is no logging to stderr
|
||||
FILE *logfile = fopen("log.txt", "w");
|
||||
log_tofile(logfile, LOG_INFO);
|
||||
log_debug("debug line. The code is %d", LOG_DEBUG);
|
||||
log_info("info line. The code is %d", LOG_INFO);
|
||||
log_warning("warning line. The code is %d", LOG_WARNING);
|
||||
log_error("error line. The code is %d", LOG_ERROR);
|
||||
my_func();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
File log.txt will look like:
|
||||
|
||||
info line. The code is 1
|
||||
WARNING: warning line. The code is 2
|
||||
ERROR: error line. The code is 3
|
||||
From my_func!
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can combine loggin to stderr and to a file with different
|
||||
levels in the same program.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_LOGGER_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_LOGGER_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/* Needed for definition of FILE */
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Logging level for debug messages */
|
||||
#define LOG_DEBUG 1
|
||||
/** Logging level for general information */
|
||||
#define LOG_INFO 2
|
||||
/** Logging level for warning messages */
|
||||
#define LOG_WARNING 3
|
||||
/** Logging level for error messages */
|
||||
#define LOG_ERROR 4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Keep the information on the global logger */
|
||||
typedef struct logger_struct
|
||||
{
|
||||
int level; /**< level of logging */
|
||||
int filelogging; /**< flag to know wether loggint to a file is enabled */
|
||||
int file_level; /**< logging level for the file */
|
||||
FILE *logfile; /**< file to log to */
|
||||
|
||||
} LOGGER;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Global logger struct. Only declare in the main program! */
|
||||
//LOGGER logger;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Setup logging to stderr.
|
||||
|
||||
@param level level of logging to be made. Can be one of:
|
||||
- LOG_DEBUG
|
||||
- LOG_INFO
|
||||
- LOG_WARNING
|
||||
- LOG_ERROR
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_init(int level);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Set logging to a file.
|
||||
|
||||
@param logfile FILE pointer to the already open file to log to.
|
||||
@param level level of logging to be made to the file. Can be one of:
|
||||
- LOG_DEBUG
|
||||
- LOG_INFO
|
||||
- LOG_WARNING
|
||||
- LOG_ERROR
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_tofile(FILE *logfile, int level);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Log a message at debug level.
|
||||
|
||||
Pass parameters in the same format as printf()
|
||||
|
||||
Prints a newline at the end.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_debug(const char *fmt, ...);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Log a message at info level.
|
||||
|
||||
Pass parameters in the same format as printf()
|
||||
|
||||
Does not print "INFO: " in front of the message when logging
|
||||
|
||||
Prints a newline at the end.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_info(const char *fmt, ...);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Log a message at warning level.
|
||||
|
||||
Pass parameters in the same format as printf()
|
||||
|
||||
Prints a newline at the end.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_warning(const char *fmt, ...);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Log a message at error level.
|
||||
|
||||
Pass parameters in the same format as printf()
|
||||
|
||||
Prints a newline at the end.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void log_error(const char *fmt, ...);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,678 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Input and output parsing tools.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <time.h>
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "version.h"
|
||||
#include "parsers.h"
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Parse basic command line arguments for programs */
|
||||
int parse_basic_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname,
|
||||
BASIC_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(void))
|
||||
{
|
||||
int bad_args = 0, parsed_args = 0, total_args = 1, i;
|
||||
char *params;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default values for options */
|
||||
args->verbose = 0;
|
||||
args->logtofile = 0;
|
||||
/* Parse arguments */
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(argv[i][0] == '-')
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(argv[i][1])
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 'h':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
print_help();
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(args->verbose)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -v");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
args->verbose = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'l':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(args->logtofile)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -l");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strlen(params) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument -l. Missing filename.");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->logtofile = 1;
|
||||
args->logfname = params;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case '-':
|
||||
{
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strcmp(params, "version"))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
print_version(progname);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_args == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->inputfname = argv[i];
|
||||
parsed_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'. Already given model file %s",
|
||||
argv[i], args->inputfname);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Check if parsing went well */
|
||||
if(parsed_args > total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("%s: too many input arguments. given %d, max %d.",
|
||||
progname, parsed_args, total_args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(bad_args > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("%d bad input argument(s)", bad_args);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(parsed_args < total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Parse command line arguments for tessh* programs */
|
||||
int parse_tessb_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname,
|
||||
TESSB_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(const char *))
|
||||
{
|
||||
int bad_args = 0, parsed_args = 0, total_args = 1, parsed_order = 0,
|
||||
parsed_ratio1 = 0, parsed_ratio2 = 0, parsed_ratio3 = 0, i, nchar, nread;
|
||||
char *params;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default values for options */
|
||||
args->verbose = 0;
|
||||
args->logtofile = 0;
|
||||
args->lon_order = 2;
|
||||
args->lat_order = 2;
|
||||
args->r_order = 2;
|
||||
args->adaptative = 1;
|
||||
args->ratio1 = 0; /* zero means use the default for the program */
|
||||
args->ratio2 = 0;
|
||||
args->ratio3 = 0;
|
||||
/* Parse arguments */
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(argv[i][0] == '-')
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(argv[i][1])
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 'h':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
print_help(progname);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
case 'v':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(args->verbose)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -v");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
args->verbose = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'l':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(args->logtofile)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -l");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strlen(params) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument -l. Missing filename.");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->logtofile = 1;
|
||||
args->logfname = params;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case '-':
|
||||
{
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strcmp(params, "version"))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
print_version(progname);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 'a':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!args->adaptative)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -a");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
args->adaptative = 0;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'o':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_order)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -o");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
nchar = 0;
|
||||
nread = sscanf(params, "%d/%d/%d%n", &(args->lon_order),
|
||||
&(args->lat_order), &(args->r_order), &nchar);
|
||||
if(nread != 3 || *(params + nchar) != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
parsed_order = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 't':
|
||||
{
|
||||
//ELDAR BAYKIEV///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
switch(argv[i][2])
|
||||
{
|
||||
case '1':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_ratio1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -t1");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
nchar = 0;
|
||||
nread = sscanf(params, "%lf%n", &(args->ratio1), &nchar);
|
||||
if(nread != 1 || *(params + nchar) != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
parsed_ratio1 = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case '2':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_ratio2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -t2");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
nchar = 0;
|
||||
nread = sscanf(params, "%lf%n", &(args->ratio2), &nchar);
|
||||
if(nread != 1 || *(params + nchar) != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
parsed_ratio2 = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case '3':
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_ratio3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("repeated option -t3");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
params = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
nchar = 0;
|
||||
nread = sscanf(params, "%lf%n", &(args->ratio3), &nchar);
|
||||
if(nread != 1 || *(params + nchar) != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("bad input argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
parsed_ratio3 = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//ELDAR BAYKIEV///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
}
|
||||
default:
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_args == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->modelfname = argv[i];
|
||||
parsed_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("invalid argument '%s'. Already given model file %s",
|
||||
argv[i], args->modelfname);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Check if parsing went well */
|
||||
if(bad_args > 0 || parsed_args != total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(parsed_args < total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("%s: missing input file.",
|
||||
progname, parsed_args, total_args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(parsed_args > total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("%s: too many input arguments. given %d, max %d.",
|
||||
progname, parsed_args, total_args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(bad_args > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("%d bad input argument(s)", bad_args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//parse arguments for gradient calculator
|
||||
int parse_gradcalc_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname, GRADCALC_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(const char *))
|
||||
{
|
||||
int bad_args = 0, parsed_args = 0, total_args = 5, i;
|
||||
char *params;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default values for options */
|
||||
args->verbose = 0;
|
||||
args->logtofile = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
args->gridbx_set = FALSE;
|
||||
args->gridby_set = FALSE;
|
||||
args->gridbz_set = FALSE;
|
||||
args->out_set = -1;
|
||||
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED = -1;
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED_set = FALSE;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Parse arguments */
|
||||
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(argv[i][0] == '-')
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(argv[i][1])
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 'h':
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
//log_error("invalid argument '%s'", argv[i]);
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s'\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
print_help(progname);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
case '-':
|
||||
{
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strcmp(params, "version"))
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s'\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
print_version(progname);
|
||||
return 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case 'b':
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
if(strlen(params) <= 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("bad input argument -b. Missing component and filename\n");
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
switch(argv[i][2])
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 'x':
|
||||
if(args->gridbx_set)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', gridfile bx already set\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->gridbx_set = 1;
|
||||
args->gridbx_fn = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'y':
|
||||
if(args->gridby_set)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', gridfile by already set\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->gridby_set = 1;
|
||||
args->gridby_fn = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'z':
|
||||
if(args->gridbz_set)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', gridfile by already set\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->gridbz_set = 1;
|
||||
args->gridbz_fn = &argv[i][3];
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', wrong component\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'c':
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
|
||||
if(args->bz_NEU_NED_set)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', coordinate system is already set\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(strlen(params) > 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', specify coordinate system in the input grids\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(argv[i][2] == '1')
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED_set = 1;
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if(argv[i][2] == '2')
|
||||
{
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED_set = 1;
|
||||
args->bz_NEU_NED = -1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', there are only NED (1) and NEU (2, default) coordinate systems\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 'o':
|
||||
params = &argv[i][2];
|
||||
|
||||
if(args->out_set>=0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', output format is already set\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(strlen(params) != 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s', specify output format\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
//TODO Add check if it is integer
|
||||
args->out_set = atoi(params);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
printf("invalid argument '%s'\n", argv[i]);
|
||||
bad_args++;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(parsed_args > total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//log_error("%s: too many input arguments. given %d, max %d.", progname, parsed_args, total_args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(bad_args > 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//log_error("%d bad input argument(s)", bad_args);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(parsed_args < total_args)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Strip trailing spaces and newlines from the end of a string */
|
||||
void strstrip(char *str)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
for(i = strlen(str) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(str[i] != ' ' && str[i] != '\n' && str[i] != '\r' && str[i] != '\0')
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
str[i + 1] = '\0';
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read a single tesseroid from a string */
|
||||
int gets_mag_tess(const char *str, MAG_TESSEROID *tess)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double w, e, s, n, top, bot, dens, suscept, Bx, By, Bz, Rx, Ry, Rz;
|
||||
int nread, nchars;
|
||||
|
||||
nread = sscanf(str, "%lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf%n", &w, &e, &s,
|
||||
&n, &top, &bot, &dens, &suscept, &Bx, &By, &Bz, &nchars);
|
||||
if(nread != 11 || str[nchars] != '\0')
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
tess->w = w;
|
||||
tess->e = e;
|
||||
tess->s = s;
|
||||
tess->n = n;
|
||||
tess->r1 = MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS + bot;
|
||||
tess->r2 = MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS + top;
|
||||
tess->density = dens;
|
||||
tess->suscept = suscept;
|
||||
tess->Bx = Bx;
|
||||
tess->By = By;
|
||||
tess->Bz = Bz;
|
||||
|
||||
tess->cos_a1 = cos(PI/2.0-DEG2RAD*(w+e)*0.5);
|
||||
tess->sin_a1 = sin(PI/2.0-DEG2RAD*(w+e)*0.5);
|
||||
tess->cos_b1 = cos(DEG2RAD*(s+n)*0.5);
|
||||
tess->sin_b1 = sin(DEG2RAD*(s+n)*0.5);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//ELDAR BAYKIEV////////////////////////////////
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID * read_mag_tess_model(FILE *modelfile, int *size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID *model, *tmp;
|
||||
int buffsize = 300, line, badinput = 0, error_exit = 0;
|
||||
char sbuff[10000];
|
||||
|
||||
/* Start with a single buffer allocation and expand later if necessary */
|
||||
model = (MAG_TESSEROID *)malloc(buffsize*sizeof(MAG_TESSEROID));
|
||||
if(model == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("problem allocating initial memory to load tesseroid model.");
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*size = 0;
|
||||
for(line = 1; !feof(modelfile); line++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(fgets(sbuff, 10000, modelfile) == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(ferror(modelfile))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("problem encountered reading line %d.", line);
