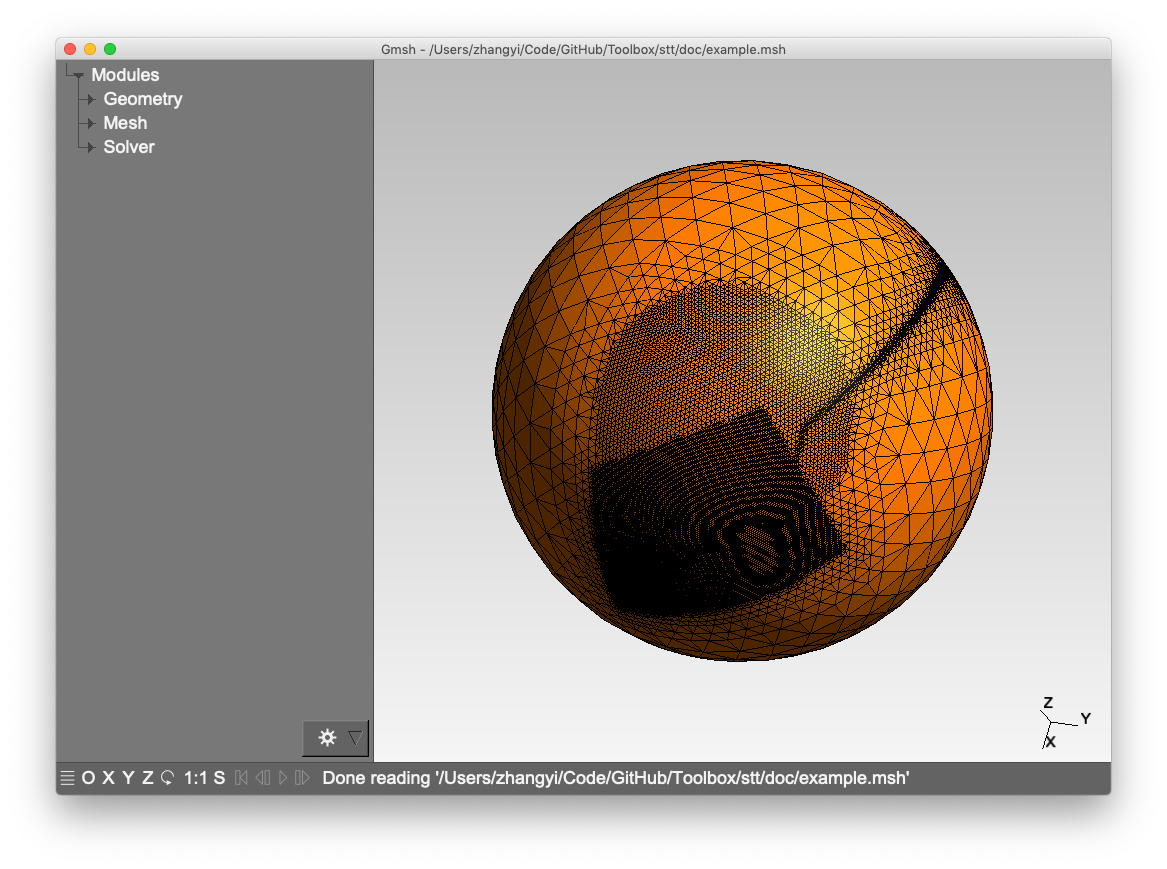
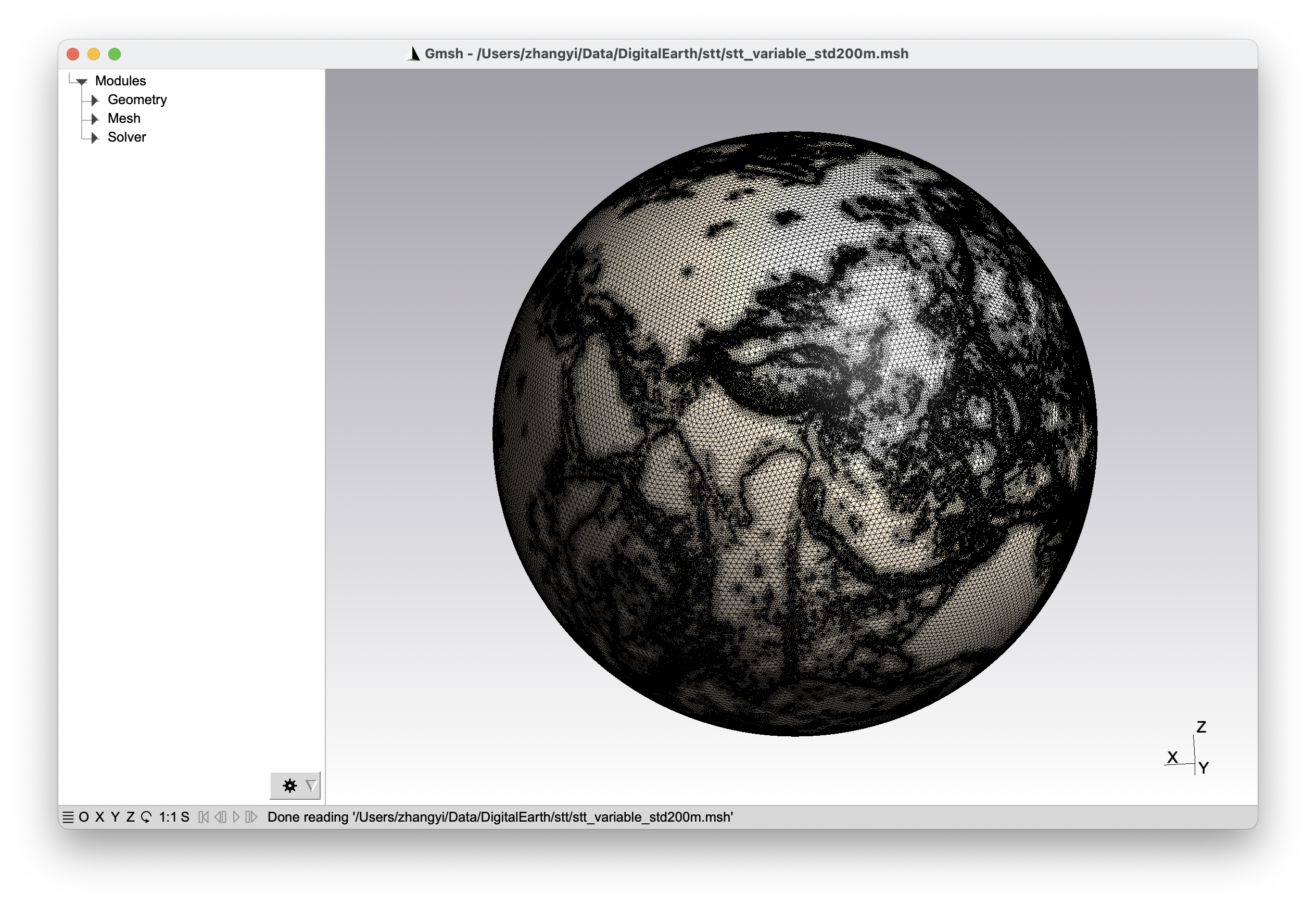
Spherical Triangular Tessellation (STT) Generator
Note: This document is automatically generated by Cursor AI.The function names,parameters,and usage instructions in the document may contain errors.Please refer to the actual function declarations in the header file(
.h).In case of any inconsistencies,the source code shall prevail.
