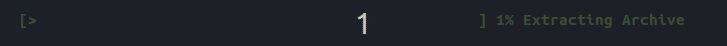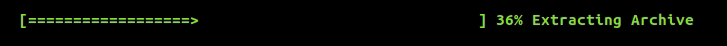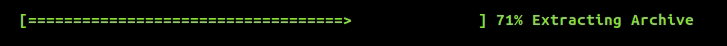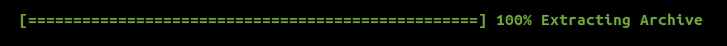Highlights
- Thread-safe progress bars and spinners
- Header-only library. Grab a copy of
include/indicators - Source for the above GIF can be found here
- MIT License
Table of Contents
Progress bar
To introduce a progress bar in your application, include indicators/progress_bar.hpp and create a ProgressBar object. Here's the general structure of a progress bar:
{prefix} {start} {fill} {lead} {remaining} {end} {percentage} [{elapsed}<{remaining}] {postfix}
^^^^^^^^^^^^^ Bar Width ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
The amount of progress in ProgressBar is maintained as a float in range [0, 100]. When progress reaches 100, the progression is complete.
From application-level code, there are two ways in which you can update this progress:
Update progress using bar.tick()
You can update the progress bar using bar.tick() which increments progress by exactly 1%.
#include <indicators/progress_bar.hpp>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
int main() {
using namespace indicators;
ProgressBar bar{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{"["},
option::Fill{"="},
option::Lead{">"},
option::Remainder{" "},
option::End{"]"},
option::PostfixText{"Extracting Archive"};
option::ForegroundColor{Color::green};
};
// Update bar state
while (true) {
bar.tick();
if (bar.is_completed())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
return 0;
}
The above code will print a progress bar that goes from 0 to 100% at the rate of 1% every 100 ms.
Updating progress using bar.set_progress(value)
If you'd rather control progress of the bar in discrete steps, consider using bar.set_progress(value). Example:
#include <chrono>
#include <indicators/progress_bar.hpp>
#include <thread>
int main() {
// Hide cursor
std::cout << "\e[?25l";
using namespace indicators;
ProgressBar bar{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{"["},
option::Fill{"■"},
option::Lead{"■"},
option::Remainder{"-"},
option::End{" ]"},
option::PostfixText{"Loading dependency 1/4"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::cyan}
};
// Update bar state
bar.set_progress(10); // 10% done
// do some work
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(800));
bar.set_option(option::PostfixText{"Loading dependency 2/4"});
bar.set_progress(30); // 30% done
// do some more work
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(700));
bar.set_option(option::PostfixText{"Loading dependency 3/4"});
bar.set_progress(65); // 65% done
// do final bit of work
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(900));
bar.set_option(option::PostfixText{"Loaded dependencies!"});
bar.set_progress(100); // all done
bar.mark_as_completed();
// Show cursor
std::cout << "\e[?25h";
return 0;
}
Showing Time Elapsed/Remaining
All progress bars and spinners in indicators support showing time elapsed and time remaining. Inspired by python's tqdm module, the format of this meter is [{elapsed}<{remaining}]:
#include <chrono>
#include <indicators/progress_bar.hpp>
#include <thread>
int main() {
using namespace indicators;
indicators::ProgressBar bar{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{" ["},
option::Fill{"█"},
option::Lead{"█"},
option::Remainder{"-"},
option::End{"]"},
option::PrefixText{"Training Gaze Network 👀"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::yellow}
option::ShowElapsedTime{true};
option::ShowRemainingTime{true};
};
// Update bar state
while (true) {
bar.tick();
if (bar.is_completed())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
}
// Show cursor
std::cout << "\e[?25h";
return 0;
}
Block Progress Bar
Are you in need of a smooth block progress bar using unicode block elements? Use BlockProgressBar instead of ProgressBar. Thanks to this blog post for making BlockProgressBar an easy addition to the library.