|
||||
error_exit = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Check for comments and blank lines */
|
||||
if(sbuff[0] == '#' || sbuff[0] == '\r' || sbuff[0] == '\n')
|
||||
{
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(*size == buffsize)
|
||||
{
|
||||
buffsize += buffsize;
|
||||
tmp = (MAG_TESSEROID *)realloc(model, buffsize*sizeof(MAG_TESSEROID));
|
||||
if(tmp == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Need to free because realloc leaves unchanged in case of
|
||||
error */
|
||||
free(model);
|
||||
log_error("problem expanding memory for tesseroid model.\nModel is too big.");
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
model = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Remove any trailing spaces or newlines */
|
||||
strstrip(sbuff);
|
||||
if(gets_mag_tess(sbuff, &model[*size]))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("bad/invalid tesseroid at line %d.", line);
|
||||
badinput = 1;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
(*size)++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(badinput || error_exit)
|
||||
{
|
||||
free(model);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Adjust the size of the model */
|
||||
if(*size != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
tmp = (MAG_TESSEROID *)realloc(model, (*size)*sizeof(MAG_TESSEROID));
|
||||
if(tmp == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Need to free because realloc leaves unchanged in case of
|
||||
error */
|
||||
free(model);
|
||||
log_error("problem freeing excess memory for tesseroid model.");
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
model = tmp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return model;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read a single rectangular prism from a string */
|
||||
@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Input and output parsing tools.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _MAG_TESSEROIDS_PARSERS_H_
|
||||
#define _MAG_TESSEROIDS_PARSERS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/* Needed for definition of MAG_TESSEROID and PRISM */
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
/* Need for the definition of FILE */
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/** Store basic input arguments and option flags */
|
||||
typedef struct basic_args
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *inputfname; /**< name of the input file */
|
||||
int verbose; /**< flag to indicate if verbose printing is enabled */
|
||||
int logtofile; /**< flag to indicate if logging to a file is enabled */
|
||||
char *logfname; /**< name of the log file */
|
||||
} BASIC_ARGS;
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct tessh_args
|
||||
{
|
||||
int lon_order; /**< glq order in longitude integration */
|
||||
int lat_order; /**< glq order in latitude integration */
|
||||
int r_order; /**< glq order in radial integration */
|
||||
char *modelfname; /**< name of the file with the tesseroid model */
|
||||
int verbose; /**< flag to indicate if verbose printing is enabled */
|
||||
int logtofile; /**< flag to indicate if logging to a file is enabled */
|
||||
char *logfname; /**< name of the log file */
|
||||
int adaptative; /**< flat to indicate wether to use the adaptative size
|
||||
of tesseroid algorithm */
|
||||
double ratio1; /**< distance-size ratio used for recusive division */
|
||||
double ratio2; /**< distance-size ratio used for recusive division */
|
||||
double ratio3; /**< distance-size ratio used for recusive division */
|
||||
} TESSB_ARGS;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
typedef struct gradcalc_args
|
||||
{
|
||||
int gridbx_set;
|
||||
int gridby_set;
|
||||
int gridbz_set;
|
||||
|
||||
char* gridbx_fn;
|
||||
char* gridby_fn;
|
||||
char* gridbz_fn;
|
||||
|
||||
int out_set;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int bz_NEU_NED;
|
||||
int bz_NEU_NED_set;
|
||||
|
||||
int verbose; /**< flag to indicate if verbose printing is enabled */
|
||||
int logtofile; /**< flag to indicate if logging to a file is enabled */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
} GRADCALC_ARGS;
|
||||
|
||||
int parse_basic_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname, BASIC_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(void));
|
||||
int parse_tessb_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname, TESSB_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(const char *));
|
||||
|
||||
int parse_gradcalc_args(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname, GRADCALC_ARGS *args, void (*print_help)(const char *));
|
||||
|
||||
void strstrip(char *str);
|
||||
|
||||
int gets_mag_tess(const char *str, MAG_TESSEROID *tess);
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID * read_mag_tess_model(FILE *modelfile, int *size);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,385 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Generic main function for the tessb* programs.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include <time.h>
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "version.h"
|
||||
#include "grav_tess.h"
|
||||
#include "glq.h"
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
#include "parsers.h"
|
||||
#include "tessb_main.h"
|
||||
#include "linalg.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/* Print the help message for tessh* programs */
|
||||
void print_tessb_help(const char *progname)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("MAGNETIC MAG_TESSEROIDS\n");
|
||||
printf("Usage: %s MODELFILE [OPTIONS]\n\n", progname);
|
||||
if(strcmp(progname + 4, "pot") == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("Calculate the potential due to a tesseroid model on\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("Calculate the %s component due to a tesseroid model on\n",
|
||||
progname + 4);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("TODO\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Run the main for a generic tessh* program */
|
||||
int run_tessb_main(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname,
|
||||
double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ),
|
||||
double ratio1, double ratio2, double ratio3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
TESSB_ARGS args;
|
||||
GLQ *glq_lon, *glq_lat, *glq_r;
|
||||
MAG_TESSEROID *model;
|
||||
|
||||
int modelsize, rc, line, points = 0, error_exit = 0, bad_input = 0;
|
||||
char buff[10000];
|
||||
|
||||
double lon, lat, height, res;
|
||||
|
||||
/*variables for precalculation of trigonometrical functions for tesseroid centers*/
|
||||
double cos_a2, sin_a2, cos_b2, sin_b2;
|
||||
|
||||
/*variables for precalculation of trigonometrical functions for grid points*/
|
||||
double lon_prev, lat_prev;
|
||||
double cos_a2_prev, sin_a2_prev, cos_b2_prev, sin_b2_prev;
|
||||
|
||||
FILE *logfile = NULL, *modelfile = NULL;
|
||||
time_t rawtime;
|
||||
clock_t tstart;
|
||||
struct tm * timeinfo;
|
||||
|
||||
double (*field1)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ);
|
||||
double (*field2)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ);
|
||||
double (*field3)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ);
|
||||
void (*field_triple)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ, double*);
|
||||
double ggt_1, ggt_2, ggt_3;
|
||||
double gtt_v[3];
|
||||
int n_tesseroid;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
log_init(LOG_INFO);
|
||||
|
||||
rc = parse_tessb_args(argc, argv, progname, &args, &print_tessb_help);
|
||||
if(rc == 2)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(rc == 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Set the appropriate logging level and log to file if necessary */
|
||||
if(!args.verbose)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_init(LOG_WARNING);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
{
|
||||
logfile = fopen(args.logfname, "w");
|
||||
if(logfile == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("unable to create log file %s", args.logfname);
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
log_tofile(logfile, LOG_DEBUG);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Check if a custom distance-size ratio is given */
|
||||
if(args.ratio1 != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ratio1 = args.ratio1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(args.ratio2 != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ratio2 = args.ratio2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(args.ratio3 != 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ratio3 = args.ratio3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Print standard verbose */
|
||||
log_info("%s (Tesseroids project) %s", progname, tesseroids_version);
|
||||
time(&rawtime);
|
||||
timeinfo = localtime(&rawtime);
|
||||
log_info("(local time) %s", asctime(timeinfo));
|
||||
log_info("Use recursive division of tesseroids: %s",
|
||||
args.adaptative ? "True" : "False");
|
||||
log_info("Distance-size ratio1 for recusive division: %g", ratio1);
|
||||
log_info("Distance-size ratio2 for recusive division: %g", ratio2);
|
||||
log_info("Distance-size ratio3 for recusive division: %g", ratio3);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Make the necessary GLQ structures */
|
||||
log_info("Using GLQ orders: %d lon / %d lat / %d r", args.lon_order,
|
||||
args.lat_order, args.r_order);
|
||||
glq_lon = glq_new(args.lon_order, -1, 1);
|
||||
glq_lat = glq_new(args.lat_order, -1, 1);
|
||||
glq_r = glq_new(args.r_order, -1, 1);
|
||||
if(glq_lon == NULL || glq_lat == NULL || glq_r == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("failed to create required GLQ structures");
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
fclose(logfile);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read the tesseroid model file */
|
||||
log_info("Reading magnetic tesseroid model from file %s", args.modelfname);
|
||||
modelfile = fopen(args.modelfname, "r");
|
||||
if(modelfile == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("failed to open model file %s", args.modelfname);
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
fclose(logfile);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
model = read_mag_tess_model(modelfile, &modelsize);
|
||||
fclose(modelfile);
|
||||
if(modelsize == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("tesseroid file %s is empty", args.modelfname);
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
fclose(logfile);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(model == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("failed to read model from file %s", args.modelfname);
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to bad input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
fclose(logfile);
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
log_info("Total of %d tesseroid(s) read", modelsize);
|
||||
|
||||
/* Print a header on the output with provenance information */
|
||||
if(strcmp(progname + 4, "pot") == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("# Potential calculated with %s %s:\n", progname,
|
||||
tesseroids_version);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("# %s component calculated with %s %s:\n", progname+4, progname,
|
||||
tesseroids_version);
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("# local time: %s", asctime(timeinfo));
|
||||
printf("# model file: %s (%d tesseroids)\n", args.modelfname, modelsize);
|
||||
printf("# GLQ order: %d lon / %d lat / %d r\n", args.lon_order,
|
||||
args.lat_order, args.r_order);
|
||||
printf("# Use recursive division of tesseroids: %s\n",
|
||||
args.adaptative ? "True" : "False");
|
||||
printf("# Distance-size ratio1 for recusive division: %g\n", ratio1);
|
||||
printf("# Distance-size ratio2 for recusive division: %g\n", ratio2);
|
||||
printf("# Distance-size ratio3 for recusive division: %g\n", ratio3);
|
||||
|
||||
/////////////ELDAR BAYKIEV//////////////
|
||||
/* Assign pointers to functions that calculate gravity gradient tensor components */
|
||||
if (!strcmp("tessbx", progname))
|
||||
{
|
||||
field1 = &tess_gxx;
|
||||
field2 = &tess_gxy;
|
||||
field3 = &tess_gxz;
|
||||
|
||||
field_triple = &tess_gxx_gxy_gxz;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp("tessby", progname))
|
||||
{
|
||||
field1 = &tess_gxy;
|
||||
field2 = &tess_gyy;
|
||||
field3 = &tess_gyz;
|
||||
|
||||
field_triple = &tess_gxy_gyy_gyz;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (!strcmp("tessbz", progname))
|
||||
{
|
||||
field1 = &tess_gxz;
|
||||
field2 = &tess_gyz;
|
||||
field3 = &tess_gzz;
|
||||
|
||||
field_triple = &tess_gxz_gyz_gzz;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/////////////ELDAR BAYKIEV//////////////
|
||||
|
||||
/* Read each computation point from stdin and calculate */
|
||||
log_info("Calculating (this may take a while)...");
|
||||
tstart = clock();
|
||||
|
||||
///////////////
|
||||
lon_prev = 0;
|
||||
lat_prev = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for(line = 1; !feof(stdin); line++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(fgets(buff, 10000, stdin) == NULL)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(ferror(stdin))
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_error("problem encountered reading line %d", line);
|
||||
error_exit = 1;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Check for comments and blank lines */
|
||||
if(buff[0] == '#' || buff[0] == '\r' || buff[0] == '\n')
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("%s", buff);
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(sscanf(buff, "%lf %lf %lf", &lon, &lat, &height) != 3)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("bad/invalid computation point at line %d", line);
|
||||
log_warning("skipping this line and continuing");
|
||||
bad_input++;
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Need to remove \n and \r from end of buff first to print the
|
||||
result in the end */
|
||||
strstrip(buff);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/////////////ELDAR BAYKIEV//////////////
|
||||
res = 0;
|
||||
if(args.adaptative)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(n_tesseroid = 0; n_tesseroid < modelsize; n_tesseroid++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
gtt_v[0] = 0;
|
||||
gtt_v[1] = 0;
|
||||
gtt_v[2] = 0;
|
||||
double B_to_H = model[n_tesseroid].suscept/(M_0);//IMPORTANT
|
||||
double M_vect[3] = {model[n_tesseroid].Bx * B_to_H, model[n_tesseroid].By * B_to_H, model[n_tesseroid].Bz * B_to_H};
|
||||
double M_vect_p[3] = {0, 0, 0};
|
||||
|
||||
conv_vect_cblas(M_vect, (model[n_tesseroid].w + model[n_tesseroid].e)*0.5, (model[n_tesseroid].s + model[n_tesseroid].n)*0.5, lon, lat, M_vect_p);
|
||||
|
||||
ggt_1 = calc_tess_model_adapt(&model[n_tesseroid], 1, lon, lat, height + MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, glq_lon, glq_lat, glq_r, field1, ratio1);
|
||||
ggt_2 = calc_tess_model_adapt(&model[n_tesseroid], 1, lon, lat, height + MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, glq_lon, glq_lat, glq_r, field2, ratio2);
|
||||
ggt_3 = calc_tess_model_adapt(&model[n_tesseroid], 1, lon, lat, height + MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, glq_lon, glq_lat, glq_r, field3, ratio3);
|
||||
|
||||
res = res + M_0*EOTVOS2SI*(ggt_1 * M_vect_p[0] + ggt_2 * M_vect_p[1] + ggt_3 * M_vect_p[2]) /(G*model[n_tesseroid].density*4*PI);
|
||||
|
||||
//printf("res %g\n", res);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
//precalculate trigonometrical functions
|
||||
|
||||
if(lon == lon_prev)
|
||||
{
|
||||
cos_b2 = cos_b2_prev;
|
||||
sin_b2 = sin_b2_prev;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
cos_b2 = cos(DEG2RAD*lon);
|
||||
sin_b2 = sin(DEG2RAD*lon);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if(lat == lat_prev)
|
||||
{
|
||||
cos_a2 = cos_a2_prev;
|
||||
sin_a2 = sin_a2_prev;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
cos_a2 = cos(PI/2.0-DEG2RAD*lat);
|
||||
sin_a2 = sin(PI/2.0-DEG2RAD*lat);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
for(n_tesseroid = 0; n_tesseroid < modelsize; n_tesseroid++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
gtt_v[0] = 0;
|
||||
gtt_v[1] = 0;
|
||||
gtt_v[2] = 0;
|
||||
//ELDAR: TODO: PRECALCULATE SIC COSINE TABLES
|
||||
double B_to_H = model[n_tesseroid].suscept/(M_0);//IMPORTANT
|
||||
double M_vect[3] = {model[n_tesseroid].Bx * B_to_H, model[n_tesseroid].By * B_to_H, model[n_tesseroid].Bz * B_to_H};
|
||||
double M_vect_p[3] = {0, 0, 0};
|
||||
|
||||
//conv_vect_cblas(M_vect, (model[n_tesseroid].w + model[n_tesseroid].e)*0.5, (model[n_tesseroid].s + model[n_tesseroid].n)*0.5, lon, lat, M_vect_p);
|
||||
conv_vect_cblas_precalc(M_vect, model[n_tesseroid].cos_a1, model[n_tesseroid].sin_a1, model[n_tesseroid].cos_b1, model[n_tesseroid].sin_b1, cos_a2, sin_a2, cos_b2, sin_b2, M_vect_p);
|
||||
|
||||
calc_tess_model_triple(&model[n_tesseroid], 1, lon, lat, height + MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS, glq_lon, glq_lat, glq_r, field_triple, gtt_v);
|
||||
|
||||
res = res + M_0*EOTVOS2SI*(gtt_v[0] * M_vect_p[0] + gtt_v[1] * M_vect_p[1] + gtt_v[2] * M_vect_p[2]) /(G*model[n_tesseroid].density*4*PI);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
lon_prev = lon;
|
||||
lat_prev = lat;
|
||||
|
||||
cos_a2_prev = cos_a2;
|
||||
sin_a2_prev = sin_a2;
|
||||
|
||||
cos_b2_prev = cos_b2;
|
||||
sin_b2_prev = sin_b2;
|
||||
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
}
|
||||
printf("%s %.15g\n", buff, res);
|
||||
points++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(bad_input)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Encountered %d bad computation points which were skipped",
|
||||
bad_input);
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(error_exit)
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_warning("Terminating due to error in input");
|
||||
log_warning("Try '%s -h' for instructions", progname);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
log_info("Calculated on %d points in %.5g seconds", points,
|
||||
(double)(clock() - tstart)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
|
||||
}
|
||||
/* Clean up */
|
||||
free(model);
|
||||
glq_free(glq_lon);
|
||||
glq_free(glq_lat);
|
||||
glq_free(glq_r);
|
||||
log_info("Done");
|
||||
if(args.logtofile)
|
||||
fclose(logfile);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Generic main function for the tessb* programs.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _MAG_TESSEROIDS_TESSH_MAIN_H_
|
||||
#define _MAG_TESSEROIDS_TESSH_MAIN_H_
|
||||
|
||||
