Fixes #513 Implement the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) method as a Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) example. * **Add DPO Functions**: Add `get_batched_logps` and `dpo_loss` functions to `llms/mlx_lm/utils.py` for DPO implementation. * **Update Training Logic**: Update `llms/mlx_lm/tuner/trainer.py` to include DPO-specific training logic, including a new `dpo_loss` function and condition to check for DPO loss in the training loop. * **Add Configuration Options**: Add configuration options for DPO in `llms/mlx_lm/examples/lora_config.yaml`. * **Update Documentation**: Update `llms/mlx_lm/README.md` to include instructions for using DPO. * **Add Unit Tests**: Add `llms/tests/test_dpo.py` with unit tests for `get_batched_logps`, `dpo_loss`, and DPO-specific training logic. --- For more details, open the [Copilot Workspace session](https://copilot-workspace.githubnext.com/ml-explore/mlx-examples/issues/513?shareId=XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX).
4.1 KiB
Generate Text with MLX and 🤗 Hugging Face
This an example of large language model text generation that can pull models from the Hugging Face Hub.
For more information on this example, see the README in the parent directory.
This package also supports fine tuning with LoRA or QLoRA. For more information see the LoRA documentation.
Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) with Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)
This package now includes an example of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) using the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) method.
Paper
Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model
Notes
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO): A Simplified Explanation by João Lages
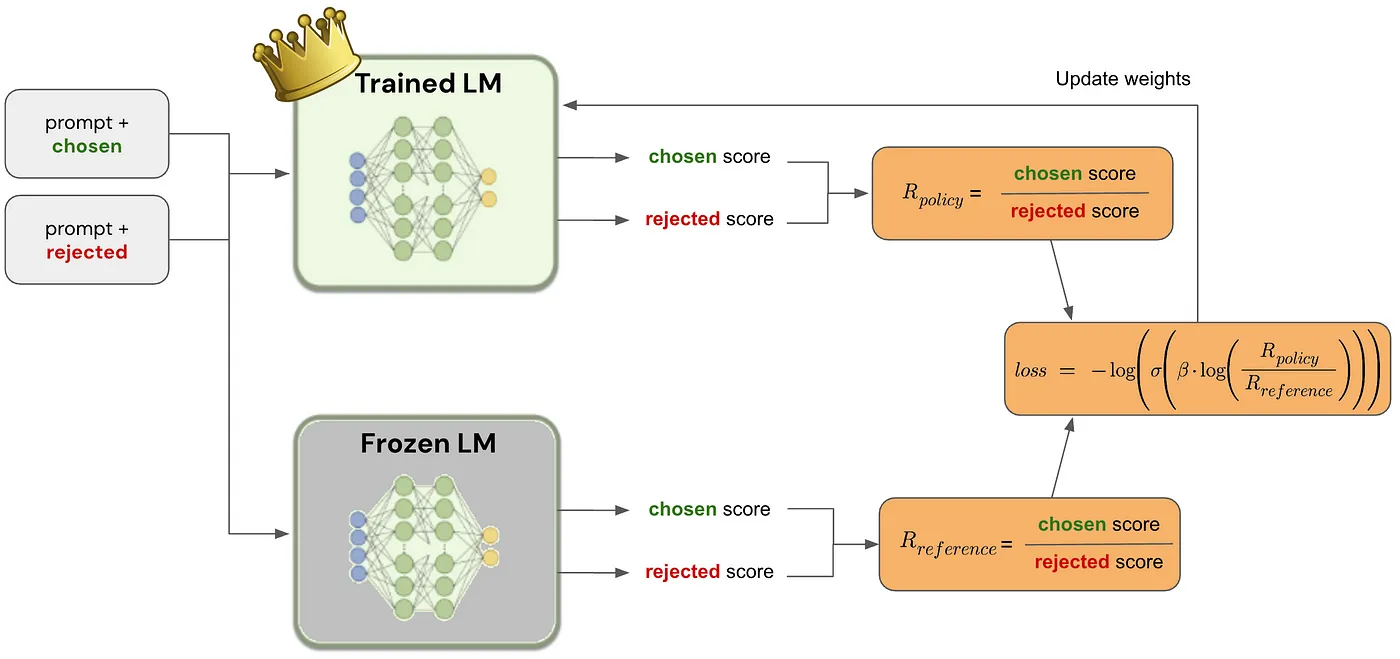
Implementation examples
- huggingface/trl: TRL - Transformer Reinforcement Learning
- eric-mitchell/direct-preference-optimization: Direct Preference Optimization
Possible MLX implementation
Policy and reference log probabilities:
def get_batched_logps(model, inputs, targets):
logits, _ = model(inputs)
logits = logits.astype(mx.float32)
loss_mask = targets != 0
per_token_logps = mx.take_along_axis(nn.log_softmax(logits), targets[..., None], axis=2).squeeze(2)
return tuple((per_token_logps * loss_mask).sum(-1).split(2))
Loss:
def dpo_loss(model, beta, label_smoothing, reference_chosen_logps, reference_rejected_logps, inputs, targets):
chosen_logps, rejected_logps = get_batched_logps(model, inputs, targets)
pi_logratios = chosen_logps - rejected_logps
reference_logratios = reference_chosen_logps - reference_rejected_logps
logits = pi_logratios - reference_logratios
losses = -nn.log_sigmoid(beta * logits) * (1.0 - label_smoothing) - nn.log_sigmoid(-beta * logits) * label_smoothing
chosen_rewards = beta * (chosen_logps - reference_chosen_logps)
rejected_rewards = beta * (rejected_logps - reference_rejected_logps)
reward_accuracies = (chosen_rewards > rejected_rewards).astype(mx.float32)
reward_margins = chosen_rewards - rejected_rewards
ntoks = (inputs != 0).sum()
return (
losses.mean(),
chosen_rewards.mean(),
rejected_rewards.mean(),
reward_accuracies.mean(),
reward_margins.mean(),
ntoks,
)
Beta: The temperature parameter for the DPO loss is typically set in the range of 0.1 to 0.5. The reference model is ignored when beta equals 0.
Label smoothing: This parameter represents the conservativeness for DPO loss, assuming that preferences are noisy and can be flipped with a probability of label_smoothing.
Note
label_smoothing > 0defines the Conservative DPO loss.
Usage Instructions
To use the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) method in your training, follow these steps:
-
Add Configuration Options: Update your configuration file (e.g.,
llms/mlx_lm/examples/lora_config.yaml) to include the DPO-specific options:loss_type: "dpo" beta: 0.1 label_smoothing: 0.0 -
Implement DPO Functions: Ensure that the
get_batched_logpsanddpo_lossfunctions are implemented in yourllms/mlx_lm/utils.pyfile. -
Update Training Logic: Modify your training script (e.g.,
llms/mlx_lm/tuner/trainer.py) to include DPO-specific training logic. This involves updating thetrainfunction to check for the DPO loss type and apply the DPO loss calculation accordingly. -
Run Training: Execute your training script with the updated configuration and logic to train your model using the DPO method.
By following these steps, you can leverage the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) method for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) in your MLX training pipeline.