Introduction
The spherical triangular tessellation (STT) is a method to partition a spherical surface into triangular cells. This program generates STT based on an icosahedron and provides various refinement options:
- Geometric refinement around:
- Points
- Lines
- Polygons
- Circles
- Topographic refinement based on elevation data
- Customizable exterior and interior boundaries
Technical Details
Core Algorithm
-
Base Structure
- Starts with an icosahedron (20 triangular faces)
- Uses quad-tree data structure for adaptive refinement
- Each face of the icosahedron becomes the root of a quad-tree
-
Refinement Process
- Adaptive refinement based on various constraints
- Uses vector calculations for spherical geometry
- Supports multiple levels of refinement (controlled by depth parameter)
-
Constraint Types
- Point constraints: Refines mesh around specific points
- Line constraints: Refines along great circle paths
- Polygon constraints: Refines within or around polygon boundaries
- Circle constraints: Refines within spherical caps
- Topographic constraints: Refines based on elevation data
-
Coordinate Systems
- Supports multiple reference systems:
- WGS84 ellipsoid
- Spherical Earth
- Lunar sphere
- Custom ellipsoid
- Custom flattened sphere
- Configurable orientation of the base icosahedron
- Supports multiple reference systems:
Algorithm Details
-
Initialization
- Creates base icosahedron
- Sets up coordinate system and orientation
- Initializes quad-tree structure
-
Refinement Process
- Reads constraint files
- For each triangle:
- Tests intersection with constraints
- Subdivides if needed based on depth and resolution
- Maintains neighbor relationships
-
Output Generation
- Generates final mesh
- Computes vertex locations
- Creates neighbor lists
- Exports in various formats
-
Memory Management
- Uses dynamic allocation for tree structures
- Automatically cleans up temporary data
- Efficient handling of large datasets
Files and folders
- CMakeLists.txt: CMake project configuration file
- src/: Source code directory containing all implementation files
- doc/: Example files and test cases
- README.md: Documentation (this file)
- archived/: Legacy source files (for reference only)
Installation
To compile and install using CMake:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
make install
Usage
Usage: stt -d<minimal-depth>/<maximal-depth> [options]
Required:
-d<min>/<max> Minimal and maximal depths of the quad-tree structure
Example: -d3/7 for refinement from depth 3 to 7
Optional:
-r<ref> Coordinate reference system:
- 'WGS84': WGS84 ellipsoid
- 'Earth': Spherical Earth
- 'Moon': Lunar sphere
- <eq-rad>/<pole-rad>: Custom ellipsoid
- <eq-rad>,<flat-rate>: Custom flattened sphere
-o<lon>/<lat> Orientation of icosahedron top vertex
Default: 0/90 (North Pole)
Output options:
-m<file> Output Gmsh(.msh) mesh file
-v<file> Output vertices' locations
-t<file> Output triangle centers
-n<file> Output triangle neighbors
Refinement control:
-p<file> Control points file
-l<file> Control lines file
-g<file> Control polygons file
-c<file> Control circles file
-t<file> Topography control file
-s<file> Outline shape file
-k<file> Hole shape file
-z<file> Topography data file
Help:
-h Show this help message
Input File Formats
Point Control Format
Controls refinement around specific points. Each point is defined by its location and refinement parameters:
# <longitude> <latitude> <maximal-depth> <minimal-resolution> <physical-group>
# longitude, latitude: Coordinates in degrees
# maximal-depth: Maximum refinement depth for this point
# minimal-resolution: Minimum cell size in degrees
# physical-group: Group identifier for the refined region
-45 -45 5 1.0 7
45 -45 5 1.0 7
Circle Control Format
Controls refinement around spherical caps. Each circle is defined by its center, radius, and refinement parameters:
# <longitude> <latitude> <spherical-cap-degree> <maximal-depth> <minimal-resolution> <physical-group>
# spherical-cap-degree: Angular radius of the cap in degrees
45 60 30 5 0.1 12
-20 -45 20 6 0.1 13
Line/Polygon Control Format
Controls refinement along lines or around polygons. Each shape is defined by a sequence of points and refinement parameters:
# First line: <number-of-points> <maximal-depth> <minimal-resolution> <physical-group>
# Following lines: <longitude> <latitude> of each point
# Points are connected in sequence, last point connects to first for polygons
4 6 0.1 5
-10 10
50 15
60 55
-15 50
Topography Control Format
Controls refinement based on elevation data. The refinement is based on elevation variation within triangles:
# First line: <maximum-STD> <maximal-depth> <minimal-resolution> <physical-group>
# Following lines: <longitude> <latitude> <elevation(meters)>
# maximum-STD: Maximum allowed standard deviation of elevation within a triangle
200.0 10 -1 5
-179.95 89.95 -4203.20
-179.85 89.95 -4203.07
-179.75 89.95 -4203.47
Note: maximum-STD represents the maximum standard deviation of elevation allowed in a triangle. A triangle will be refined if the elevation variation within it exceeds this threshold.
Examples
- Multi-resolution STT with geometric constraints:
# Creates a mesh with depth range 3-7, refined around lines, polygons and circles
stt -d 3/7 -m example.msh -l doc/control_lines.txt -g doc/control_poly.txt -c doc/control_circle.txt
- Topography-constrained STT:
# Creates a mesh with depth range 6-10, refined based on topography data
stt -d 6/10 -m topo_example.msh -t doc/control_topo.txt
Contact
For any bug reports or you need some help. Please contact Dr. Yi Zhang (yizhang-geo@zju.edu.cn).