#include "glq.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
|
||||
void print_tessb_help(const char *progname);
|
||||
int run_tessb_main(int argc, char **argv, const char *progname, double (*field)(MAG_TESSEROID, double, double, double, GLQ, GLQ, GLQ), double ratio1, double ratio2, double ratio3);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Hold the version number of the project.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include "version.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Print version and license information */
|
||||
void print_version(const char *progname)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("%s (Magnetic Tesseroids) %s\n\n", progname, tesseroids_version);
|
||||
printf("Copyright (C) 2015, Eldar Baykiev.\n");
|
||||
printf("This program is based on the code of Leonardo Uieda.\n");
|
||||
printf("<http://tesseroids.readthedocs.org/>\n");
|
||||
printf("Developed by Eldar Baykiev.\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Hold the version number of the project.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_VERSION_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_VERSION_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/** Current project version number */
|
||||
const char tesseroids_version[] = "1.1";
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Print version and license information
|
||||
|
||||
@param progname name of the program
|
||||
*/
|
||||
void print_version(const char *progname);
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
sudo stow --dir=/opt/stow --target=/usr/local -S magtess
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 设置编译选项
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -O3")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -O3")
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置可执行文件的输出地址
|
||||
set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/bin/toolkits)
|
||||
|
||||
# 下面设置tools的编译命令 首先设置一个宏
|
||||
macro(add_tools name)
|
||||
# 添加可执行程序名称
|
||||
add_executable(${name} ${name}.cpp)
|
||||
# 设置安装后的动态库调用地址
|
||||
set_target_properties(${name} PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
# 链接动态库
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${name} PUBLIC magtess)
|
||||
# 将可执行程序安装到bin
|
||||
install(TARGETS ${name} RUNTIME DESTINATION sbin)
|
||||
endmacro()
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加tools
|
||||
add_tools(tessbx)
|
||||
add_tools(tessby)
|
||||
add_tools(tessbz)
|
||||
add_tools(tessutil_combine_grids)
|
||||
add_tools(tessutil_gradient_calculator)
|
||||
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux" OR ${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Darwin")
|
||||
# 添加可执行程序名称
|
||||
add_executable(tessutil_magnetize_model tessutil_magnetize_model.c)
|
||||
# 设置安装后的动态库调用地址
|
||||
set_target_properties(tessutil_magnetize_model PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
# 链接动态库
|
||||
target_link_libraries(tessutil_magnetize_model PUBLIC magtess)
|
||||
# 将可执行程序安装到bin
|
||||
install(TARGETS tessutil_magnetize_model RUNTIME DESTINATION sbin)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#include "../lib/constants.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/grav_tess.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/tessb_main.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Main tessbx*/
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return run_tessb_main(argc, argv, "tessbx", 0, TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#include "../lib/constants.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/grav_tess.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/tessb_main.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Main tessby*/
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return run_tessb_main(argc, argv, "tessby", 0, TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#include "../lib/constants.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/grav_tess.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/tessb_main.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/** Main tessbz*/
|
||||
int main(int argc, char **argv)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return run_tessb_main(argc, argv, "tessbz", 0, TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO, TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <iostream> // Added by Zhang Yi on 2021-08-26
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_GRID_POINTS 16000
|
||||
|
||||
#define GRID_FORMAT "%lf %lf %f %lf"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) /* Added for windows by Yi Zhang on 2021-08-26*/
|
||||
#include <BaseTsd.h>
|
||||
typedef SSIZE_T ssize_t;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
void printresult_withalt(double* longitudes, double* latitudes, float* altitudes, double* values, int n_values)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int h = 0; h < n_values; h++)
|
||||
printf( "%lf %lf %f %lf\n", longitudes[h], latitudes[h], altitudes[h], values[h]);
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void printresult(double* longitudes, double* latitudes, double* values, int n_values)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int h = 0; h < n_values; h++)
|
||||
printf( "%lf %lf %lf\n", longitudes[h], latitudes[h], values[h]);
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char**argv)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int n_files = (argc-1)/2;
|
||||
|
||||
double lons[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double lats[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
float alts[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
double vals[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
double factor = 1;
|
||||
|
||||
//char * line = NULL;
|
||||
std::string line;
|
||||
size_t len = 0;
|
||||
ssize_t read;
|
||||
|
||||
int n_lines = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < n_files; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//FILE * fp = fopen(argv[1+2*i], "r");
|
||||
std::ifstream fp(argv[1+2*i], std::ios::in);
|
||||
sscanf(argv[1+2*i+1], "%lf", &factor);
|
||||
|
||||
//if (fp == NULL)
|
||||
if (!fp)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Can not open file with grid values.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_lines = 0;
|
||||
//while ((read = getline(&line, &len, fp )) != -1)
|
||||
while (std::getline(fp, line))
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
//if ((line[0] != '#') && (strlen(line) > 2))
|
||||
if ((line[0] != '#') && (line.length() > 2))
|
||||
{
|
||||
n_lines++;
|
||||
if (n_lines>MAX_GRID_POINTS)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Too many grid points (> %d) in the input. Recompile program with a bigger value of MAX_GRID_POINTS.\n", n_lines);
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
double value;
|
||||
|
||||
sscanf(line.c_str(), GRID_FORMAT, &lons[n_lines-1], &lats[n_lines-1], &alts[n_lines-1], &value);
|
||||
vals[n_lines-1] = vals[n_lines-1] + value*factor;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fclose(fp);
|
||||
fp.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int no_alt = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
if (no_alt)
|
||||
printresult(lons, lats, vals, n_lines);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printresult_withalt(lons, lats, alts, vals, n_lines);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,366 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <fstream>
|
||||
#include <iostream> // Added by Zhang Yi on 2021-08-26
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
|
||||
#include "../lib/constants.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/parsers.h"
|
||||
#include "../lib/linalg.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#define MAX_GRID_POINTS 50000
|
||||
|
||||
#define GRID_FORMAT "%lf %lf %f %lf"
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined(_MSC_VER) /* Added for windows by Yi Zhang on 2021-08-26*/
|
||||
#include <BaseTsd.h>
|
||||
typedef SSIZE_T ssize_t;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO conversion of input/output units nT/km pT/km nT/m pT/m
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void printcomp(double* longitudes, double* latitudes, double* values, int n_values)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int h = 0; h < n_values; h++)
|
||||
printf("%lf %lf %lf\n", longitudes[h], latitudes[h], values[h]);
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void printall(double* longitudes, double* latitudes, int n_values, double* values1, double* values2, double* values3, double* values4, double* values5, double* values6, double* values7)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for (int h = 0; h < n_values; h++)
|
||||
printf("%lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf %lf\n", longitudes[h], latitudes[h], values1[h], values2[h], values3[h], values4[h], values5[h], values6[h], values7[h]);
|
||||
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void print_gradcalc_help(const char *progname)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("MAGNETIC TESSEROIDS: Gradient Calculator\n");
|
||||
printf("Usage: %s [OPTIONS]\n\n", progname);
|
||||
printf("Options:\n");
|
||||
printf("\t-h\t\t\t Help\n\n");
|
||||
|
||||
printf("\t-bx[GRID FILENAME]\t Grid filename with Bx component\n");
|
||||
printf("\t-by[GRID FILENAME]\t Grid filename with By component\n");
|
||||
printf("\t-bz[GRID FILENAME]\t Grid filename with Bz component\n");
|
||||
printf("\tNOTE:\tall grids must be in format LON LAT ALT B*,\n\t\tstart from West-South corner and longitudes must increment first.\n\t\tLON, LAT in [deg], B* in [nT] and ALT in [m].\n\n");
|
||||
|
||||
printf("\t-c[COORD SYSTEM]\t Coordinate system in input grids. 1 - North-East-Down, 2 - North-East-Up\n");
|
||||
printf("\t-o[COMPONENT]\t\t If 0, then output format is LON LAT BXX BYX BZX BXY BYY BZY BZZ, if 1-7, then \n");
|
||||
printf("\tonly corresponding component would be printed with format LON LAT B**.\n");
|
||||
printf("\tNOTE: output is always in North-East-Down coordinate system.\n\t\tLON, LAT in [deg], B** in [nT/km].\n");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//printf("TODO\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
int main(int argc, char**argv)
|
||||
{
|
||||
const char * progname = "tessutil_gradient_calculator";
|
||||
GRADCALC_ARGS args;
|
||||
int rc;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//log_init(LOG_INFO);
|
||||
|
||||
rc = parse_gradcalc_args(argc, argv, progname, &args, &print_gradcalc_help);
|
||||
if(rc == 2) //help
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(rc == 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("Terminating due to bad input\n");
|
||||
printf("Try '%s -h' for instructions\n", progname);
|
||||
|
||||
return 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ((args.gridbx_set == 0) || (args.gridbx_set == 0) || (args.gridbx_set == 0))
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("no input grids\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (args.bz_NEU_NED == 1)
|
||||
printf("#Coordinate system in input grids: North-East-Down\n");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("#Coordinate system in input grids: North-East-Up\n");
|
||||
printf("#Coordinate system in output grid: North-East-Down\n");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
double lons[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double lats[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
float alts[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
double bx[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double by[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double bz[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
//read file with bx
|
||||
|
||||
//char * line = NULL;
|
||||
std::string line;
|
||||
size_t len = 0;
|
||||
ssize_t read;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//FILE * bxfp = fopen(args.gridbx_fn, "r");
|
||||
//if (bxfp == NULL)
|
||||
std::ifstream bxfp(args.gridbx_fn, std::ios::in); // Updated by Yi Zhang on 2021-08-26
|
||||
if (!bxfp)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Can not open file with Bx values.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int n_lines = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
//while ((read = getline(&line, &len, bxfp )) != -1)
|
||||
while (getline(bxfp, line))
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
//if ((line[0] != '#') && (strlen(line) > 2))
|
||||
if ((line[0] != '#') && (line.length() > 2))
|
||||
{
|
||||
n_lines++;
|
||||
if (n_lines>MAX_GRID_POINTS)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Too many grid points (> %d) in the input. Recompile program with a bigger value of MAX_GRID_POINTS.\n", n_lines);
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
sscanf(line.c_str(), GRID_FORMAT, &lons[n_lines-1], &lats[n_lines-1], &alts[n_lines-1], &bx[n_lines-1]);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fclose(bxfp);
|
||||
bxfp.close();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*number of grid points*/
|
||||
printf("#Number of grid points: %d\n", n_lines);
|
||||
|
||||
/*grid spacing*/
|
||||
|
||||
double lon_min = lons[0];
|
||||
double lon_max = lons[n_lines-1];
|
||||
|
||||
double lon_step = lons[1]-lons[0];
|
||||
if ((lon_step == 0) || (lon_step <= 0) || (lon_max < lon_min))
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Wrong grid format. Longitudes must increment first. Use the format of tessgrd.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int lon_n = 1;
|
||||
while ((lats[lon_n] == lats[0]) && (lon_n < n_lines))
|
||||
{
|
||||
lon_n++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
double lat_step = lats[lon_n]-lats[0];
|
||||
|
||||
int lat_n = n_lines / lon_n;
|
||||
|
||||
double lat_min = lats[0];
|
||||
double lat_max = lats[n_lines-1];
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if ((lat_step <= 0) || (lat_step <= 0) || (lat_max < lat_min))
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Wrong grid format. Latitudes must increment. Use the format of tessgrd.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
printf("#Longitudinal step: %lf, latitudinal step: %lf \n", lon_step, lat_step);
|
||||
printf("#Longitudinal points: %d, latitudinal points: %d \n", lon_n, lat_n);
|
||||
printf("#Edges: W %lf, E %lf, S %lf, N %lf \n", lon_min, lon_max, lat_min, lat_max);
|
||||
|
||||
/* read other grids */
|
||||
// By
|
||||
//FILE * byfp = fopen(args.gridby_fn, "r");
|
||||
//if (byfp == NULL)
|
||||
|
||||
std::ifstream byfp(args.gridby_fn, std::ios::in);
|
||||
if (!byfp)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Can not open file with Bx values.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int n_lines2 = 0;
|
||||
//while ((read = getline(&line, &len, byfp )) != -1)
|
||||
while (getline(byfp, line))
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
//if ((line[0] != '#') && (strlen(line) > 2))
|
||||
if ((line[0] != '#') && (line.length() > 2))
|
||||
{
|
||||
n_lines2++;
|
||||
//printf("%s", line);
|
||||
double dummy1, dummy2;
|
||||
float dummy3;
|
||||
sscanf(line.c_str(), GRID_FORMAT , &dummy1, &dummy2, &dummy3, &by[n_lines2-1]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fclose(byfp);
|
||||
byfp.close();
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_lines2 != n_lines)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Grid points of Bx and By do not coincide.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bz
|
||||
//FILE * bzfp = fopen(args.gridbz_fn, "r");
|
||||
//if (bzfp == NULL)
|
||||
std::ifstream bzfp(args.gridbz_fn, std::ios::in);
|
||||
if (!bzfp)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Can not open file with Bx values.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
n_lines2 = 0;
|
||||
//while ((read = getline(&line, &len, bzfp )) != -1)
|
||||
while (getline(bzfp, line))
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((line[0] != '#') && (line.length() > 2))
|
||||
{
|
||||
n_lines2++;
|
||||
//printf("%s", line);
|
||||
double dummy1, dummy2;
|
||||
float dummy3;
|
||||
double bz_curr;
|
||||
sscanf(line.c_str(), GRID_FORMAT, &dummy1, &dummy2, &dummy3,&bz_curr);
|
||||
|
||||
bz[n_lines2-1] = args.bz_NEU_NED* bz_curr; //COORDINATE SYSTEM NEU or NED
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
//fclose(byfp);
|
||||
byfp.close();
|
||||
|
||||
if (n_lines2 != n_lines)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printf("ERROR: Grid points of Bx and Bz do not coincide.\n");
|
||||
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* calculate gradients */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
double bxx[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double byx[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double bzx[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
double bxy[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double byy[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
double bzy[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
double bzz[MAX_GRID_POINTS];
|
||||
|
||||
int cent_ind, west_ind, east_ind, south_ind, north_ind;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i<lon_n-1; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int j = 1; j<lat_n-1; j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
cent_ind = (j) *lon_n + (i);
|
||||
west_ind = (j) *lon_n + (i-1);
|
||||
east_ind = (j) *lon_n + (i+1);
|
||||
south_ind = (j-1) *lon_n + (i);
|
||||
north_ind = (j+1) *lon_n + (i);
|
||||
|
||||
//double vect_cent[3] = {bx[cent_ind], by[cent_ind], bz[cent_ind]};
|
||||
double vect_west[3] = {bx[west_ind], by[west_ind], bz[west_ind]};
|
||||
double vect_east[3] = {bx[east_ind], by[east_ind], bz[east_ind]};
|
||||
double vect_south[3] = {bx[south_ind], by[south_ind], bz[south_ind]};
|
||||
double vect_north[3] = {bx[north_ind], by[north_ind], bz[north_ind]};
|
||||
|
||||
double vect_c_west[3];
|
||||
double vect_c_east[3];
|
||||
double vect_c_south[3];
|
||||
double vect_c_north[3];
|
||||
|
||||
from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(vect_west, lats[west_ind], lons[west_ind], lats[cent_ind], lons[cent_ind], vect_c_west);
|
||||
from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(vect_east, lats[east_ind], lons[east_ind], lats[cent_ind], lons[cent_ind], vect_c_east);
|
||||
from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(vect_south, lats[south_ind], lons[south_ind], lats[cent_ind], lons[cent_ind], vect_c_south);
|
||||
from_loc_sphr_to_loc_sphr(vect_north, lats[north_ind], lons[north_ind], lats[cent_ind], lons[cent_ind], vect_c_north);
|
||||
|
||||
double cent_ang_sn = acos(sin(lats[south_ind]*DEG2RAD)*sin(lats[north_ind]*DEG2RAD) + cos(lats[south_ind]*DEG2RAD)*cos(lats[north_ind]*DEG2RAD)*cos(abs(lons[south_ind]-lons[north_ind])*DEG2RAD));