#include <indicators/block_progress_bar.hpp>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
int main() {
// Hide cursor
std::cout << "\e[?25l";
using namespace indicators;
BlockProgressBar bar{
option::BarWidth{80},
option::Start{"["},
option::End{"]"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::white}
};
// Update bar state
auto progress = 0.0f;
while (true) {
bar.set_progress(progress);
progress += 0.25f;
if (bar.is_completed())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(50));
}
// Show cursor
std::cout << "\e[?25h";
return 0;
}
MultiProgress
indicators supports management of multiple progress bars with the MultiProgress class template.
template <typename Indicator, size_t count> class MultiProgress is a class template that holds references to multiple progress bars and provides a safe interface to update the state of each bar. MultiProgress works with both ProgressBar and BlockProgressBar classes.
Below is an example MultiProgress object that manages three ProgressBar objects.
#include <indicators/multi_progress.hpp>
#include <indicators/progress_bar.hpp>
int main() {
using namespace indicators;
// Configure first progress bar
ProgressBar bar1{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{"["},
option::Fill{"■"},
option::Lead{"■"},
option::Remainder{" "},
option::End{" ]"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::yellow},
option::ShowElapsedTime{true},
option::ShowRemainingTime{true},
option::PrefixText{"Progress Bar #1 "}
};
// Configure second progress bar
ProgressBar bar1{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{"["},
option::Fill{"="},
option::Lead{">"},
option::Remainder{" "},
option::End{" ]"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::cyan},
option::ShowElapsedTime{true},
option::ShowRemainingTime{true},
option::PrefixText{"Progress Bar #2 "}
};
// Configure third progress bar
indicators::ProgressBar bar3{
option::BarWidth{50},
option::Start{"["},
option::Fill{"#"},
option::Lead{"#"},
option::Remainder{" "},
option::End{" ]"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::red},
option::ShowElapsedTime{true},
option::ShowRemainingTime{true},
option::PrefixText{"Progress Bar #3 "}
};
// Construct MultiProgress object
indicators::MultiProgress<indicators::ProgressBar, 3> bars(bar1, bar2, bar3);
std::cout << "Multiple Progress Bars:\n";
auto job1 = [&bars]() {
while (true) {
bars.tick<0>();
if (bars.is_completed<0>())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
};
auto job2 = [&bars]() {
while (true) {
bars.tick<1>();
if (bars.is_completed<1>())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(200));
}
};
auto job3 = [&bars]() {
while (true) {
bars.tick<2>();
if (bars.is_completed<2>())
break;
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(60));
}
};
std::thread first_job(job1);
std::thread second_job(job2);
std::thread third_job(job3);
first_job.join();
second_job.join();
third_job.join();
return 0;
}
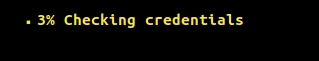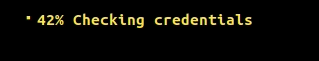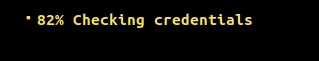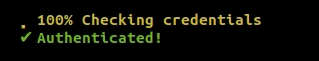
Progress Spinner
To introduce a progress spinner in your application, include indicators/progress_spinner.hpp and create a ProgressSpinner object. Here's the general structure of a progress spinner:
{prefix} {spinner} {percentage} [{elapsed}<{remaining}] {postfix}
ProgressSpinner has a vector of strings: spinner_states. At each update, the spinner will pick the next string from this sequence to print to the console. The spinner state can be updated similarly to ProgressBars: Using either tick() or set_progress(value).
#include <indicators/progress_spinner.hpp>
int main() {
using namespace indicators;
indicators::ProgressSpinner spinner{
option::PostfixText{"Checking credentials"},
option::ForegroundColor{Color::yellow},
option::SpinnerStates{std::vector<std::string>{"⠈", "⠐", "⠠", "⢀", "⡀", "⠄", "⠂", "⠁"}}
};
// Update spinner state
auto job = [&spinner]() {
while (true) {
if (spinner.is_completed()) {
spinner.set_option(option::ForegroundColor{Color::green});
spinner.set_option(option::PrefixText{"✔"});
spinner.set_option(option::ShowSpinner{false});
spinner.set_option(option::ShowPercentage{false});
spinner.set_option(option::PostfixText{"Authenticated!"});
spinner.mark_as_completed();
break;
} else
spinner.tick();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(40));
}
};
std::thread thread(job);
thread.join();
return 0;
}
Contributing
Contributions are welcome, have a look at the CONTRIBUTING.md document for more information.
License
The project is available under the MIT license.