|
||||
double cent_ang_we = acos(sin(lats[west_ind]*DEG2RAD)*sin(lats[east_ind]*DEG2RAD) + cos(lats[west_ind]*DEG2RAD)*cos(lats[east_ind]*DEG2RAD)*cos(abs(lons[west_ind]-lons[east_ind])*DEG2RAD));
|
||||
|
||||
double dist_sn = (MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS + alts[cent_ind])*cent_ang_sn;
|
||||
double dist_we = (MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS + alts[cent_ind])*cent_ang_we;
|
||||
|
||||
bxx[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_south[0]-vect_c_north[0])/dist_sn*1000.0;
|
||||
byx[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_south[1]-vect_c_north[1])/dist_sn*1000.0;
|
||||
bzx[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_south[2]-vect_c_north[2])/dist_sn*1000.0;
|
||||
|
||||
bxy[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_west[0]-vect_c_east[0])/dist_we*1000.0;
|
||||
byy[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_west[1]-vect_c_east[1])/dist_we*1000.0;
|
||||
bzy[cent_ind] = -(vect_c_west[2]-vect_c_east[2])/dist_we*1000.0;
|
||||
|
||||
bzz[cent_ind] = -bxx[cent_ind] - byy[cent_ind];
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
switch(args.out_set)
|
||||
{
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
printf("#Component Bxx\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, bxx, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 2:
|
||||
printf("#Component Byx\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, byx, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
printf("#Component Bzx\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, bzx, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 4:
|
||||
printf("#Component Bxy\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, bxy, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 5:
|
||||
printf("#Component Byy\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, byy, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 6:
|
||||
printf("#Component Bzy\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, bzy, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 7:
|
||||
printf("#Component Bzz\n");
|
||||
printcomp(lons, lats, bzz, n_lines);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
printf("#All components: Bxx, Byx, Bzx, Bxy, Byy, Bzy, Bzz\n");
|
||||
printall(lons, lats, n_lines, bxx, byx, bzx, bxy, byy, bzy, bzz);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# netcdfcxx_win
|
||||
|
||||
#### Description
|
||||
一个windows下netcdf c++接口的编译项目,注意使用的是4.2版本的老接口。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Software Architecture
|
||||
Software architecture description
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation
|
||||
|
||||
1. xxxx
|
||||
2. xxxx
|
||||
3. xxxx
|
||||
|
||||
#### Instructions
|
||||
|
||||
1. xxxx
|
||||
2. xxxx
|
||||
3. xxxx
|
||||
|
||||
#### Contribution
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the repository
|
||||
2. Create Feat_xxx branch
|
||||
3. Commit your code
|
||||
4. Create Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Gitee Feature
|
||||
|
||||
1. You can use Readme\_XXX.md to support different languages, such as Readme\_en.md, Readme\_zh.md
|
||||
2. Gitee blog [blog.gitee.com](https://blog.gitee.com)
|
||||
3. Explore open source project [https://gitee.com/explore](https://gitee.com/explore)
|
||||
4. The most valuable open source project [GVP](https://gitee.com/gvp)
|
||||
5. The manual of Gitee [https://gitee.com/help](https://gitee.com/help)
|
||||
6. The most popular members [https://gitee.com/gitee-stars/](https://gitee.com/gitee-stars/)
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# netcdfcxx_legacy
|
||||
|
||||
#### 介绍
|
||||
一个windows下netcdf c++接口的编译项目,注意使用的是4.2版本的老接口。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 软件架构
|
||||
软件架构说明
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装教程
|
||||
|
||||
1. xxxx
|
||||
2. xxxx
|
||||
3. xxxx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用说明
|
||||
|
||||
1. xxxx
|
||||
2. xxxx
|
||||
3. xxxx
|
||||
|
||||
#### 参与贡献
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork 本仓库
|
||||
2. 新建 Feat_xxx 分支
|
||||
3. 提交代码
|
||||
4. 新建 Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 特技
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用 Readme\_XXX.md 来支持不同的语言,例如 Readme\_en.md, Readme\_zh.md
|
||||
2. Gitee 官方博客 [blog.gitee.com](https://blog.gitee.com)
|
||||
3. 你可以 [https://gitee.com/explore](https://gitee.com/explore) 这个地址来了解 Gitee 上的优秀开源项目
|
||||
4. [GVP](https://gitee.com/gvp) 全称是 Gitee 最有价值开源项目,是综合评定出的优秀开源项目
|
||||
5. Gitee 官方提供的使用手册 [https://gitee.com/help](https://gitee.com/help)
|
||||
6. Gitee 封面人物是一档用来展示 Gitee 会员风采的栏目 [https://gitee.com/gitee-stars/](https://gitee.com/gitee-stars/)
|
||||
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
cmd=${1}
|
||||
package=netcdfcxx_legacy
|
||||
address=/opt/stow
|
||||
targetdir=/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||
if [[ ${cmd} == "configure" && ! -d "build/" ]]; then
|
||||
mkdir build && cd build && cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${address}/${package} -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
|
||||
elif [[ ${cmd} == "configure" ]]; then
|
||||
cd build && rm -rf * && cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=${address}/${package} -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
|
||||
elif [[ ${cmd} == "build" ]]; then
|
||||
cd build && make
|
||||
elif [[ ${cmd} == "install" ]]; then
|
||||
cd build && sudo make install
|
||||
sudo stow --dir=${address} --target=${targetdir} ${package}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
@ -11,8 +11,5 @@ set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIB netcdfcxx_legacy)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIBRARY netcdfcxx_legacy)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_FOUND 1)
|
||||
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_OPENMP @LibLCG_OPENMP@)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_EIGEN @LibLCG_EIGEN@)
|
||||
|
||||
# include target information
|
||||
include("${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@PROJECT_NAME@Targets.cmake")
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# 设定源文件文件夹
|
||||
aux_source_directory(lib/ NETCDF_SRC)
|
||||
|
||||
find_package(HDF5 REQUIRED)
|
||||
|
||||
# 寻找netCDF库地址
|
||||
find_package(netCDF REQUIRED)
|
||||
if(netCDF_FOUND)
|
||||
@ -26,10 +28,18 @@ set_target_properties(netcdfcxx_legacy PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
set_target_properties(netcdfcxx_legacy_static PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
# 设置动态库的版本号
|
||||
set_target_properties(netcdfcxx_legacy PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}.${PROJECT_VERSION_MINOR})
|
||||
# 设置动态库的运行搜索地址
|
||||
set_target_properties(netcdfcxx_legacy PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
set_target_properties(netcdfcxx_legacy_static PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
find_library(NETCDF_LIBRARY netcdf ${netCDF_LIB_DIR})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy PUBLIC ${NETCDF_LIBRARY})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy_static ${NETCDF_LIBRARY})
|
||||
#find_library(NETCDF_LIBRARY netcdf ${netCDF_LIB_DIR})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy PUBLIC ${netCDF_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy_static ${netCDF_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy PUBLIC ${HDF5_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
target_link_libraries(netcdfcxx_legacy_static ${HDF5_LIBRARIES})
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置库文件的输出地址
|
||||
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
set(CONFIG_FILE_PATH lib/cmake/${PROJECT_NAME})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
340
dep/partow/include/dsv_filter.hpp
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,340 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
******************************************************************
|
||||
* Delimiter Seperated Values Filter Library *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Author: Arash Partow (2004) *
|
||||
* URL: http://www.partow.net/programming/dsvfilter/index.html *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
* Copyright notice: *
|
||||
* Free use of the Delimiter Seperated Values Filter Library is *
|
||||
* permitted under the guidelines of the MIT License. *
|
||||
* http://www.opensource.org/licenses/MIT *
|
||||
* *
|
||||
******************************************************************
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef INCLUDE_DSV_FILTER_HPP
|
||||
#define INCLUDE_DSV_FILTER_HPP
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <deque>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
#define strtk_no_tr1_or_boost
|
||||
|
||||
#include "exprtk.hpp"
|
||||
#include "strtk.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef dsv_filter_use_mmap
|
||||
#include <boost/iostreams/device/mapped_file.hpp>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class dsv_filter
|
||||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
|
||||
struct column_properties
|
||||
{
|
||||
enum column_type
|
||||
{
|
||||
e_none = 0,
|
||||
e_string = 1,
|
||||
e_number = 2
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
column_properties()
|
||||
: type(e_none),
|
||||
name (""),
|
||||
value_s(""),
|
||||
value_n(0.0),
|
||||
process(false)
|
||||
{}
|
||||
|
||||
column_type type;
|
||||
std::string name;
|
||||
std::string value_s;
|
||||
double value_n;
|
||||
strtk::util::value value;
|
||||
bool process;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
dsv_filter()
|
||||
: file_name_ ("" ),
|
||||
input_delimiter_ (","),
|
||||
output_delimiter_("|")
|
||||
{
|
||||
symbol_table_.add_constants();
|
||||
expression_.register_symbol_table(symbol_table_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::string file_name() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return file_name_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void set_input_delimiter(const std::string& input_delimiter)
|
||||
{
|
||||
input_delimiter_ = input_delimiter;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void set_output_delimiter(const std::string& output_delimiter)
|
||||
{
|
||||
output_delimiter_ = output_delimiter;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::string input_delimiter() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return input_delimiter_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::string output_delimiter() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return output_delimiter_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::size_t column_count() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return column_.size();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::size_t row_count() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return grid_.row_count();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline const column_properties& column(const std::size_t& index) const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return column_[index];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline bool load(const std::string& file_name)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (!strtk::fileio::file_exists(file_name))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
file_name_ = file_name;
|
||||
strtk::token_grid::options options;
|
||||
options.column_delimiters = input_delimiter_;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef dsv_filter_use_mmap
|
||||
input_source.close();
|
||||
input_source.open(file_name_);
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned char* data = reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>(const_cast<char*>(input_source.data()));
|
||||
|
||||
if (!grid_.load(data,input_source.size(),options))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
#else
|
||||
if (!grid_.load(file_name_,options))
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
if (0 == grid_.row_count())
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
else if (grid_.row_count() < 2)
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
else if (!process_column_header())
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline bool add_filter(const std::string& filter_expression)
|
||||
{
|
||||
error_ = "";
|
||||
parser_.dec().collect_variables() = true;
|
||||
|
||||
if (!parser_.compile(filter_expression,expression_))
|
||||
{
|
||||
error_ = "Error: " + parser_.error() + "\tFilter: " + filter_expression;
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Only extract for processing, the column values
|
||||
// that are being used in the current expression.
|
||||
typedef exprtk::parser<double> parser_t;
|
||||
typedef parser_t::dependent_entity_collector::symbol_t symbol_t;
|
||||
|
||||
std::deque<symbol_t> symbol_list;
|
||||
|
||||
parser_.dec().symbols(symbol_list);
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < column_.size(); ++i)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (column_[i].name.empty())
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
|
||||
column_[i].process = false;
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::size_t j = 0; j < symbol_list.size(); ++j)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (strtk::imatch(symbol_list[j].first,column_[i].name))
|
||||
{
|
||||
column_[i].process = true;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
template <typename Allocator,
|
||||
template <typename,typename> class Sequence>
|
||||
inline bool row(const std::size_t& r,
|
||||
const Sequence<bool,Allocator>& selected_column,
|
||||
std::string& row_result)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (selected_column.size() != column_.size())
|
||||
{
|
||||
error_ = "Error: number of selected columns larger than number of columns";
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (r >= grid_.row_count())
|
||||
{
|
||||
strtk::build_string s;
|
||||
s << "Error: row[" << r << "] out of bounds.";
|
||||
error_ = s.to_str();
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (row_.index() != r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
row_ = grid_.row(r);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool append_delimeter = false;
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::size_t c = 0; c < column_.size(); ++c)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (selected_column[c])
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (append_delimeter)
|
||||
row_result.append(output_delimiter_);
|
||||
else
|
||||
append_delimeter = true;
|
||||
|
||||
strtk::token_grid::range_t token = row_.token(c);
|
||||
row_result.append(token.first,token.second);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline std::string error()
|
||||
{
|
||||
return error_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
enum filter_result
|
||||
{
|
||||
e_error,
|
||||
e_match,
|
||||
e_mismatch
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
inline filter_result operator[](const std::size_t& r)
|
||||
{
|
||||
row_ = grid_.row(r);
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::size_t c = 0; c < column_.size(); ++c)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (!column_[c].process)
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
else if (!row_.parse_with_index(c,column_[c].value))
|
||||
{
|
||||
strtk::build_string s;
|
||||
s << "Error: Failed to process element at row/col["<< r << "," << c << "] value:" << row_.get<std::string>(c);
|
||||
error_ = s.to_str();
|
||||
|
||||
return e_error;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return (1.0 == expression_.value()) ? e_match : e_mismatch;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const strtk::token_grid& grid() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return grid_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
inline bool process_column_header()
|
||||
{
|
||||
static const std::string string_id ("_s");
|
||||
static const std::string number_id ("_n");
|
||||
|
||||
expression_.get_symbol_table().clear();
|
||||
column_.clear();
|
||||
column_.resize(grid_.row(0).size());
|
||||
|
||||
strtk::token_grid::row_type row = grid_.row(0);
|
||||
std::string col_name = "";
|
||||
std::string col_suffix = "";
|
||||
|
||||
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < row.size(); ++i)
|
||||
{
|
||||
column_properties& column = column_[i];
|
||||
|
||||
column.process = false;
|
||||
|
||||
col_name = row.get<std::string>(i);
|
||||
col_suffix = (col_name.size() >= 2) ? strtk::text::remaining_string(col_name.size() - 2,col_name) : "";
|
||||
col_name = col_name.substr(0,col_name.size() - 2);
|
||||
|
||||
if (symbol_table_.symbol_exists(col_name))
|
||||
{
|
||||
error_ = "Error: Redefinition of column " + col_name;
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (strtk::iends_with("_s",col_suffix))
|
||||
{
|
||||
column.type = dsv_filter::column_properties::e_string;
|
||||
column.name = col_name;
|
||||
column.value = strtk::util::value(column.value_s);
|
||||
column.process = true;
|
||||
|
||||
symbol_table_.add_stringvar(col_name,column.value_s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (strtk::iends_with("_n",col_suffix))
|
||||
{
|
||||
column.type = dsv_filter::column_properties::e_number;
|
||||
column.name = col_name;
|
||||
column.process = true;
|
||||
column.value = strtk::util::value(column.value_n);
|
||||
|
||||
symbol_table_.add_variable(col_name,column.value_n);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::string file_name_;
|
||||
std::string input_delimiter_;
|
||||
std::string output_delimiter_;
|
||||
std::string error_;
|
||||
std::vector<column_properties> column_;
|
||||
strtk::token_grid grid_;
|
||||
exprtk::symbol_table<double> symbol_table_;
|
||||
exprtk::parser<double> parser_;
|
||||
exprtk::expression<double> expression_;
|
||||
strtk::token_grid::row_type row_;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef dsv_filter_use_mmap
|
||||
boost::iostreams::mapped_file_source input_source;
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
44311
dep/partow/include/exprtk.hpp
Normal file
24518
dep/partow/include/strtk.hpp
Normal file
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Citing
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Geophysics paper
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
To cite *Tesseroids* in publications, please use our paper published in
|
||||
*Geophysics*:
|
||||
|
||||
Uieda, L., V. Barbosa, and C. Braitenberg (2016), Tesseroids:
|
||||
Forward-modeling gravitational fields in spherical coordinates, GEOPHYSICS,
|
||||
F41-F48,
|
||||
doi:`10.1190/geo2015-0204.1 <http://dx.doi.org/10.1190/geo2015-0204.1>`__.
|
||||
|
||||
You can download a copy of the `paper PDF
|
||||
<http://www.leouieda.com/papers/paper-tesseroids-2016.html>`__ and see all
|
||||
source code used in the paper at
|
||||
`the Github repository <https://github.com/pinga-lab/paper-tesseroids>`__.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that **citing the paper is prefered** over citing the previous
|
||||
conference proceedings.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're a BibTeX user::
|
||||
|
||||
@article{uieda2016,
|
||||
title = {Tesseroids: {{Forward}}-modeling gravitational fields in spherical coordinates},
|
||||
author = {Uieda, L. and Barbosa, V. and Braitenberg, C.},
|
||||
issn = {0016-8033},
|
||||
doi = {10.1190/geo2015-0204.1},
|
||||
url = {http://library.seg.org/doi/abs/10.1190/geo2015-0204.1},
|
||||
journal = {GEOPHYSICS},
|
||||
month = jul,
|
||||
year = {2016},
|
||||
pages = {F41--F48},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Source code
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
|
||||
You can refer to individual versions of Tesseroids through their DOIs.
|
||||
However, please **also cite the Geophysics paper**.
|
||||
|
||||
For example. if you want to mention that you used the 1.1.1 version,
|
||||
you can go to :ref:`the Releases page <releases>` of the documentation
|
||||
and get the DOI link for that version.
|
||||
This link will not be broken, even if I move the site somewhere else.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also cite the specific version instead of just providing the link.
|
||||
If you click of the DOI link for 1.1.1, the Zenodo page will
|
||||
recommend that you cite it as:
|
||||
|
||||
Uieda, Leonardo. (2015). Tesseroids v1.1.1: Forward modeling of
|
||||
gravitational fields in spherical coordinates. Zenodo. 10.5281/zenodo.15800
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Conference proceeding
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
The previous way citation for Tesseroids was a conference proceeding from the
|
||||
2011 GOCE User Workshop:
|
||||
|
||||
Uieda, L., E. P. Bomfim, C. Braitenberg, and E. Molina (2011),
|
||||
Optimal forward calculation method of the Marussi tensor
|
||||
due to a geologic structure at GOCE height,
|
||||
Proceedings of the 4th International GOCE User Workshop.
|
||||
|
||||
Download a `PDF version of the proceedings
|
||||
<http://www.leouieda.com/pdf/goce-2011.pdf>`__.
|
||||
You can also see the poster and source code at
|
||||
the `Github repository <https://github.com/leouieda/goce2011>`__.
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.15.2)
|
||||
# 设置项目名称与语言
|
||||
project(LibTess VERSION 1.6 LANGUAGES C)
|
||||
# 添加配置配件编写的函数
|
||||
include(CMakePackageConfigHelpers)
|
||||
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Windows")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX D:/Library)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
message(STATUS "Platform: " ${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Install prefix: " ${CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX})
|
||||
message(STATUS "Build type: " ${CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE})
|
||||
|
||||
# 添加库源文件地址
|
||||
add_subdirectory(lib)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(toolkits)
|
||||
add_subdirectory(test)
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2012-2017, Leonardo Uieda
|
||||
All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification,
|
||||
are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
||||
|
||||
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
||||
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
|
||||
this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
|
||||
and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
|
||||
* Neither the name of Leonardo Uieda nor the names of any contributors
|
||||
may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
|
||||
without specific prior written permission.
|
||||
|
||||
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND
|
||||
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
|
||||
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
|
||||
DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR
|
||||
ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
|
||||
(INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
|
||||
LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON
|
||||
ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
|
||||
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
|
||||
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
||||
@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
||||
@PACKAGE_INIT@
|
||||
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_VERSION "@PROJECT_VERSION@")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INSTALL_PREFIX "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INC_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_INCULDE_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/include")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIB_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/lib")
|
||||
set_and_check(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIBRARY_DIR "${PACKAGE_PREFIX_DIR}/lib")
|
||||
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIB tess)
|
||||
set(@PROJECT_NAME@_LIBRARY tess)
|
||||
|
||||
# include target information
|
||||
include("${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/@PROJECT_NAME@Targets.cmake")
|
||||
|
||||
check_required_components(@PROJECT_NAME@)
|
||||
@ -1,210 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 
|
||||
|
||||
[Documentation](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com) |
|
||||
[Download](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/releases)
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/releases)
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/leouieda/tesseroids)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/blob/master/LICENSE.txt)
|
||||
[](http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.582366)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Forward modeling of gravitational fields in spherical coordinates.*
|
||||
|
||||
Developed by [Leonardo Uieda](http://www.leouieda.com)
|
||||
in cooperation with [Carla Braitenberg](http://lithoflex.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
## About
|
||||
|
||||
*Tesseroids* is a collection of **command-line tools**
|
||||
for modeling the gravitational potential, acceleration, and
|
||||
gradient (Marussi) tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
The mass models can be made of right rectangular prisms or tesseroids
|
||||
(spherical prisms).
|
||||
Computation for rectangular prisms can be made in Cartesian or spherical
|
||||
(geocentric) coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
[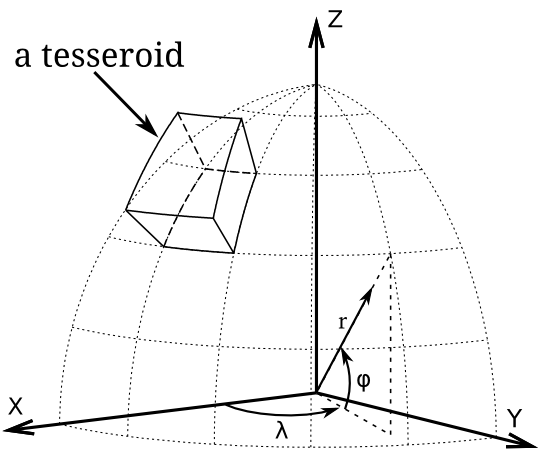](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com/en/latest/theory.html#what-is-a-tesseroid-anyway)
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
*Tesseroids* is [free software](http://www.fsf.org/about/what-is-free-software)
|
||||
made available under the terms of the
|
||||
BSD 3-clause license.
|
||||
See [LICENSE.txt](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/blob/master/LICENSE.txt).
|
||||
|
||||
## Citing
|
||||
|
||||
*Tesseroids* is research software made by scientists.
|
||||
If you use it in your research,
|
||||
please **cite** our *Geophysics* paper in your publications:
|
||||
|
||||
> Uieda, L., V. Barbosa, and C. Braitenberg (2016), Tesseroids: Forward-modeling gravitational fields in spherical coordinates, GEOPHYSICS, F41-F48, doi:[10.1190/geo2015-0204.1](http://dx.doi.org/10.1190/geo2015-0204.1).
|
||||
|
||||
You can download a copy of the paper PDF at
|
||||
[leouieda.com/papers/paper-tesseroids-2016.html](http://www.leouieda.com/papers/paper-tesseroids-2016.html)
|
||||
and see all source code used in the paper at the Github repository
|
||||
[pinga-lab/paper-tesseroids](https://github.com/pinga-lab/paper-tesseroids).
|
||||
|
||||
See [CITATION.txt](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/blob/master/CITATION.txt)
|
||||
or the [Citing](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com/en/latest/citation.html)
|
||||
page of the documentation for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installing
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to install is to download the latest compiled binary
|
||||
distribution from:
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/releases/latest
|
||||
|
||||
We offer binaries for Windows (32 and 64 bit)
|
||||
and GNU/Linux (32 and 64 bit).
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded, simply unpack the archive in the desired directory.
|
||||
The executables will be in the `bin` folder.
|
||||
For easier access to the programs, consider
|
||||
[adding the bin folder to your PATH environment
|
||||
variable](http://www.computerhope.com/issues/ch000549.htm).
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the examples in the
|
||||
[Cookbook](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com/en/latest/cookbook.html).
|
||||
They contain scripts that run *Tesseroids* and some Python code to plot the
|
||||
results.
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation contains sections on
|
||||
[the theory and equations](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com/en/latest/theory.html)
|
||||
and [usage instructions](http://tesseroids.leouieda.com/en/latest/usage.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, all programs accept the `-h` flag to print the instructions for using
|
||||
that particular program. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tessgrd -h
|
||||
Usage: tessgrd [PARAMS] [OPTIONS]
|
||||
|
||||
Make a regular grid of points.
|
||||
|
||||
All units either SI or degrees!
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
Printed to standard output (stdout) in the format:
|
||||
lon1 lat1 height
|
||||
lon2 lat1 height
|
||||
... ... ...
|
||||
lonNLON lat1 height
|
||||
lon1 lat2 height
|
||||
... ... ...
|
||||
... ... ...
|
||||
lonNLON latNLAT height
|
||||
|
||||
* Comments about the provenance of the data are inserted into
|
||||
the top of the output
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
-r W/E/S/N: Bounding region of the grid.
|
||||
-b NLON/NLAT: Number of grid points in the
|
||||
longitudinal and latitudinal directions.
|
||||
-z HEIGHT: Height of the grid with respect to the
|
||||
mean Earth radius.
|
||||
-h Print instructions.
|
||||
--version Print version and license information.
|
||||
|
||||
Options:
|
||||
-v Enable verbose printing to stderr.
|
||||
-lFILENAME Print log messages to file FILENAME.
|
||||
|
||||
Part of the Tesseroids package.
|
||||
Project site: <http://fatiando.org/software/tesseroids>
|
||||
Report bugs at: <http://code.google.com/p/tesseroids/issues/list>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting help
|
||||
|
||||
Write an e-mail to [Leonardo Uieda](http://www.leouieda.com/),
|
||||
or [tweet](https://twitter.com/leouieda),
|
||||
or [Google Hangout](https://plus.google.com/+LeonardoUieda).
|
||||
**Even better**, submit a bug report/feature request/question to the
|
||||
[Github issue tracker](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
## Compiling from source
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to build *Tesseroids* from source, you'll need:
|
||||
|
||||
* A C compiler (preferably [GCC](http://gcc.gnu.org))
|
||||
* The build tool [SCons](http://www.scons.org/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting up SCons
|
||||
|
||||
Tesseroids uses the build tool SCons.
|
||||
A `SConstruct` file (`Makefile` equivalent)
|
||||
is used to define the compilation rules.
|
||||
The advantage of SCons over Make is that it automatically detects your system
|
||||
settings.
|
||||
You will have to download and install SCons
|
||||
in order to easily compile Tesseroids.
|
||||
SCons is available for both GNU/Linux and Windows
|
||||
so compiling should work the same on both platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
SCons requires that you have [Python](http://www.python.org) installed.
|
||||
Follow the instructions in the [SCons website](http://www.scons.org/)
|
||||
to install it.
|
||||
Python is usually installed by default on most GNU/Linux systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Under Windows you will have to put SCons on
|
||||
your `PATH` environment variable
|
||||
in order to use it from the command line.
|
||||
It is usually located in the `Scripts` directory of your Python installation.
|
||||
|
||||
On GNU/Linux, SCons will generally use
|
||||
the GCC compiler to compile sources.
|
||||
On Windows it will search for an existing compiler.
|
||||
We recommend that you install GCC on Windows using
|
||||
[MinGW](http://mingw.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Compiling
|
||||
|
||||
Download a source distribution and
|
||||
unpack the archive anywhere you want
|
||||
(e.g., `~/tesseroids` or `C:\tesseroids` or whatever).
|
||||
To compile,
|
||||
open a terminal (or `cmd.exe` on Windows)
|
||||
and go to the directory where you unpacked (use the `cd` command).
|
||||
Then, type the following and hit `Enter`:
|
||||
|
||||
scons
|
||||
|
||||
If everything goes well, the compiled executables will be placed on a `bin`
|
||||
folder.
|
||||
|
||||
To clean up the build (delete all generated files), run:
|
||||
|
||||
scons -c
|
||||
|
||||
If you get any strange errors or the code doesn't compile for some reason,
|
||||
please [submit a bug report](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/issues).
|
||||
Don't forget to copy the output of running `scons`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing the build
|
||||
|
||||
After the compilation,
|
||||
a program called `tesstest`
|
||||
will be placed in the directory where you unpacked the source.
|
||||
This program runs the [unit tests](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unit_testing)
|
||||
for *Tesseroids* (sources in the `test` directory).
|
||||
|
||||
To run the test suite, simply execute `tesstest` with no arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
tesstest
|
||||
|
||||
or on GNU/Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
./tesstest
|
||||
|
||||
A summary of all tests (pass or fail) will be printed on the screen.
|
||||
If all tests pass,
|
||||
the compilation probably went well.
|
||||
If any test fail,
|
||||
please [submit a bug report](https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/issues)
|
||||
with the output of running `tesstest`.
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
:: Calculate effect of the model at a low height using difference distance-size
|
||||
:: ratios for the recursive division of tesseroids.
|
||||
:: WARNING: This is only an example. You should not use the -t option in
|
||||
:: practice
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-3/3/-3/3 -b50/50 -z4e03 | ^
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t0.0001 -lratio1.log | ^
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t0.5 -lratio2.log | ^
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t1 -lratio3.log | ^
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -v -lratio-default.log > output.txt
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate effect of the model at a low height using difference distance-size
|
||||
# ratios for the recursive division of tesseroids.
|
||||
# WARNING: This is only an example. You should not use the -t option in practice
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-3/3/-3/3 -b50/50 -z4e03 | \
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t0.0001 -lratio1.log | \
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t0.5 -lratio2.log | \
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -t1 -lratio3.log | \
|
||||
tessgzz model.txt -v -lratio-default.log > output.txt
|
||||
@ -1,2 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
-1.5 1.5 -1.5 1.5 0 -5000 200
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
data = np.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = np.reshape(data[0], shape)
|
||||
lat = np.reshape(data[1], shape)
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
value = np.reshape(value, shape)
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
plt.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
plt.contourf(lon, lat, value, 50)
|
||||
plt.colorbar()
|
||||
plt.savefig('column%d.png' % (i + 4))
|
||||
@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:: First, insert the density information into
|
||||
:: the DEM file using the Python script.
|
||||
python dem_density.py dem.xyz > dem-dens.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Next, use the modified DEM with tessmodgen
|
||||
:: to create a tesseroid model
|
||||
tessmodgen -s0.166667/0.166667 -z0 -v < dem-dens.txt ^
|
||||
> dem-tess.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Calculate the GGT on a regular grid at 250km
|
||||
:: use the -l option to log the processes to files
|
||||
:: (usefull to diagnose when things go wrong)
|
||||
:: The output is dumped to dem-ggt.txt
|
||||
tessgrd -r-60/-45/-30/-15 -b50/50 -z250e03 | ^
|
||||
tessgxx dem-tess.txt -lgxx.log | ^
|
||||
tessgxy dem-tess.txt -lgxy.log | ^
|
||||
tessgxz dem-tess.txt -lgxz.log | ^
|
||||
tessgyy dem-tess.txt -lgyy.log | ^
|
||||
tessgyz dem-tess.txt -lgyz.log | ^
|
||||
tessgzz dem-tess.txt -lgzz.log -v > dem-ggt.txt
|
||||
@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# First, insert the density information into
|
||||
# the DEM file using the Python script.
|
||||
python dem_density.py dem.xyz > dem-dens.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Next, use the modified DEM with tessmodgen
|
||||
# to create a tesseroid model
|
||||
tessmodgen -s0.166667/0.166667 -z0 -v < dem-dens.txt \
|
||||
> dem-tess.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Calculate the GGT on a regular grid at 250km
|
||||
# use the -l option to log the processes to files
|
||||
# (usefull to diagnose when things go wrong)
|
||||
# The output is dumped to dem-ggt.txt
|
||||
tessgrd -r-60/-45/-30/-15 -b50/50 -z250e03 | \
|
||||
tessgxx dem-tess.txt -lgxx.log | \
|
||||
tessgxy dem-tess.txt -lgxy.log | \
|
||||
tessgxz dem-tess.txt -lgxz.log | \
|
||||
tessgyy dem-tess.txt -lgyy.log | \
|
||||
tessgyz dem-tess.txt -lgyz.log | \
|
||||
tessgzz dem-tess.txt -lgzz.log -v > dem-ggt.txt
|
||||
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Assign density values for the DEM points.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import numpy
|
||||
|
||||
lons, lats, heights = numpy.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in xrange(len(heights)):
|
||||
if heights[i] >=0:
|
||||
print "%lf %lf %lf %lf" % (lons[i], lats[i], heights[i], 2670.0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print "%lf %lf %lf %lf" % (lons[i], lats[i], heights[i], 1670.0)
|
||||
@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Make some nice plots of the DEM, the densities used and the calculated GGT
|
||||
import numpy
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
|
||||
|
||||
# Plot the DEM and density maps
|
||||
################################################################################
|
||||
lons, lats, heights, dens = numpy.loadtxt('dem-dens.txt', unpack=True)
|
||||
nlons = 151 # Number of points in the longitude direction
|
||||
nlats = len(lats)/nlons
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert the lists to 2D grids
|
||||
glons = numpy.reshape(lons, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
glats = numpy.reshape(lats, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
gheights = numpy.reshape(heights, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
gdens = numpy.reshape(dens, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up a Mercator projection
|
||||
bm = Basemap(projection='merc',
|
||||
llcrnrlon=lons[0], llcrnrlat=lats[-1],
|
||||
urcrnrlon=lons[-1], urcrnrlat=lats[0],
|
||||
lon_0=lons[nlons//2], lat_0=lats[len(lats)//2],
|
||||
resolution='l',
|
||||
area_thresh=10000)
|
||||
glons, glats = bm(glons, glats)
|
||||
|
||||
# Plot the DEM first
|
||||
print "Plotting DEM"
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
bm.drawmeridians(numpy.arange(lons[0]+5., lons[-1], 5.),
|
||||
labels=[0,0,0,1], fontsize=12, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawparallels(numpy.arange(lats[-1]+5., lats[0], 5.),
|
||||
labels=[1,0,0,0], fontsize=12, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawcoastlines(linewidth=1)
|
||||
bm.drawmapboundary()
|
||||
bm.drawcountries(linewidth=0.8)
|
||||
# Do the pseudocolor plot
|
||||
cf = bm.pcolor(glons, glats, gheights, cmap=plt.cm.gist_earth, \
|
||||
vmin=-1000, vmax=1000)
|
||||
cb = plt.colorbar()
|
||||
cb.set_label("Height [m]")
|
||||
# Plot the calculation area used later
|
||||
w = -60
|
||||
e = -45
|
||||
s = -30
|
||||
n = -15
|
||||
areax, areay = bm([w, w, e, e, w], \
|
||||
[n, s, s, n, n])
|
||||
bm.plot(areax, areay, '-r', label="Computation grid", linewidth=1.8)
|
||||
plt.legend(shadow=True, loc='lower right', prop={'size':10})
|
||||
# Save a png figure
|
||||
plt.savefig('dem.png')
|
||||
|
||||
# Now plot the densities
|
||||
print "Plotting density model"
|
||||
plt.figure()
|
||||
bm.drawmeridians(numpy.arange(lons[0]+5., lons[-1], 5.),
|
||||
labels=[0,0,0,1], fontsize=12, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawparallels(numpy.arange(lats[-1]+5., lats[0], 5.),
|
||||
labels=[1,0,0,0], fontsize=12, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawcoastlines(linewidth=1)
|
||||
bm.drawmapboundary()
|
||||
bm.drawcountries(linewidth=0.8)
|
||||
# Do the pseudocolor plot
|
||||
cf = bm.pcolor(glons, glats, gdens, cmap=plt.cm.jet)
|
||||
cb = plt.colorbar()
|
||||
cb.set_label(r"Density [$g.cm^{-3}$]")
|
||||
# Save a png figure
|
||||
plt.savefig('dem-dens.png')
|
||||
|
||||
# Plot the GGT
|
||||
################################################################################
|
||||
print "Plotting GGT"
|
||||
data = numpy.loadtxt('dem-ggt.txt')
|
||||
lons, lats, heights, gxx, gxy, gxz, gyy, gyz, gzz = data.T
|
||||
nlons = 50 # Number of points in the longitude direction
|
||||
nlats = len(lats)/nlons
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert the lists to 2D grids
|
||||
glons = numpy.reshape(lons, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
glats = numpy.reshape(lats, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up a Mercator projection
|
||||
bm = Basemap(projection='merc', \
|
||||
llcrnrlon=lons[0], llcrnrlat=lats[0], \
|
||||
urcrnrlon=lons[-1], urcrnrlat=lats[-1], \
|
||||
lon_0=lons[nlons//2], lat_0=lats[len(lats)//2],
|
||||
resolution='l', area_thresh=10000)
|
||||
glons, glats = bm(glons, glats)
|
||||
|
||||
# Plot each component
|
||||
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(14,9))
|
||||
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.35)
|
||||
titles = [r"$g_{xx}$", r"$g_{xy}$", r"$g_{xz}$", r"$g_{yy}$", r"$g_{yz}$",
|
||||
r"$g_{zz}$"]
|
||||
fields = [gxx, gxy, gxz, gyy, gyz, gzz]
|
||||
for i, args in enumerate(zip(fields, titles)):
|
||||
field, title = args
|
||||
ax = plt.subplot(2, 3, i + 1, aspect='equal')
|
||||
plt.title(title, fontsize=18)
|
||||
# Make it a 2D grid
|
||||
gfield = numpy.reshape(field, (nlats, nlons))
|
||||
# Plot the coastlines and etc
|
||||
mer = bm.drawmeridians(numpy.arange(lons[0]+3, lons[-1]-3, 3),
|
||||
labels=[0,0,0,1], fontsize=9, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawparallels(numpy.arange(lats[0]+3, lats[-1]-3, 3),
|
||||
labels=[1,0,0,0], fontsize=9, linewidth=0.5)
|
||||
bm.drawcoastlines(linewidth=1)
|
||||
bm.drawmapboundary()
|
||||
bm.drawcountries(linewidth=1)
|
||||
bm.drawstates(linewidth=0.2)
|
||||
# Make a pseudocolor plot
|
||||
cf = bm.pcolor(glons, glats, gfield, cmap=plt.cm.jet)
|
||||
cb = plt.colorbar(orientation='vertical', format='%.2f', shrink=0.8)
|
||||
cb.set_label(r"$E\"otv\"os$")
|
||||
# Save a png figure
|
||||
plt.savefig('dem-ggt.png')
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 150 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 372 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 260 KiB |
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Test prism model file
|
||||
2000 5000 2000 15000 0 5000 1000
|
||||
10000 18000 10000 18000 0 5000 -1000
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import pylab
|
||||
|
||||
data = pylab.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = pylab.reshape(data[0], shape)
|
||||
lat = pylab.reshape(data[1], shape)
|
||||
xmin, xmax = lon.min(), lon.max()
|
||||
ymin, ymax = lat.min(), lat.max()
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
value = pylab.reshape(value, shape)
|
||||
pylab.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
pylab.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
pylab.axis('scaled')
|
||||
pylab.pcolor(lon, lat, value)
|
||||
pylab.colorbar()
|
||||
pylab.contour(lon, lat, value, 12, color='k')
|
||||
#pylab.xlabel("Longitude")
|
||||
#pylab.ylabel("Latitude")
|
||||
pylab.xlim(xmin, xmax)
|
||||
pylab.ylim(ymin, ymax)
|
||||
pylab.savefig('column%d.png' % (i + 4))
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:: Generate a regular grid, pipe it to all the computation programs,
|
||||
:: and write the result to output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r0/20000/0/20000 -b50/50 -z1000 | ^
|
||||
prismpot model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgx model.txt | prismgy model.txt | prismgz model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgxx model.txt | prismgxy model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgxz model.txt | prismgyy model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgyz model.txt | prismgzz model.txt > output.txt
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 585 KiB |
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a regular grid, pipe it to all the computation programs,
|
||||
# and write the result to output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r0/20000/0/20000 -b50/50 -z1000 | \
|
||||
prismpot model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgx model.txt | prismgy model.txt | prismgz model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgxx model.txt | prismgxy model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgxz model.txt | prismgyy model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgyz model.txt | prismgzz model.txt > output.txt
|
||||
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
10 20 10 20 0 -50000 200
|
||||
-20 -10 -20 -10 0 -30000 -500
|
||||
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
|
||||
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up a projection
|
||||
bm = Basemap(projection='ortho', lon_0=0, lat_0=0,
|
||||
resolution='l', area_thresh=10000)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the data and make them into matrices
|
||||
data = np.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = data[0].reshape(shape)
|
||||
lat = data[1].reshape(shape)
|
||||
glon, glat = bm(lon, lat)
|
||||
|
||||
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 12))
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
plt.subplot(3, 4, i + 1)
|
||||
plt.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
bm.drawcoastlines()
|
||||
bm.drawmapboundary()
|
||||
bm.contourf(glon, glat, value.reshape(shape), 15, cmap=plt.cm.RdBu_r)
|
||||
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal", pad=0, aspect=30)
|
||||
plt.tight_layout()
|
||||
plt.savefig('output.png')
|
||||
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
:: Generate a regular grid, pipe it to all the computation programs,
|
||||
:: and write the result to output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-45/45/-45/45 -b101/101 -z260e03 | ^
|
||||
tesspot model.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgx model.txt | tessgy model.txt | tessgz model.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgxx model.txt | tessgxy model.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgxz model.txt | tessgyy model.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgyz model.txt | tessgzz model.txt -v -llog.txt > output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Make a plot with the columns of output.txt
|
||||
python plot.py output.txt 101 101
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 389 KiB |
@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a regular grid, pipe it to all the computation programs,
|
||||
# and write the result to output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-45/45/-45/45 -b101/101 -z260e03 | \
|
||||
tesspot model.txt | \
|
||||
tessgx model.txt | tessgy model.txt | tessgz model.txt | \
|
||||
tessgxx model.txt | tessgxy model.txt | \
|
||||
tessgxz model.txt | tessgyy model.txt | \
|
||||
tessgyz model.txt | tessgzz model.txt -v -llog.txt > output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Make a plot with the columns of output.txt
|
||||
python plot.py output.txt 101 101
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import pylab
|
||||
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up a projection
|
||||
bm = Basemap(projection='ortho', lon_0=-80, lat_0=-40,
|
||||
resolution='l', area_thresh=10000)
|
||||
|
||||
data = pylab.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = pylab.reshape(data[0], shape)
|
||||
lat = pylab.reshape(data[1], shape)
|
||||
glon, glat = bm(lon, lat)
|
||||
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
value = pylab.reshape(value, shape)
|
||||
pylab.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
pylab.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
bm.drawcoastlines()
|
||||
#bm.fillcontinents(color='coral',lake_color='aqua')
|
||||
#bm.drawmapboundary(fill_color='aqua')
|
||||
bm.drawmapboundary()
|
||||
bm.drawparallels(pylab.arange(-90.,120.,30.))
|
||||
bm.drawmeridians(pylab.arange(0.,420.,60.))
|
||||
#bm.bluemarble()
|
||||
bm.pcolor(glon, glat, value)
|
||||
pylab.colorbar()
|
||||
#bm.contour(glon, glat, value, 12, linewidth=3)
|
||||
pylab.savefig('column%d.png' % (i + 4))
|
||||
@ -1,134 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
|
||||
<!-- Created with Inkscape (http://www.inkscape.org/) -->
|
||||
|
||||
<svg
|
||||
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
|
||||
xmlns:cc="http://creativecommons.org/ns#"
|
||||
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
|
||||
xmlns:svg="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
|
||||
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
|
||||
xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink"
|
||||
xmlns:sodipodi="http://sodipodi.sourceforge.net/DTD/sodipodi-0.dtd"
|
||||
xmlns:inkscape="http://www.inkscape.org/namespaces/inkscape"
|
||||
width="1088.5714"
|
||||
height="1122.8572"
|
||||
id="svg2"
|
||||
version="1.1"
|
||||
inkscape:version="0.48.2 r9819"
|
||||
sodipodi:docname="result.svg"
|
||||
inkscape:export-filename="/home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/tess2prism.png"
|
||||
inkscape:export-xdpi="90"
|
||||
inkscape:export-ydpi="90">
|
||||
<defs
|
||||
id="defs4" />
|
||||
<sodipodi:namedview
|
||||
id="base"
|
||||
pagecolor="#ffffff"
|
||||
bordercolor="#666666"
|
||||
borderopacity="1.0"
|
||||
inkscape:pageopacity="1"
|
||||
inkscape:pageshadow="2"
|
||||
inkscape:zoom="0.35"
|
||||
inkscape:cx="182.14285"
|
||||
inkscape:cy="492.85716"
|
||||
inkscape:document-units="px"
|
||||
inkscape:current-layer="layer1"
|
||||
showgrid="false"
|
||||
inkscape:window-width="1680"
|
||||
inkscape:window-height="1003"
|
||||
inkscape:window-x="0"
|
||||
inkscape:window-y="25"
|
||||
inkscape:window-maximized="1"
|
||||
fit-margin-top="0"
|
||||
fit-margin-left="0"
|
||||
fit-margin-right="0"
|
||||
fit-margin-bottom="0" />
|
||||
<metadata
|
||||
id="metadata7">
|
||||
<rdf:RDF>
|
||||
<cc:Work
|
||||
rdf:about="">
|
||||
<dc:format>image/svg+xml</dc:format>
|
||||
<dc:type
|
||||
rdf:resource="http://purl.org/dc/dcmitype/StillImage" />
|
||||
<dc:title></dc:title>
|
||||
</cc:Work>
|
||||
</rdf:RDF>
|
||||
</metadata>
|
||||
<g
|
||||
inkscape:label="Layer 1"
|
||||
inkscape:groupmode="layer"
|
||||
id="layer1"
|
||||
transform="translate(165.71428,783.35211)">
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-509.06641"
|
||||
x="522.85712"
|
||||
id="image3026"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column7.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-234.78065"
|
||||
x="522.85712"
|
||||
id="image3059"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column10.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="39.505058"
|
||||
x="522.85712"
|
||||
id="image3092"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column13.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-783.35211"
|
||||
x="179.99997"
|
||||
id="image2993"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column4.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-509.06641"
|
||||
x="179.99997"
|
||||
id="image3015"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column6.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-234.78065"
|
||||
x="179.99997"
|
||||
id="image3048"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column9.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="39.505058"
|
||||
x="179.99997"
|
||||
id="image3081"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column12.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-509.06641"
|
||||
x="-165.71428"
|
||||
id="image3004"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column5.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="-234.78065"
|
||||
x="-165.71428"
|
||||
id="image3037"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column8.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
<image
|
||||
y="39.505058"
|
||||
x="-165.71428"
|
||||
id="image3070"
|
||||
xlink:href="file:///home/leo/src/tesseroids/dev/cookbook/tess2prism/column11.png"
|
||||
height="300"
|
||||
width="400" />
|
||||
</g>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 3.9 KiB |
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Prisms converted from tesseroid model with tess2prism 1.1dev
|
||||
# local time: Wed May 16 14:34:47 2012
|
||||
# tesseroids file: stdin
|
||||
# conversion type: equal mass|spherical coordinates
|
||||
# format: dx dy dz density lon lat r
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
221766.31696055 169882.854778591 50000 499.977196258595 -76 -40 6378137
|
||||
221766.31696055 169882.854778591 50000 499.977196258595 -78 -40 6378137
|
||||
221766.31696055 169882.854778591 50000 499.977196258595 -80 -40 6378137
|
||||
221766.31696055 169882.854778591 50000 499.977196258595 -82 -40 6378137
|
||||
221766.31696055 169882.854778591 50000 499.977196258595 -84 -40 6378137
|
||||
@ -1,6 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
-77 -75 -41 -39 0 -50000 500
|
||||
-79 -77 -41 -39 0 -50000 500
|
||||
-81 -79 -41 -39 0 -50000 500
|
||||
-83 -81 -41 -39 0 -50000 500
|
||||
-85 -83 -41 -39 0 -50000 500
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:: Generate a prism model from a tesseroid model.
|
||||
:: Prisms will have the same mass as the tesseroids and
|
||||
:: associated spherical coordinates of the center of
|
||||
:: the top of the tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
tess2prism.exe < tess-model.txt > prism-model.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Generate a regular grid in spherical coordinates,
|
||||
:: pipe the grid to the computation programs,
|
||||
:: and dump the result on output.txt
|
||||
:: prismpots calculates the potential in spherical
|
||||
:: coordinates, prismgs calculates the full
|
||||
:: gravity vector, and prismggts calculates the full
|
||||
:: gravity gradient tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-160/0/-80/0 -b100/100 -z250e03 | ^
|
||||
prismpots prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgs prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismggts prism-model.txt -v > output.txt
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 888 KiB |
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a prism model from a tesseroid model.
|
||||
# Prisms will have the same mass as the tesseroids and
|
||||
# associated spherical coordinates of the center of
|
||||
# the top of the tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
tess2prism < tess-model.txt > prism-model.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a regular grid in spherical coordinates,
|
||||
# pipe the grid to the computation programs,
|
||||
# and dump the result on output.txt
|
||||
# prismpots calculates the potential in spherical
|
||||
# coordinates, prismgs calculates the full
|
||||
# gravity vector, and prismggts calculates the full
|
||||
# gravity gradient tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-160/0/-80/0 -b100/100 -z250e03 | \
|
||||
prismpots prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgs prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismggts prism-model.txt -v > output.txt
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import pylab
|
||||
|
||||
data = pylab.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = pylab.reshape(data[0], shape)*0.001
|
||||
lat = pylab.reshape(data[1], shape)*0.001
|
||||
xmin, xmax = lon.min(), lon.max()
|
||||
ymin, ymax = lat.min(), lat.max()
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
value = pylab.reshape(value, shape)
|
||||
pylab.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
pylab.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
pylab.axis('scaled')
|
||||
pylab.pcolor(lon, lat, value)
|
||||
pylab.colorbar()
|
||||
pylab.contour(lon, lat, value, 12, color='k')
|
||||
#pylab.xlabel("Longitude")
|
||||
#pylab.ylabel("Latitude")
|
||||
pylab.xlim(xmin, xmax)
|
||||
pylab.ylim(ymin, ymax)
|
||||
pylab.savefig('column%d.png' % (i + 4))
|
||||
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Prisms converted from tesseroid model with tess2prism 1.1dev
|
||||
# local time: Tue May 8 14:55:02 2012
|
||||
# tesseroids file: stdin
|
||||
# conversion type: flatten
|
||||
# format: x1 x2 y1 y2 z1 z2 density
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
1111100 1666650 1111100 1666650 0 30000 487.534658568521
|
||||
-1111100 1111100 -1666650 -1111100 0 50000 198.175508383774
|
||||
-1777760 -1111100 -1666650 555550 0 30000 -291.9029748328
|
||||
@ -1,4 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Test tesseroid model file
|
||||
10 15 10 15 0 -30000 500
|
||||
-15 -10 -10 10 0 -50000 200
|
||||
-15 5 -16 -10 0 -30000 -300
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:: Generate a prism model from a tesseroid model by
|
||||
:: flattening the tesseroids (1 degree = 111.11 km).
|
||||
:: This way the converted prisms can be used
|
||||
:: with the prism* programs in Cartesian coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
tess2prism --flatten < tess-model.txt > prism-model.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Generate a regular grid in Cartesian coordinates,
|
||||
:: pipe the grid to the computation programs,
|
||||
:: and dump the result on output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-3e06/3e06/-3e06/3e06 -b50/50 -z250e03 | ^
|
||||
prismpot prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgx prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgy prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgz prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgxx prism-model.txt | prismgxy prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgxz prism-model.txt | prismgyy prism-model.txt | ^
|
||||
prismgyz prism-model.txt | prismgzz prism-model.txt > output.txt
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 575 KiB |
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a prism model from a tesseroid model by
|
||||
# flattening the tesseroids (1 degree = 111.11 km).
|
||||
# This way the converted prisms can be used
|
||||
# with the prism* programs in Cartesian coordinates.
|
||||
|
||||
tess2prism --flatten < tess-model.txt > prism-model.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate a regular grid in Cartesian coordinates,
|
||||
# pipe the grid to the computation programs,
|
||||
# and dump the result on output.txt
|
||||
|
||||
tessgrd -r-3e06/3e06/-3e06/3e06 -b50/50 -z250e03 | \
|
||||
prismpot prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgx prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgy prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgz prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgxx prism-model.txt | prismgxy prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgxz prism-model.txt | prismgyy prism-model.txt | \
|
||||
prismgyz prism-model.txt | prismgzz prism-model.txt > output.txt
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 45 KiB |
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import fatiando as ft
|
||||
|
||||
shape = (41, 41)
|
||||
x, y = ft.grd.regular((-10, 10, 30, 50), shape)
|
||||
height = 800 - 1000*ft.utils.gaussian2d(x, y, 3, 1, x0=0, y0=37)
|
||||
rel = -7000*ft.utils.gaussian2d(x, y, 3, 5, x0=0, y0=40)
|
||||
thick = height - rel
|
||||
dens = 1900*np.ones_like(thick)
|
||||
data = np.transpose([x, y, height, thick, dens])
|
||||
with open('layers.txt', 'w') as f:
|
||||
f.write("# Synthetic layer model of sediments and topography\n")
|
||||
f.write("# Columns are:\n")
|
||||
f.write("# lon lat height thickness density\n")
|
||||
np.savetxt(f, data, fmt='%g')
|
||||
ft.vis.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
ft.vis.title('Depth of sediments [m]')
|
||||
ft.vis.axis('scaled')
|
||||
ft.vis.pcolor(x, y, rel, shape)
|
||||
ft.vis.colorbar()
|
||||
ft.vis.savefig('depth.png')
|
||||
ft.vis.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
ft.vis.title('Topography [m]')
|
||||
ft.vis.axis('scaled')
|
||||
ft.vis.pcolor(x, y, height, shape)
|
||||
ft.vis.colorbar()
|
||||
ft.vis.savefig('topography.png')
|
||||
ft.vis.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
ft.vis.title('Thickness of sediment layer [m]')
|
||||
ft.vis.axis('scaled')
|
||||
ft.vis.pcolor(x, y, thick, shape)
|
||||
ft.vis.colorbar()
|
||||
ft.vis.savefig('thickness.png')
|
||||
ft.vis.show()
|
||||
@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Plot the columns of the output files
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import pylab
|
||||
|
||||
data = pylab.loadtxt(sys.argv[1], unpack=True)
|
||||
shape = (int(sys.argv[2]), int(sys.argv[3]))
|
||||
lon = pylab.reshape(data[0], shape)
|
||||
lat = pylab.reshape(data[1], shape)
|
||||
for i, value in enumerate(data[3:]):
|
||||
value = pylab.reshape(value, shape)
|
||||
pylab.figure(figsize=(4, 3))
|
||||
pylab.axis('scaled')
|
||||
pylab.title("Column %d" % (i + 4))
|
||||
pylab.pcolor(lon, lat, value)
|
||||
pylab.colorbar()
|
||||
pylab.xlim(lon.min(), lon.max())
|
||||
pylab.ylim(lat.min(), lat.max())
|
||||
pylab.savefig('column%d.png' % (i + 4))
|
||||
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:: Convert the layer grids in layers.txt to tesseroids.
|
||||
:: The grid spacing passed to -s is used as the size of the tesseroids,
|
||||
:: so be careful!
|
||||
tesslayers.exe -s0.5/0.5 -v < layers.txt > tessmodel.txt
|
||||
|
||||
:: Now calculate the gz and tensor effect of this model at 100km height
|
||||
tessgrd -r-8/8/32/48 -b50/50 -z100000 | ^
|
||||
tessgz tessmodel.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgxx tessmodel.txt | tessgxy tessmodel.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgxz tessmodel.txt | tessgyy tessmodel.txt | ^
|
||||
tessgyz tessmodel.txt | tessgzz tessmodel.txt -v > output.txt
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 154 KiB |
@ -1,13 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert the layer grids in layers.txt to tesseroids.
|
||||
# The grid spacing passed to -s is used as the size of the tesseroids,
|
||||
# so be careful!
|
||||
tesslayers -s0.5/0.5 -v < layers.txt > tessmodel.txt
|
||||
|
||||
# Now calculate the gz and tensor effect of this model at 100km height
|
||||
tessgrd -r-8/8/32/48 -b50/50 -z100000 | \
|
||||
tessgz tessmodel.txt | \
|
||||
tessgxx tessmodel.txt | tessgxy tessmodel.txt | \
|
||||
tessgxz tessmodel.txt | tessgyy tessmodel.txt | \
|
||||
tessgyz tessmodel.txt | tessgzz tessmodel.txt -v > output.txt
|
||||
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# 设置编译选项
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -O3")
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -lm")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# 设置库文件的输出地址
|
||||
set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
# 设定库源文件
|
||||
aux_source_directory(. LIBTESS_SRC)
|
||||
|
||||
# 以下部分为库的编译
|
||||
# 注意目标名必须唯一 所以不能直接生成相同名称的动态库与静态库
|
||||
# 注意此处不必为目标名称添加lib前缀和相应后缀,cmake会自行添加
|
||||
add_library(tess SHARED ${LIBTESS_SRC})
|
||||
# 首先添加静态库的生成命令
|
||||
add_library(tess_static STATIC ${LIBTESS_SRC})
|
||||
# 设置静态库的输出名称从而获得与动态库名称相同的静态库
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess_static PROPERTIES OUTPUT_NAME "tess")
|
||||
# 设置输出目标属性以同时输出动态库与静态库
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess_static PROPERTIES CLEAN_DIRECT_OUTPUT 1)
|
||||
# 设置动态库的版本号
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess PROPERTIES VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION} SOVERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION_MAJOR}.${PROJECT_VERSION_MINOR})
|
||||
# 设置动态库的运行搜索地址
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
set_target_properties(tess_static PROPERTIES INSTALL_RPATH /usr/local/lib)
|
||||
|
||||
# 链接动态库
|
||||
if(${CMAKE_HOST_SYSTEM_NAME} STREQUAL "Linux")
|
||||
target_link_libraries(tess PUBLIC m)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(tess_static m.a)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
set(CONFIG_FILE_PATH lib/cmake/${PROJECT_NAME})
|
||||
|
||||
configure_package_config_file(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake.in
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake
|
||||
INSTALL_DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH})
|
||||
|
||||
write_basic_package_version_file(${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}ConfigVersion.cmake
|
||||
VERSION ${PROJECT_VERSION}
|
||||
COMPATIBILITY SameMajorVersion)
|
||||
|
||||
# 库的安装命令 安装到/opt/lib
|
||||
if(WIN32)
|
||||
install(TARGETS tess DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
install(TARGETS tess_static DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
install(TARGETS tess tess_static
|
||||
EXPORT ${PROJECT_NAME}Targets
|
||||
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
|
||||
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib)
|
||||
install(EXPORT ${PROJECT_NAME}Targets
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH})
|
||||
install(FILES
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}Config.cmake
|
||||
${CMAKE_BINARY_DIR}/${PROJECT_NAME}ConfigVersion.cmake
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CONFIG_FILE_PATH})
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
# 头文件安装命令
|
||||
file(GLOB LIBTESS_HEAD *.h)
|
||||
# 安装到include/tess
|
||||
install(FILES ${LIBTESS_HEAD} DESTINATION include/tess)
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Define constants used, like the gravitational constant and unit conversions.
|
||||
|
||||
All values are in SI units!
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
|
||||
/* Mean Earth radius [\f$ m \f$] */
|
||||
const double MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS = 6378137.0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* The gravitational constant [\f$ m^3*kg^{-1}*s^{-1} \f$] */
|
||||
const double G = 0.00000000006673;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to Eotvos
|
||||
[\f$ \frac{1}{s^2} = 10^9\ Eotvos \f$] */
|
||||
const double SI2EOTVOS = 1000000000.0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to mGal
|
||||
[\f$ 1 \frac{m}{s^2} = 10^5\ mGal \f$] */
|
||||
const double SI2MGAL = 100000.0;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Pi */
|
||||
const double PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
|
||||
|
||||
/* minimum distance-to-size ratio for potential computations to be accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_POT_SIZE_RATIO = 1;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity computations to be accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GX_SIZE_RATIO = 1.5;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GY_SIZE_RATIO = 1.5;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GZ_SIZE_RATIO = 1.5;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity gradient computations to be
|
||||
accurate */
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GYY_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GYZ_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
const double TESSEROID_GZZ_SIZE_RATIO = 8;
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Define constants used, like the gravitational constant and unit conversions.
|
||||
|
||||
Values are assigned in file constants.c
|
||||
|
||||
All values are in SI units!
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_CONSTANTS_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_CONSTANTS_H_
|
||||
|
||||
/* Mean Earth radius [\f$ m \f$] */
|
||||
extern const double MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS;
|
||||
|
||||
/* The gravitational constant [\f$ m^3*kg^{-1}*s^{-1} \f$] */
|
||||
extern const double G;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to Eotvos
|
||||
[\f$ \frac{1}{s^2} = 10^9\ Eotvos \f$] */
|
||||
extern const double SI2EOTVOS;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Conversion factor from SI units to mGal
|
||||
[\f$ 1 \frac{m}{s^2} = 10^5\ mGal \f$] */
|
||||
extern const double SI2MGAL;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Pi */
|
||||
extern const double PI;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for potential computations to be accurate */
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_POT_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity computations to be accurate */
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GX_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GY_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GZ_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
/* Minimum distance-to-size ratio for gravity gradient computations to be
|
||||
accurate */
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GXX_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GXY_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GXZ_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GYY_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GYZ_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
extern const double TESSEROID_GZZ_SIZE_RATIO;
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
@ -1,175 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Data structures for geometric elements and functions that operate on them.
|
||||
Defines the TESSEROID, SPHERE, and PRISM structures.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
#include "constants.h"
|
||||
#include "logger.h"
|
||||
#include "geometry.h"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Split a tesseroid. */
|
||||
int split_tess(TESSEROID tess, int nlon, int nlat, int nr, TESSEROID *split)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double dlon, dlat, dr, w, s, r1;
|
||||
int i, j, k, t = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
dlon = (double)(tess.e - tess.w)/nlon;
|
||||
dlat = (double)(tess.n - tess.s)/nlat;
|
||||
dr = (double)(tess.r2 - tess.r1)/nr;
|
||||
for(r1=tess.r1, k=0; r1 + dr <= tess.r2 || k < nr; r1 += dr, k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(s=tess.s, j=0; s + dlat <= tess.n || j < nlat; s += dlat, j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(w=tess.w, i=0; w + dlon <= tess.e || i < nlon; w += dlon, i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
split[t].w = w;
|
||||
split[t].e = w + dlon;
|
||||
split[t].s = s;
|
||||
split[t].n = s + dlat;
|
||||
split[t].r1 = r1;
|
||||
split[t].r2 = r1 + dr;
|
||||
split[t].density = tess.density;
|
||||
t++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return t;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the total mass of a tesseroid model. */
|
||||
double tess_total_mass(TESSEROID *model, int size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double mass;
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
for(mass = 0, i = 0; i < size; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
mass += model[i].density*tess_volume(model[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return mass;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the mass of a tesseroid model within a density range. */
|
||||
double tess_range_mass(TESSEROID *model, int size, double low_dens,
|
||||
double high_dens)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double mass;
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
for(mass = 0, i = 0; i < size; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(model[i].density >= low_dens && model[i].density <= high_dens)
|
||||
{
|
||||
mass += model[i].density*tess_volume(model[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return mass;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid to a rectangular prism of equal volume and append
|
||||
* the spherical coordinates of the center top surface (needed to calculate
|
||||
* the effect in spherical coordinates). */
|
||||
void tess2prism(TESSEROID tess, PRISM *prism)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double deg2rad = PI/180., r0, dx, dy;
|
||||
|
||||
r0 = 0.5*(tess.r1 + tess.r2);
|
||||
dx = r0*deg2rad*(tess.n - tess.s);
|
||||
dy = r0*cos(deg2rad*0.5*(tess.n + tess.s))*deg2rad*(tess.e - tess.w);
|
||||
prism->x1 = -0.5*dx;
|
||||
prism->x2 = 0.5*dx;
|
||||
prism->y1 = -0.5*dy;
|
||||
prism->y2 = 0.5*dy;
|
||||
/* z1 = 0 because the center of the top face of the prism is the origin of
|
||||
the coordiante system */
|
||||
prism->z1 = 0.;
|
||||
prism->z2 = tess.r2 - tess.r1;
|
||||
/* Calculate the density of the prism so that they will have exactly
|
||||
the same mass */
|
||||
prism->density = (double)tess.density*
|
||||
tess_volume(tess)/prism_volume(*prism);
|
||||
/* Set the coordinates of the center of the prisms top face */
|
||||
prism->lon = 0.5*(tess.e + tess.w);
|
||||
prism->lat = 0.5*(tess.n + tess.s);
|
||||
prism->r = tess.r2; /* The top face */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid to a rectangular prism of equal volume by approximating
|
||||
* 1 degree by 111.11 km. */
|
||||
void tess2prism_flatten(TESSEROID tess, PRISM *prism)
|
||||
{
|
||||
prism->x1 = tess.s*111110.;
|
||||
prism->x2 = tess.n*111110.;
|
||||
prism->y1 = tess.w*111110.;
|
||||
prism->y2 = tess.e*111110.;
|
||||
/* r1 is not z1 because r1 is the bottom face (because Nagy et al., 2000,
|
||||
use z->Down) */
|
||||
prism->z1 = MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS - tess.r2;
|
||||
prism->z2 = MEAN_EARTH_RADIUS - tess.r1;
|
||||
/* Calculate the density of the prism so that they will have exactly
|
||||
the same mass */
|
||||
prism->density = (double)tess.density*
|
||||
tess_volume(tess)/prism_volume(*prism);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid to a sphere of equal volume. */
|
||||
void tess2sphere(TESSEROID tess, SPHERE *sphere)
|
||||
{
|
||||
sphere->density = tess.density;
|
||||
sphere->lonc = 0.5*(tess.e + tess.w);
|
||||
sphere->latc = 0.5*(tess.n + tess.s);
|
||||
sphere->rc = 0.5*(tess.r1 + tess.r2);
|
||||
sphere->r = pow(3*tess_volume(tess)/(4.*PI), (double)1./3.);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a rectangular prism into a sphere of equal volume. */
|
||||
void prism2sphere(PRISM prism, double lonc, double latc, double rc,
|
||||
SPHERE *sphere)
|
||||
{
|
||||
sphere->density = prism.density;
|
||||
sphere->lonc = lonc;
|
||||
sphere->latc = latc;
|
||||
sphere->rc = rc;
|
||||
sphere->r = pow(3*prism_volume(prism)/(4.*PI), (double)1./3.);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a tesseroid */
|
||||
double tess_volume(TESSEROID tess)
|
||||
{
|
||||
double d2r = PI/180., vol;
|
||||
|
||||
vol = d2r*(tess.e - tess.w)*(pow(tess.r2, 3) - pow(tess.r1, 3))*
|
||||
(sin(d2r*tess.n) - sin(d2r*tess.s))/3.;
|
||||
|
||||
return vol;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a sphere */
|
||||
double sphere_volume(SPHERE sphere)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return 4.*PI*pow(sphere.r, 3)/3.;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a prism */
|
||||
double prism_volume(PRISM prism)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return (prism.x2 - prism.x1)*(prism.y2 - prism.y1)*(prism.z2 - prism.z1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,168 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Data structures for geometric elements and functions that operate on them.
|
||||
Defines the TESSEROID, SPHERE, and PRISM structures.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef _TESSEROIDS_GEOMETRY_H_
|
||||
#define _TESSEROIDS_GEOMETRY_H_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Store information on a tesseroid */
|
||||
typedef struct tess_struct {
|
||||
/* s, n, w, e in degrees. r1 and r2 are the smaller and larger radius */
|
||||
double density; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double w; /* western longitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double e; /* eastern longitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double s; /* southern latitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double n; /* northern latitude border in degrees */
|
||||
double r1; /* smallest radius border in SI units */
|
||||
double r2; /* largest radius border in SI units */
|
||||
} TESSEROID;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Store information on a rectangular prism */
|
||||
typedef struct prism_struct {
|
||||
double density; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double x1; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double x2; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double y1; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double y2; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double z1; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double z2; /* in SI units */
|
||||
/* Geodetic coordinates of the center of the top face of the prism */
|
||||
double lon, lat, r;
|
||||
} PRISM;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Store information on a sphere */
|
||||
typedef struct sphere_struct {
|
||||
double density; /* in SI units */
|
||||
double r; /* radius of the sphere in SI units */
|
||||
double lonc; /* longitude of the center of the sphere in degrees */
|
||||
double latc; /* latitude of the center of the sphere in degrees */
|
||||
double rc; /* radial coordinate of the center of the sphere in SI units */
|
||||
} SPHERE;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Split a tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
@param tess tesseroid that will be split
|
||||
@param split array of nlon*nlat*nr tesseroids with memory allocated.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Number of tesseroids in split.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern int split_tess(TESSEROID tess, int nlon, int nlat, int nr,
|
||||
TESSEROID *split);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the total mass of a tesseroid model.
|
||||
|
||||
Give all in SI units and degrees!
|
||||
|
||||
@param model array of tesseroids
|
||||
@param size size of the model
|
||||
|
||||
@return The calculated mass
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern double tess_total_mass(TESSEROID *model, int size);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the mass of a tesseroid model within a density range.
|
||||
|
||||
Give all in SI units and degrees!
|
||||
|
||||
@param model array of tesseroids
|
||||
@param size size of the model
|
||||
@param low_dens lower bound of the density range
|
||||
@param high_dens upper bound of the density range
|
||||
|
||||
@return The calculated mass
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern double tess_range_mass(TESSEROID *model, int size, double low_dens,
|
||||
double high_dens);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid into a rectangular prism of equal volume (Wild-Pfeiffer, 2008).
|
||||
|
||||
\f[
|
||||
\Delta x = \frac{r_1 + r_2}{2} \Delta \phi,
|
||||
\f]
|
||||
\f[
|
||||
\Delta y = \frac{r_1 + r_2}{2} \cos\left(\frac{\phi_1 + \phi_2}{2}\right) \Delta\lambda,
|
||||
\f]
|
||||
\f[
|
||||
\Delta z = \Delta r,
|
||||
\f]
|
||||
|
||||
<b>References</b>
|
||||
|
||||
- Wild-Pfeiffer, F. (2008). A comparison of different mass elements for use in
|
||||
gravity gradiometry. Journal of Geodesy, 82(10), 637-653.
|
||||
|
||||
@param tess tesseroid to convert
|
||||
@param prism prism with equal volume of the tesseroid (used to return)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern void tess2prism(TESSEROID tess, PRISM *prism);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid into a rectangular prism of equal volume by
|
||||
approximating 1 degree by 111.11 km.
|
||||
|
||||
@param tess tesseroid to convert
|
||||
@param prism prism with equal volume of the tesseroid (used to return)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern void tess2prism_flatten(TESSEROID tess, PRISM *prism);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a tesseroid into a sphere of equal volume.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
@param tess tesseroid to convert
|
||||
@param sphere sphere with equal volume of the tesseroid (used to return)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern void tess2sphere(TESSEROID tess, SPHERE *sphere);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert a rectangular prism into a sphere of equal volume.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
@param prism prism to convert
|
||||
@param lonc longitude of the desired center of the sphere, in degrees
|
||||
@param latc latitude of the desired center of the sphere, in degrees
|
||||
@param rc radial coordinate of the desired center of the sphere, in SI units
|
||||
@param sphere sphere with equal volume of the prism (used to return)
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern void prism2sphere(PRISM prism, double lonc, double latc, double rc,
|
||||
SPHERE *sphere);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a tesseroid.
|
||||
|
||||
@param tess the tesseroid whose volume will be calculated
|
||||
|
||||
@return the volume in the respective units
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern double tess_volume(TESSEROID tess);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a sphere.
|
||||
|
||||
@param sphere the sphere whose volume will be calculated
|
||||
|
||||
@return the volume in the respective units
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern double sphere_volume(SPHERE sphere);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Calculate the volume of a prism
|
||||
|
||||
@param prism the prism whose volume will be calculated
|
||||
|
||||
@return the volume in the respective units
|
||||
*/
|
||||
extern double prism_volume(PRISM prism);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||